Sentry Page Protection
|
New Kreuterbuch, Matthiolus, 1563
|
Krauterbuch, Lonitzer, 1578
|
Rubia tinctorum
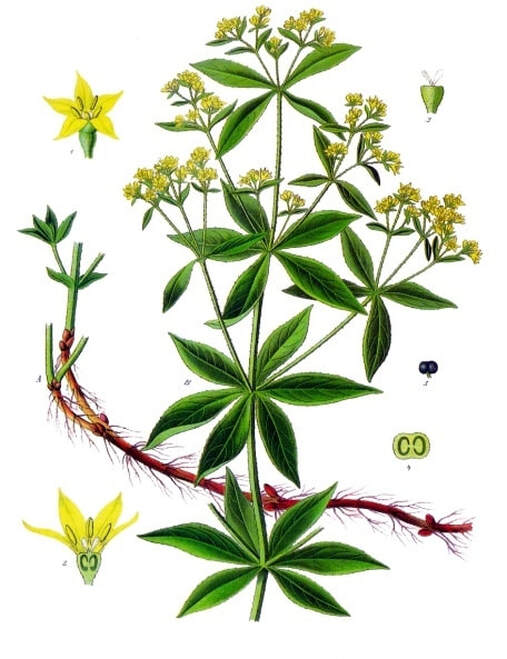
Medizinal-Pflanzen, Köhler, 1897
Medizinal-Pflanzen, Köhler, 1897
Madder root as used in Tibetan Medicine (Adam, 2016)
Botanical name:
Rubia spp.
Two main species are used:
Garden (R. tinctorium) and Wild (R. sylvestris) were known in the West.
In some parts of China (Xinjiang) R. tinctorum is used as Qian Cao Gen, meaning that the two species are synonymous.
Parts used:
Root
Temperature & Taste:
Cool, dry. Bitter, Sweet, Pungent, some said also Sour
Due to its circulatory stimulant effect and its ability to resolve obstruction, some sources regard it as Warming.
Classifications:
2A APERIENT. 2D ATTENUATERS OF CONGEALED BLOOD. 2F. PURIFYING. 2G. CLEANSING. 2P. HEMOSTATIC
3E. DIURETIC. 3F. LITHONTRIPTIC. 3G. EMMENAGOGUE
4f. SPLENETIC. 4h. NEPHRITIC. 4i. UTERINE. 4k. ARTHRITIC
TCM:
B. Clears Heat, Cools the Blood K. Move the Blood L. Stop Bleeding:
Rubia spp.
Two main species are used:
- R. tinctorum (Europe)
- R. cordifolia (syn. R. manjistha) the Indian Madder (TCM, Tibetan Medicine, Ayurveda)
Garden (R. tinctorium) and Wild (R. sylvestris) were known in the West.
In some parts of China (Xinjiang) R. tinctorum is used as Qian Cao Gen, meaning that the two species are synonymous.
Parts used:
Root
Temperature & Taste:
Cool, dry. Bitter, Sweet, Pungent, some said also Sour
Due to its circulatory stimulant effect and its ability to resolve obstruction, some sources regard it as Warming.
Classifications:
2A APERIENT. 2D ATTENUATERS OF CONGEALED BLOOD. 2F. PURIFYING. 2G. CLEANSING. 2P. HEMOSTATIC
3E. DIURETIC. 3F. LITHONTRIPTIC. 3G. EMMENAGOGUE
4f. SPLENETIC. 4h. NEPHRITIC. 4i. UTERINE. 4k. ARTHRITIC
TCM:
B. Clears Heat, Cools the Blood K. Move the Blood L. Stop Bleeding:
Uses:
1. Cools the Blood, Stops Bleeding (West, TCM, Ayurveda, Tibetan Medicine):
-Bleeding with heat, or when associated with Blood stasis
-functional Uterine Bleeding, Coughing or Vomiting blood, blood in the Stool;
-bleeding from excess heat (TCM).
