Sentry Page Protection
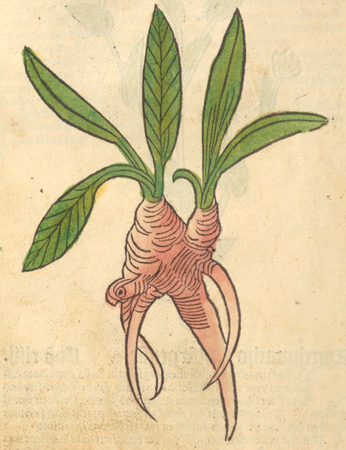
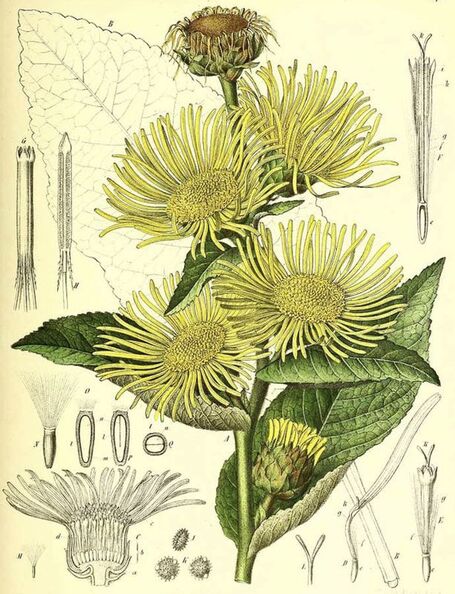
Inula helenium
Berg,, Atlas der officinellen Pflanzen (1891)
Berg,, Atlas der officinellen Pflanzen (1891)
ELECAMPANE ROOT
Notes on Pharmacognosy
By Otto Augustus Wall, 1902
Notes on Pharmacognosy
By Otto Augustus Wall, 1902
Botanical name:
Inula spp.
Two main species are used:
Parts used:
Root
Temperature & Taste:
Warm, dry. Sweet, a little Bitter and Pungent
"Hot and Dry in the Third degree". (Avicenna)
Classifications:
2B ATTENUATERS. 2G. CLEANSING. 2H. CARMINATIVES. 2M. DRAWING. 2Q. ANODYNE. 2S. STRENGTHENING
3C. ALEXIPHARMICS. 3D. CORDIALS & CARDIACS. 3F. LITHONTRIPTIC. 3K. EXPECTORANT. 3L. ANTI-TUSSIVE. 3M. ARTHRITICS
4b. OPTHALMICS. 4c. CARDIAC. 4d. PECTORAL. 4e. STOMACHIC. 4f. SPLENETIC. 4g. HEPATIC. 4j. NERVINES. 4k. ARTHRITIC
Inula spp.
Two main species are used:
- I. helenium (Europe)
- I. racemosa is used very similarly in Ayurveda and Tibetan Medicine (Pharmacographica Indica, Dymock, 1891)
Parts used:
Root
Temperature & Taste:
Warm, dry. Sweet, a little Bitter and Pungent
"Hot and Dry in the Third degree". (Avicenna)
Classifications:
2B ATTENUATERS. 2G. CLEANSING. 2H. CARMINATIVES. 2M. DRAWING. 2Q. ANODYNE. 2S. STRENGTHENING
3C. ALEXIPHARMICS. 3D. CORDIALS & CARDIACS. 3F. LITHONTRIPTIC. 3K. EXPECTORANT. 3L. ANTI-TUSSIVE. 3M. ARTHRITICS
4b. OPTHALMICS. 4c. CARDIAC. 4d. PECTORAL. 4e. STOMACHIC. 4f. SPLENETIC. 4g. HEPATIC. 4j. NERVINES. 4k. ARTHRITIC
Uses:
1. Benefits the Stomach and Spleen, clears Damp, Tonifies Qi:
-strengthens Stomach and digestion; Spleen Qi deficiency (like Atractylodes Bai Zhu)
-vomiting, diarrhea (Chinese Pharmacopoeia)
-removes 'Crudities' (Dampness)
-Hernia, Colic, Wind, Stitches
2. Move Qi, Eases Pain:
-'useful in all types of Cold pains'. (Avicenna)
-distention in the chest, epigastrium and hypochondria (Chinese Pharmacopoeia)
-bruise or sudden sprain of the Chest with pain during Breathing (Chinese Pharmacopoeia)
3. Clears Cold Phlegm, Stops Cough, Strengthens the Lungs:
-all diseases of the Lungs, Cough, Asthma, shortness of Breath, Whooping Cough
-Lung Ulcers, spitting of Blood
-'strengthening for the Heart'. (Avicenna)
4. Resists Poison, Promotes Sweat:
-biting of Rabid Dogs and other venomous Bites;
-infectious and epidemic diseases, both to prevent and cure
-‘great force in the Plague, and Pestilential Fevers’. (Salmon)
-Herpes, Eczema, putrid Sores and Leprosy
5. Benefits the Kidneys, Clears Damp, Promotes Urine:
-Edema, water retention, stoppage of Urine
-Gravel, Stones
-Sciatica, lower body joint pain
-'The person who is accustomed to take Elecampane regularly will not suffer from frequent urination'. (Avicenna)
-decoction is the best form as a diuretic (Avicenna)
6. Moves the Blood, Promotes Menstruation:
-suppressed Menstruation, delayed or scanty Menstruation
-Pain of the Uterus
-Threatened Abortion (Chinese Pharmacopoeia)
7. Clears Wind, Stops Spasms, Benefits Sinews:
-Cramps, Convulsions, Paralysis
-useful in Sciatica and Arthralgia'. (Avicenna)
-Gout, Arthritic and Rheumatic pain, Neuralgia
-loose joints from Damp; Galen used it for joints prone to dislocation.
8. Benefits Eyesight:
-eye weakness, poor eyesight and to strengthen the sight (Decoction in Wine, Salmon)
9. Externally:
-externally for Scabs, Itch, Herpes
-old Ulcers and Sores
-fastens the Teeth if the root is chewed.
-wine decoction is gargled for toothache, loose teeth and to prevent putrefaction of the gums
-topically to the joints to tighten loose ligaments, strengthen the joints, and to help remove their pain.
-applied to Sciatica and Hemicrania
-Saline tincture (tincture in salt water) is used as a wash for Dandruff, Spots, Freckles, Herpes, Eczema etc.
Dose:
1. Taken with Honey for Cough and Lung complaints. The powder may be mixed with Honey to form a linctus, or a decoction may be made into a syrup with Honey.
2. Taken with Oxymel to clear thick and cold Phlegm.
3. With alcohol to move the Blood and Qi, and ease pain.
Decoction: 3–15 grams
Decoction in Wine (1 in 8): 3–5 oz. twice daily
Powder: 1500mg–5 grams
Tincture (1 in 8): 5–8 mls
Spirit: 1 spoonful (5 mls) or more, diluted in a suitable vehicle
Essential Oil: 6–12 drops, up to 20 drops has been given, mixed with sugar, then dissolved in wine
Juice: 2–3 spoonfuls in Wine
Oily Tincture: 10–30 drops for Convulsions, Cramps, Contraction of the Muscles or Tendons
Comment:
1. I. helenium and I. racemosa are similar in taste, appearance and effect. Inula helenium and I. racemosa are used as the source for a type of Costus (Mu Xiang) under the name Tu Mu Xiang, indicating they are used synonymously.
2. Inula and Costus are similar and mutually benefiting, often being used together in the Eastern systems. Inula is a better Qi tonic, Costus is better to regulate Qi. In this way Inula is similar to Atractylodes Bai Zhu, another close relative with similar properties. Together, they mutually enhance. It is also noted that in some parts of China,
3. The preserved Root is a greater tonic, increases Qi and benefits Digestion. It is better for deficiency and chronic diseases of the Lungs and Kidneys; Consumption, lower body weakness, Night Sweats etc.
Preparation:
1. Confected Elecampane:
It can be preserved to make it more tonifying.
2. Honey and Vinegar Prepared Elecampane:
Dry Elecampane root, cut small, and steep in vinegar until soft, then take out and dry. The add to a pot with clarified Honey and boil gently into a confection.