-‘It stencheth bleeding, mitigate inflammations, and helpeth those parts that be hurt and bruised’. (Gerard)
-may be carbonised to increase its hemostatic effect.
2. Clears Heat, Moves the Blood, Opens Obstruction, Clears Stasis (West, TCM, Ayurveda, Tibet):
-swelling and hardness of the Spleen or Liver; Seed with Oxymel for swelling of the Spleen (Dioscorides)
-Jaundice and chronic Hepatitis
-Scrofula, Tumors and Cancer.
-Heart disease.
-Amenorrhea and failure of the Lochia to descend after childbirth;
-‘being but only applied, it bringeth down the menses, the birth, and afterbirth’. (Gerard)
-Trauma, wounds of the chest, ‘deadly wounds of the entrails’ and joint pain from congealed blood.
-Ayurveda uses it for Vaginal disorders and to promote Complexion.
3. Clears Heat and Poison (West, Ayurveda, Tibet):
-Ayurveda says it is ‘the best blood purifier’
-Eczema, Psoriasis, Dermatitis, Vitiligo, Herpes, Leprosy, Acne and other obstinate skin diseases with burning and itching
-various Poisons and Venoms including Snake Bite.
-Syphilis (TCM: Porter Smith)
-Fevers including Chronic and Puerperal Fevers (Ayurveda, Tibetan Medicine, Unani)
-effective against the Influenza virus.
4. Clears Damp, Promotes Urine, Clears Gravel and Stones (West, Ayurveda, Tibet):
-Edema, Fluid retention
-Gravel, and Stones (has been regarded as specific for Stones)
-in Ayurveda it is used for Stones of the Kidney or Gall Bladder; it can both help clear Stones, and hinder their formation.
-it cleanses the kidneys and bladder.
-in Tibetan Medicine for chronic Kidney disease including Nephritis
-Arthritis and Rheumatism (Unani, TCM: Porter Smith); Dioscorides used it for Sciatica.
5. Clears Deficient Heat, Benefits the Bones:
-aid in the treatment of Rickets, Fractures, especially slow-healing Fractures (West, Ayurveda)
-chronic inflammations, Hectic Fever
-Arthritis, Rheumatoid Arthritis and Sciatica. Avicenna listed Sciatica when taken with Hydromel.
-in Tibetan formulas for Lumbago, Arthritis and Gout.
-"When taken with Honey water it proves to be useful in Sciatica, [and] Paralysis" (Avicenna)
-Li Shen Zen in his Pen Tsao Kang Mu (1590) said it ‘Unblocks channels and vessels, treats Wind pain in the bones and Joints’, which is not a modern TCM indication, however.
6. Clears Heat and Phlegm, Benefits the Throat, Stops Cough:
-traditionally in Ayurveda to Benefit the Throat and is used in Tonsillitis and Hoarseness, as well as Lung conditions.
-Chronic Bronchitis (TCM)
-Salmon listed it for Cough and Lung Ulcers.
-Pneumonia (Tibet)
-water extract has a strong antitussive and expectorant effect (Chen & Chen)
7. Rasayana (Tonic to the 7 Body Tissues):
-Diabetes
-Mental disorders (inc. Insanity),
-Menopause (Ayurveda, TCM)
-to help promote Conception (Ayurveda and Tibetan Medicine)
-chronic Joint disease (Ayurveda); Sciatica (Dioscorides)
-Paralysis (Dioscorides, Tibetan); Atrophy (Tabernaemontanus)
-'Tonifies the Interior'. (Shen Nong Ban Cao)
-'Long term use makes one feel happy and vigorous and energetic'. (Ming Yi Bie Lu)
-'Good for treating the Six Exaustions [Qi, Blood, Tendons, Bones, Muscles, Essence]' (Zhen Quan)
8. Externally:
-external Injury and Trauma.
-a paste of the root and Honey is applied to Swellings and Inflammations.