This was specifically used for Pthisick and Shortness of Breath. (Ram's little Dodeon, 1606)
3. Vinegar Prepared:
Avicenna said preserved with Vinegar reduces its heat.
Correctives:
1. Honey
2. Lemon juice (Unani)
Substitutes:
1. According to Unani sources, Elecampane and Inula racemosa can substitute one another.
2. Atractylodes Bai Zhu can be substituted, especially to strengthen Qi and benefit Digestion.
1. Taken with Honey for Cough and Lung complaints. The powder may be mixed with Honey to form a linctus, or a decoction may be made into a syrup with Honey.
2. Taken with Oxymel to clear thick and cold Phlegm.
3. With alcohol to move the Blood and Qi, and ease pain.
Decoction: 3–15 grams
Decoction in Wine (1 in 8): 3–5 oz. twice daily
Powder: 1500mg–5 grams
Tincture (1 in 8): 5–8 mls
Spirit: 1 spoonful (5 mls) or more, diluted in a suitable vehicle
Essential Oil: 6–12 drops, up to 20 drops has been given, mixed with sugar, then dissolved in wine
Juice: 2–3 spoonfuls in Wine
Oily Tincture: 10–30 drops for Convulsions, Cramps, Contraction of the Muscles or Tendons
Comment:
1. I. helenium and I. racemosa are similar in taste, appearance and effect. Inula helenium and I. racemosa are used as the source for a type of Costus (Mu Xiang) under the name Tu Mu Xiang, indicating they are used synonymously.
2. Inula and Costus are similar and mutually benefiting, often being used together in the Eastern systems. Inula is a better Qi tonic, Costus is better to regulate Qi. In this way Inula is similar to Atractylodes Bai Zhu, another close relative with similar properties. Together, they mutually enhance. It is also noted that in some parts of China,
3. The preserved Root is a greater tonic, increases Qi and benefits Digestion. It is better for deficiency and chronic diseases of the Lungs and Kidneys; Consumption, lower body weakness, Night Sweats etc.
Preparation:
1. Confected Elecampane:
It can be preserved to make it more tonifying.
2. Honey and Vinegar Prepared Elecampane:
Dry Elecampane root, cut small, and steep in vinegar until soft, then take out and dry. The add to a pot with clarified Honey and boil gently into a confection.
This was specifically used for Pthisick and Shortness of Breath. (Ram's little Dodeon, 1606)
3. Vinegar Prepared:
Avicenna said preserved with Vinegar reduces its heat.
Correctives:
1. Honey
2. Lemon juice (Unani)
Substitutes:
1. According to Unani sources, Elecampane and Inula racemosa can substitute one another.
2. Atractylodes Bai Zhu can be substituted, especially to strengthen Qi and benefit Digestion.
Main Combinations:
Elecampane & Licorice
Lungs:
1. Cough:
i. acute Cough, Elecampane, Elder berry, Hyssop, Licorice
ii. Cold-Phlegm ('Wet') Cough, Elecampane, Rosemary, Sage, Licorice
iii. Cold-Phlegm, Elecampane, Ginger, Licorice
iv. Cold-Phlegm or Wind-Cold, Elecampane, Thyme, Hyssop, Raisins, Licorice
v. Elecmpane, Coltsfoot, Licorice, Bitter Almond, Figs
vi. Elececampne, Marshmallow root, Rosemary,
2. Bronchitis:
i. Elecampane with Thyme, Nettle leaf, Lungwort (Fischer)
ii. Elecampane with Myrrh, Mullein, Cinnamon
iii. Elecampane with Elecampane, Coltsfoot
iv. Elecampane with Marshmallow, Hyssop, Thyme
3. Whooping Cough:
i. Elecampane with Thyme
ii. Elecmpane, Thyme, Hyssop, Plantain, Raisins
4. Asthma:
i. Elecampane with Coltsfoot, Gentian, Licorice, Hyssop, Sweet Almond, Pine nuts, Dates, Figs (as in Asthmatic Water of Frankfurt)
ii. Tincture Against Asthma, Elecampane with Orris, Aniseed, Caraway, Licorice, Blessed Thistle, Raisins, Senna.
iii. Elecampane with Angelica, Comfrey, Horehound
iv. Elecampane with Horehound, Coltsfoot, Licorice (as in Decoction of Horehound)
v. Elecampane with Squill, Coltsfoot, Hyssop, Fennel, Marshmallow
vi. Elecampane, Orris, Calamus, Licorice, Aniseed (Anti-Asthmatic Elixir)
5. Shortness of Breath:
i. Elecampane, Hyssop, Coltsfoot
ii. Elecampane, Coltsfoot, Raisins, Licorice
6. Lung deficiency, Cough, Asthma:
i. Elecampane with Licorice, Figs
ii. Elecampane with Fig, Licorice, Comfrey, Coltsfoot (as in Decoction to Strengthen the Lungs)
7. Persistent Cough, Elecampane with Marshmallow root and Licorice (Ulrich)
8. Chronic catarrh, Asthma, Aneurisms of the Heart, Elecampane with Hyssop and Ground Ivy (Katier)
9. Pectoral Elixir, Elecampane, Orris, Squill (6 each), Benzoin, Myrrh, Gum Ammoniac, Licorice juice (3 parts each), Saffron (2 parts) in alcohol (40%, 65 parts); dose: 60–80 drops. (Hufeland)
10. Pectoral Mixture: Elecampane extract (2 scruples), Gum Arabic (2 drams), Hyssop water (½ oz.), Oxymel of Squill, Syrup of Hyssop (1 1/2 oz. each). Mix. Dose:a spoonful. (Formulaire Magistral et Memorial Pharmaceutique, 1823)
Other:
11. Swelling of the Stomach, Lumbar Pain, Gravel & Stone, Phlegm, Colic, Hemorrhoids, to stop excess Menstrual Bleeding, for Cough, Epilepsy and Liver and Spleen disorders, Elecampane 1 oz., Fennel seed 3 oz., Black Pepper 2 oz. Powder and mix with boiled Honey. Give as much as a Hazel nut, either with Oxymel, with Wine, or by itslef. (The Secrets of Alexis, 1615)
12. Pain of the Spleen, take the Powder with Wine. (The Secrets of Alexis, 1615)
13. Hernia:
i. Distill water of Elecampane, 2–3 oz., morning and night. (The Secrets of Alexis, 1615)
ii. Elecampane with Rue (School of Salerno)
14. Stomach Cold, Elecampane, Cardamon, Galangal (Herbarius latinus, Petri, 1485)
15. Spleen Yang and Qi deficiency, Elecampane with Cinnamon, Galangal, Cumin, Clove, Cardamon, Ginger (as in Powder of Cinnamon Compound of Mesue)
16. Stragnury from Cold, Elecampane, Cinnamon, Galangal, Aniseed, Licorice, Orris, Ginger, Clove, Nutmeg (Herbarius latinus, Petri, 1485)
17. Kidney Yang Deficiency, back pain, impotence, Leukorrhea etc:
i. Elecampane with Nutmeg, Tormentil, Cinnamon, Clove, Mastic (as in Powder of Nutmeg Compound)
ii. Elecampane with Orchis, Black Pepper, Cinnamon, Ginger, Rocket seed (as in Antidote for Cold Kidneys and to Excite Libido of Nicholas)
18. Promote Menstruation:
i. Elecampane with Horehound (Müller)
ii. Elecampane with Mugwort, Betony, Hyssop (as in Decoction to Promote Menstruation)
19. Paralysis:
i. Elecampane with Licorice, Aniseed, Annis, Nutmeg, Peony root (as in Electuary for Paralysis of Wirtzung)
20. Cardiac Edema, combine Elecampane with Foxglove and Compound Celery Syrup.
21. Cachexia, Black Pepper, Elecampane, Fennel root (Pharmacopoeia medici practici universalis, Bruxelles, 1817)
22. Hemorrhoids, Fistulas, Elecampane, Rhubarb, Black Pepper, Licorice, Caraway (equal parts), powder and form a paste with Honey, take a teaspoonful three times daily.