-a paste of the root powder with honey is applied to skin conditions including Scabies, Tinea, Eczema, Psoriasis, Leucoderma, Pityriasis Versicolor, Pityriasis Alba, Freckles and other skin discolorations.
-"applied with vinegar to cure pityriasis alba". (Avicenna)
-"It also clears the skin and removes all kinds of spots and stains". (Avicenna)
-'creeping sores' (Lonicerus)
-a wash externally for Tubercular conditions of the skin or mucus membranes.
-Dioscorides used a cataplasm with vinegar for mild cases of Leprosy.
-in tooth powders for loose Teeth, painful and bleeding gums etc.
-in Collyriums for the eyes
-in India it is used in oils topically for Greying Hair.
-Dioscorides used a pessary to promote lochial discharge.
Dose:
1. Prepared with wine, Boiled in wine or the tincture is used to move the Blood and clear Blood Stasis, although the raw, unprepared herb takenm in other forms also has this effect.
2. To break Blood stagnation and concretions, take 1 dram (3 grams) of the powder with vinegar.
3. Charred to stop Bleeding (although the raw, unprepared herb is also used).
4. Fresh herb is better to clear Heat from the Blood.
Powder: 1–3 grams, 2–3 times daily (for stones etc.)
Decoction: 6–15 grams (double amount for the fresh herb)
Correctives:
1. Tragacanth
2. Anise
3. Oxymel (Unani)
Substitutes:
Zanthoxylum alatum and Cinnamon (Unani)
Preparation:
1. Stir-fried Madder Qian Cao:
According to some TCM texts the drug should be stir-fried before use. (Da Ming)
2. Charred Madder, Qian Cao:
In both East and West, it is sometimes charred to increase its Hemostatic effect. It does not need to be charred to facilitate Hemostatic effects, but this preparation is better for Bleeding when there is no Blood stagnation. It can be used for any type of Bleeding.
3. Wine-fried Madder Qian Cao:
Sprayed with or soaked in alcohol, then stir-fried until dry. This is more effective to move the Blood.
Comment:
This is a special medicine for the Blood; it can move the Blood to clear stasis; stop Bleeding from Heat, and clear Heat and Toxin from the Blood.
1. Prepared with wine, Boiled in wine or the tincture is used to move the Blood and clear Blood Stasis, although the raw, unprepared herb takenm in other forms also has this effect.
2. To break Blood stagnation and concretions, take 1 dram (3 grams) of the powder with vinegar.
3. Charred to stop Bleeding (although the raw, unprepared herb is also used).
4. Fresh herb is better to clear Heat from the Blood.
Powder: 1–3 grams, 2–3 times daily (for stones etc.)
Decoction: 6–15 grams (double amount for the fresh herb)
Correctives:
1. Tragacanth
2. Anise
3. Oxymel (Unani)
Substitutes:
Zanthoxylum alatum and Cinnamon (Unani)
Preparation:
1. Stir-fried Madder Qian Cao:
According to some TCM texts the drug should be stir-fried before use. (Da Ming)
2. Charred Madder, Qian Cao:
In both East and West, it is sometimes charred to increase its Hemostatic effect. It does not need to be charred to facilitate Hemostatic effects, but this preparation is better for Bleeding when there is no Blood stagnation. It can be used for any type of Bleeding.
3. Wine-fried Madder Qian Cao:
Sprayed with or soaked in alcohol, then stir-fried until dry. This is more effective to move the Blood.
Comment:
This is a special medicine for the Blood; it can move the Blood to clear stasis; stop Bleeding from Heat, and clear Heat and Toxin from the Blood.
Main Combinations:
Lacca & Madder
Madder is commonly combined with Lacca in the West, Unani and Tibetan Medicine. Both are powerful for Blood disorders, to move Blood and clear stasis; Heat and Toxin of the Blood, Arthritic pain, Gynecological disorders, to promote Urine and for Stones. They are also combined for Fractures in the East.
Madder & Rhubarb
Madder is also commonly combine with Rhubarb; together, they clear Heat and Toxin from the Blood, and stop Bleeding from Heat. They are also used for Trauma, Blood stagnation and Bruising.
Gynecology
1. Menstrual obstruction and pain, Madder with Mugwort, Savin, Calamus, Mint, Wormwood, Oregano, Calamint, Spikenard, Fennel seed, Peony (as in Syrup of Mugwort)
2. Amenorrhea, Dysmenorrhea, Leukorrhea, Madder with Restharrow, Horehound, Motherwort, Mugwort, Rosemary, Parsley seed, Saffron, Cinnamon (Formulaire de Montpellier, 1822)
3. Amenorrhea:
i. Madder, Cassia Lignea, Cassia Fistula
ii. Madder with Salvia Dan Shen
iii. Madder with Paeonia rubra Chi Shao Yao, Dang Gui, Salvia Dan Shen
iv. Madder with Dang Gui, Paeonia Bai Shao
v. Madder with Dang Gui, Cyperus rotundus Xiang Fu
4. Chlorosis, Madder with Celery root, Butchers Broom, Zedoary, Guaiacum, Motherwort, Pennyroyal, Mugwort, Feverfew, Iron (as in Ale for Chlorosis)
5. Dysmenorrhea:
i. Madder with Dang Gui, Cyperus rotundus, Safflower (TCM)
ii. Madder with Turmeric
iii. Madder with Bdellium, Asparagus root, Safflower (Ayurveda)
iv. Madder, Juniper berry, Cinnamon, Myrrh (Wirtzung)
6. Menopause:
i. Decoct 6 grams of Madder and drink in 3 equal doses daily.
ii. Madder, Rose, Sage
iii. Madder, Asparagus Shatavari, Pearl
7. Uterus obstructions, Fibroids:
i. Madder with Round Birthwort, Agaric, Cinnamon (as in Pills of Madder)
ii. Madder with Round Birthwort, Savin, Cretan Dittany, Myrrh (as in Powder of Myrrh)
8. Irregular Uterine Bleeding, Madder with Cuttlefish bone (TCM)
9. Uterine Bleeding:
i. Madder, Typha Pu Huang
ii. from excess Heat, Madder with Cuttlefish bone (TCM)
iii. with Qi deficiency, add Astragalus Huang Qi to the above.
iv. profuse Uterine Bleeding, Madder, Typha Pu Huang, Rehmannia Sheng Di, Burnet (Di Yu)
v. Madder with Astragalus Huang Qi, Atractylodes Bai Zhu, Cuttlefish bone (Hai Piao Xiao)
vi. Madder with Astragalus Huang Qi, Atractylodes Bai Zhu, Cornus Shan Zhu Yu, Fossil Bones (Long Gu)
10. Leukorrhea with Blood, Madder with Fossil Bones (Long Gu)
11. Postpartum Blood stasis:
i. Madder, Paeonia rubra Chi Shao Yao, Astragalus Huang Qi
ii. from Cold, Madder, Ligusticum Chuan Xiong, Dang Gui, blast-fried Ginger (Pao Jiang),
Skin Diseases, Scrofula:
12. Chronic skin diseases:
i. Madder with Neem, Turmeric, Gotu Kola, Aloe (Ayurveda)
ii. including Leprosy, Madder with Triphala, Tinospora, Barberry, Neem bark (as in Powder of Musaffi Khas of Unani)
iii. chronic acne: Madder with Tinospora, Hemidesmus, Neem, Catechu, Black Nightshade
iv. Psoriasis, Madder with Coptis, Rhubarb
v. Acne, Eczema, Dermatitis, Leucoderma, Madder, Cassia tora, Turmeric, Barberry, Neem, Swertia, Picrorrhiza (Ayurveda)
13. Herpes, Madder with Bittersweet, Arnica (Memorial Pharmaceutique, 1824)
14. Scrofula, Madder with Rosehip, Walnut leaf (Nouveau Formulaire Medicale et Pharmaceutique, 1820)
Bleeding:
15. from excess Heat (Bile):
i. Madder with Rehmannia Sheng Di
ii. Madder with Lotus root, Emblic Myrobalan (Ayurveda)
16. Hemoptyisis:
i. Coughing up Blood and Pus: Infuse one part of a strong infusion of Madder in half a part of wine for 24 hours (leaving the Madder in). Press the Madder well, strain, and add Honey. Heat gently over a fire until as thick as Honey. One spoonful is taken as a dose. (Syrian "Book of Medicine", trans. by Wallis Budge, 1913)
ii. Madder with Aster Zi Wan (TCM)
17. Diarrhea and Dysentery with Blood:
i. Madder with Coptis Huang Lian and Scutellaria Huang Qin (TCM)
ii. Madder, Scutellaria Huang Qin, Burnet (Di Yu)
Blood Stasis, Trauma:
18. Trauma, Bruising, Blood Stasis:
i. Madder with Myrrh (Pharmacopoeia Herbipolitania, 1796)
ii. Madder (1 dram), Rhubarb (2 drams), taken with Wine. (Avicenna)
iii. Madder with Paeonia rubra Chi Shao Yao, Dang Gui, Salvia Dan Shen
iv. Madder with Spermaceti and Shilajit (Mumia) (Herbarium Horstianum, 1630)
v. Madder with Burdock root, Rhubarb, St. John's wort, Bugle, Sanicle
vi. Madder, Safflower (Hong Hua), Dang Gui, Ligusticum Chuan Xiong (TCM)
vii. Blood Stasis (in the Chest), Madder with Lacca, Red Earth, Rhubarb (Wirtzung)
19. Fractures:
i. Madder with Comfrey root
ii. Madder with Shilajit internally; topically, mix Madder and Licorice powders with rice vinegar into a paste for topical application.
iii. Madder with Arjuna, Licorice, Myrrh (Ayurveda)
20. Tumors from Blood Stasis:
i. Madder with Bdellium, Turmeric
ii. Madder with Asarum, Rhubarb, Bitter Almond, Myrrh
Obstructions:
21. Jaundice:
i. Madder with Celandine, Wormwood, Centaury, Cinnamon, Saffron (Riverius)
ii. Madder with Horehound, Turmeric, Nettle, Celandine, Cleavers, Barberry bark
iii. Madder, Turmeric (1 oz. each), Celandine, Lesser Centaury (half handful each), decoct in a mix of water and wine (2 lbs. each); strain, add Compound Syrup of Celery (2 oz.) (Sydenham)
iv. Madder, Artemisia Yin Chen Hao, Rhubarb (Da Huang), Gardenia Zhi Zi (TCM)
v. Madder with Turmeric, Celandine, Earthworms
22. Cholelithiasis, Madder with Hedyotis Bai Hua She She Cao with Artemisia Yin Chen Hao (TCM)
23. Spleen obstructions, Madder, Asparagus root, Fennel root, Licorice, Raisins (Herbarium Horstianum, 1630)
24. Hardness of the Liver and Spleen:
i. Hardness of the Liver, Madder, Gentian, Wormwood, Asarum, Costus, Agrimony, Rue, Mastic, Fenugreek, Thyme, Parsley root, Raisins, prepared as a decoction. (Syrian 'Book of Medicine', Budge, 1913)
ii. Spleen Hardness and Liver pain, Madder, Camphor root Bark, Long Birthwort, Orris (Syrian 'Book of Medicine', Budge, 1913)
iii. Protracted Hardness of the Liver and Spleen and for Obstructions, Madder, Gentian, Rhubarb, Aniseed, Spikenard, Asarum, Saffron, Cassia, Costus, Myrrh, Licorice, Orris (equal parts), powdered and mixed with Honey. (Syrian 'Book of Medicine', Budge, 1913)
25. To open obstructions, for Fibroids, Liver swelling, Edema and Stones, Madder with Lacca, Costus, Rhubarb, Saffron, Licorice, Pepper, Myrrh (as in Powder of Gum Lacca of Mesue)
26. Resolvent Powder: Madder with Couch Grass, Dandelion, Soapwort, Fumitory, Yarrow (equal parts). (Armen Pharmacopoea, Hufeland, 1825)