23. Herpes, Elecampane as an ointment with Sulphur
24. To cause suppuration of Abscesses and Tumors, Elecampane powder, White Lily root, applied as a paste with milk or vinegar
INULA RACEMOSA:
1. Cough, Lung disease:
i. Inula racemosa with Adhatoda, Tylophora, Long Pepper
ii. with hard to clear phlegm, Inula racemosa with Basil, Long Pepper, Tylophora
iii. from Wind, Inula racemosa with Adhatoda, Celery seed, Indian Spikenard
iv. from excess Cold Phlegm, Inula racemosa with Mustard seed, Long Pepper, Tylophora
v. Dry Cough, Inula racemosa with Sesame seed, Licorice, Sida
vi. Phlegm Cough, Inula racemosa, Raisins, Triphala (3 Myrobalans), Trikatu (Ginger, Long and Black Pepper), Zedoary, Plumbago, made into a linctus with Honey and Oil. (The Bower Manuscript, Ayurveda)
vii. Cough, Asthma, Inula racemosa with Lesser Cardamon, Sacred Basil, Zedoary, Asafetida
2. Allergic Rhinitis, Atopic Asthma, Inula racemosa with Chebulic Myrobalan, Long Pepper, Licorice
3. Cold and Weak digestion:
i. Inula racemosa with Ginger, Cardamon
ii. Inula racemosa with Ginger, Plumbago, Cumin
4. Dysmenorrhea, Inula racemosa with Turmeric, Rose, Asparagus root
5. Angina pectoris, Hypertension, Inula racemosa with Arjuna, Bdellium
Major Formulas
Decoction of Elecampane and Rue
Decoction of Horehound
Decoction to Strengthen the Lungs
Syrup for Asthma (Wirtzung)
Powder of Cinnamon Compound (Mesue)
Electuary of Clove and Costus (Caryocostinum)
Electuary for Paralysis (Wirtzung)
Electuary which is Remarkably Effective
Antidote for Cold Kidneys and to Excite Libido (Nicholas)
Tincture Against Asthma
Elixir Salutis, Elixir of Health
Auscpicious Conqueror (Bkra shis rnam rgyal) (Tibetan)
Blood Medicine 7 (Khrag sman bdun pa) (Tibetan)
Cloudless Moonbeam (Sprin bral zla 'od) (Tibetan)
Cowrie Ash 6 (Mgron thal drug pa) (Tibetan)
Eliminator of All Lung Imbalances (Khrugs glo bcu gsum) (Tibetan)
Increase Awareness Pills (Tibetan)
Inula 4 Decoction (Ma nu bzhi thang) (Tibetan)
Podophyllum 25 ('Ol se nyer lnga) (Tibetan)
Six White Formula (Dkar po drug sbyor) (Tibetan)
1. Anti-Asthmatic Water:
i. Elecampane, Licorice, Florentine Orris (2 oz. each), Ground Ivy, Coltsfoot, Jerusalem Oak (½ pound), Hyssop, Horehound, Pennyroyal, Sage (3 oz. each). Annis, Fennel seed (1 oz). Digest 3 days, then distil 6 or 7 pounds. (Pharmacopoeia Wirtembergica, 1798)
ii. Elecampane (2 oz.), Burnet Saxifrage root, Florentine Orris (1 ½ oz. each), Hyssop, Horehound, Sage (2 oz. each), Annis, Fennel seed, Juniper berry, Bay berry (1 oz.), Lesser Cardamon, Cinnamon, Ginger (½ oz. each), Storax (6 drams), Alcohol (12 pounds), Water of Acacia (8 lbs.). Digest 3 days, distil off 12 pounds, then add: Rose Julep (2 pounds), Fennel water (8 pounds). Mix. (Dispensatorium Pharmaceuticum, 1777)
2. Anti-Asthmatic Elixir:
Stimulant, principally for humid Asthma. Dose: 10–30 dops.
i. Asarum root (3 parts), Florentine Orris (5 parts), Elecampane, Calamus (10 parts each), Licorice (15 parts), Aniseed (5 parts), Proof Spirit (80 parts). Infuse cold for several days, strain, and add Camphor (1 part). Dissolve. (Pharmacopee Usuelle, Louvain, 1821)
3. Theriacal Vinegar:
Used to preserve against Contagion.
i. Roots of Elecampane, Angelica, Cyperus, Zedoary, Avens, Contrayerva, Materwort, Valerian, Vipers Bugloss (½ oz. each), fresh Orange and Lemon peel, Clove, Cinnamon, Galangal, Juniper, Bay berry, Sage, Rosemary, Rue (2 drams each), Vinegar (7 lbs.). Macerate for a month in a warm place, express strongly, then add Theriac (7 oz.), Macerate for a month, and filter. Dose: a spoonful every morning. (Dispensatorium medico pharmaceuticum Palatinatus, 1764)
4. Courcelle's American Elixir:
i. Elecampane (16 lbs.), St. Johns wort (8 lbs.), Orange leaf (6 lbs.), Elder flower (5 lbs.), Balm (4 lbs.), Lime flower (2 1/2 lbs.), Root of Provence Cane, Juniper, Rosemary flowers, Opium (2 lbs.), Asarum root (1 lb.), Alcohol (120 lbs.), Water, sufficient to make 24% alcohol. Digest, strain and color with Red Poppy flowers.
This was highly regarded as a Panacea in American for a time. Specifically used for nervous spasms and for general debility.
Dose: a large spoonful, 2–3 times daily. (This version is reformed from Formulaire Magistral et Memorial Pharmaceutique, 1823)
5. Compound Oil of Elecampane:
i. Elecampane, Valerian, Burdock, St. Johns wort, Sothernwood, Wormwood, Sweet Basil, Balm, Balsamita odorata, Marjoram, Mint, savin, Sage, Elder flower (3 oz. each), Camomile, Meliot, Stoechas (2 oz. each), fresh Bay leaf, Dwarf Elder leaf, Rosemary, Rue (6 oz. each), Cumin, Fenugreek, Nettle (1 oz. each), Olive oil (12 lbs.). Macerate 4 days, then boil to the consumption of the humidity, and set aside to clarify (settle). (Pharmacopoeia Hispana, 1798)
Cautions:
1. Used cautiously during Pregnancy.
Main Preparations used:
Candied and Conserved root, Distilled Water, Extract of the Root and a Wine
1. Pastilles of Elecampane:
i. Powdered Elecampane (½ oz.), Florentine Orris (1 dram), mucilage of Tragacanth (sufficient). Form Pastilles. Used for scurvy, Edema, Chlorosis. Dose: ½ oz. (Formulaire Magistral et Memorial Pharmaceutique, 1823)
2. Water Extract of Elecampane:
i. Fresh Elecampane root and quantity. Wash well, rasp it and express the juice. Bruise the residue with a little water and express. Strain the liquor through flannel, and evaporate with gentle heat to an extract. (Pharmacopee Usuelle, Louvain, 1821)
ii. Elecampane root (1 pound), Water (6 lbs.). Macerate for 4 days warm, then boil a little; express and evaporate. (Dispensatorium Pharmaceuticum, 1777)
3. Alcohol Extract of Elecampane:
i. Elecampane (1 pound), Alcohol (5 pounds); digest, extract, strain with strong expression; digest, then boil the residue in Water (3 lbs.). Clarify the decoction with a egg white, then mix the two liquors together, distil off the alcohol, and evaporate to a proper consistency. (Pharmacopoeia Wirtembergica, 1798)
ii. Elecampane, Alcohol, Water (equal parts). Digest 12 hours, express, distil off the alcohol, then evaporate to a proper consistency. (Pharmacopoeia regni Poloniae, 1817)
4. Distilled Water of Elecampane:
i. Fresh Elecampane root (1 part), water (5 parts). Distil 2 parts. (Pharmacopoeia Gallica, 1818)
5. Wine of Elecampane:
i. Fresh Elecampane root (1 part), White Wine (16 parts). Digest without heat for several days, express and filter. (Pharmacopee Usuelle, Louvain, 1821)
6. Tincture of Elecampane:
Stimulant, carminative, principally for Lung diseases. Dose: 6 drops–1 dram
i. Elecamapane (1 part), Alcohol (6 parts). Digest, strain, filter.
ii. Elecampane root (1 oz.), Alcohol 20% (4 oz.). Infuse in a water-bath for 4 days, strain, and pour upon the residue Alcohol (2 oz.); macerate again for 2 days, strain, mix, filter.
7. Ointment of Elecampane:
i. Elecampane root (½ pound), Spring water (128 oz.). Boil, reduce to a pulp, and add Fresh Butter (4 oz.). Mix. (Niemann)
ii. Elecampane root (1 pound), Lard (½ pound), Olive oil (4 oz.). Beat in a stone mortar then boil over a slow fire until the consumption of the humidity, express, strain and add: Yellow Wax, Turpentine (1 oz. each). Mix. (Dispensatorium Pharmaceuticum, 1777)
1. Used cautiously during Pregnancy.
Main Preparations used:
Candied and Conserved root, Distilled Water, Extract of the Root and a Wine
1. Pastilles of Elecampane:
i. Powdered Elecampane (½ oz.), Florentine Orris (1 dram), mucilage of Tragacanth (sufficient). Form Pastilles. Used for scurvy, Edema, Chlorosis. Dose: ½ oz. (Formulaire Magistral et Memorial Pharmaceutique, 1823)
2. Water Extract of Elecampane:
i. Fresh Elecampane root and quantity. Wash well, rasp it and express the juice. Bruise the residue with a little water and express. Strain the liquor through flannel, and evaporate with gentle heat to an extract. (Pharmacopee Usuelle, Louvain, 1821)
ii. Elecampane root (1 pound), Water (6 lbs.). Macerate for 4 days warm, then boil a little; express and evaporate. (Dispensatorium Pharmaceuticum, 1777)
3. Alcohol Extract of Elecampane:
i. Elecampane (1 pound), Alcohol (5 pounds); digest, extract, strain with strong expression; digest, then boil the residue in Water (3 lbs.). Clarify the decoction with a egg white, then mix the two liquors together, distil off the alcohol, and evaporate to a proper consistency. (Pharmacopoeia Wirtembergica, 1798)
ii. Elecampane, Alcohol, Water (equal parts). Digest 12 hours, express, distil off the alcohol, then evaporate to a proper consistency. (Pharmacopoeia regni Poloniae, 1817)
4. Distilled Water of Elecampane:
i. Fresh Elecampane root (1 part), water (5 parts). Distil 2 parts. (Pharmacopoeia Gallica, 1818)
5. Wine of Elecampane:
i. Fresh Elecampane root (1 part), White Wine (16 parts). Digest without heat for several days, express and filter. (Pharmacopee Usuelle, Louvain, 1821)
6. Tincture of Elecampane:
Stimulant, carminative, principally for Lung diseases. Dose: 6 drops–1 dram
i. Elecamapane (1 part), Alcohol (6 parts). Digest, strain, filter.
ii. Elecampane root (1 oz.), Alcohol 20% (4 oz.). Infuse in a water-bath for 4 days, strain, and pour upon the residue Alcohol (2 oz.); macerate again for 2 days, strain, mix, filter.
7. Ointment of Elecampane:
i. Elecampane root (½ pound), Spring water (128 oz.). Boil, reduce to a pulp, and add Fresh Butter (4 oz.). Mix. (Niemann)
ii. Elecampane root (1 pound), Lard (½ pound), Olive oil (4 oz.). Beat in a stone mortar then boil over a slow fire until the consumption of the humidity, express, strain and add: Yellow Wax, Turpentine (1 oz. each). Mix. (Dispensatorium Pharmaceuticum, 1777)
Click the Tabs above for more information on this Medicine
|
'The plant was known to the ancient writers on agriculture and natural history, and even the Roman poets were acquainted with it, and mention Inula as affording a root used both as a medicine and a condiment. Vegetius Renatus, about the beginning of the 5th century, calls it Inula Campana, and St. Isidore in the beginning of the 7th names it as Inula, adding—"quam Alum rustici vocant." It is frequently
|
mentioned in the Anglo-Saxon writings on medicine current in England prior to the Norman Conquest; it is also the "marchalan" of the Welsh Physicians of the 13th century and was generally well known during the middle ages. Not only was its root much employed as a medicine, but it was also candied and eaten as a sweetmeat'. (Pharmacographia, Fluckiger & Hanbury, 1879)
|