27. Engorgement of the abdominal viscera, decoct Madder with Mutton neck, Soapwort, Chicory (Nouveau Formulaire Medicale et Pharmaceutique, 1820)
Urinary:
28. Burning Urine, Madder with Sandalwood, Tribulus, Coriander seed (Ayurveda)
29. Edema:
i. Madder, Gentian, Maidenhair, Parsley seed, Mustard seed, Cucumber seed, Pepper, Spikenard, Costus, Agrimony, Oregano, Nigella (equal parts, powdered), mixed with Honey. (Syrian 'Book of Medicine', Budge, 1913)
ii. Madder with roots of Fennel, Parsley, Bay berry, Juniper berry, Carrot and Fennel seed (as in Diuretic Hydromel)
30. Stones:
i. Madder with Peach kernel
ii. Madder with Tribulus, Shilajit (Ayurveda)
iii. Madder with Lysmachia Jin Qian Cao
Lungs:
31. Cough (Wet, dry or with Pus), Chest pain and Sore Throat, Madder, Plantain, Mountain Mint, Hyssop, Squill, Orris, Licorice, Poppy seed (Syrian 'Book of Medicine', Budge, 1913)
32. Coughing up Blood and Pus:
i. soak Madder in wine 24 hours, strain and press hard, add Honey and heat gently until as thick as Honey. Dose is a spoonful. (Syrian 'Book of Medicine', Budge, 1913)
ii. boil Madder in wine down to one-third, add Honey and heat gently until thick, then add powders of White Pepper, Myrrh and Frankincense. (Syrian 'Book of Medicine', Budge, 1913)
33. Shortness of Breath, Asthma, Madder, Rhubarb, Fenugreek, Myrrh, Saffron (Syrian 'Book of Medicine', Budge, 1913)
34. Chest Pain, Phthisis, Madder, Frankincense, Myrrh, Licorice, Hyssop, Pepper, Opium, Honey. (Syrian 'Book of Medicine', Budge, 1913)
35. Chronic Bronchitis, Madder, Citrus Ju Pi. This is a recent combination in China which has proven clinical efficacy.
Other:
36. Heat and Toxin, Fever, Madder, Black Soybean, Licorice (as in Qian Cao Wan of TCM)
37. Rickets:
i. Madder (2 drams), prepared Oyster shell (4 drams). Make 18 doses, Dose: 2–3 per day for a young child. (Nouveau Formulaire Medicale et Pharmaceutique, 1820)
ii. Madder (half oz.), Cream of Tartar (2 drams), Spring Water (64 oz.). Boil slowly for an hour, strain, add clarified Honey (2 oz.). (Nouveau Formulaire Medicale et Pharmaceutique, 1820)
38. Dysentery:
i. Madder with Burnet root
ii. Madder with Red Earth and toasted Rhubarb
39. Fistula, Madder with Red Cabbage and its seed (equal amounts); boil until three-quarters has been consumed, strain, add Honey and boil until thick. Give 2 spoonfuls twice daily. (The Secrets of Alexis, 1615)
Major Formulas:
Decoction for Jaundice
Emmenagogue Decoction (Riverius)
Emmenagogue Syrup
Syrup of Mugwort Lesser (Bononiense)
Powder for Bruising Greater (Wirtzung)
Powder of Madder (Salmon)
Powder of Madder (Lemery)
Powder of Gum Lacca Lesser of Rhasis (Dialacca Minor) (Rhasis)
Powder of Gum Lacca Lesser (Dialacca Minor) (Mesue)
Powder of Gum Lacca Greater (Dialacca Majores) (Mesue)
Powder to Promote Birth (Alexander)
Bruise Powder (Mesue)
Powder Against Bruising
Powder for Bruising Greater (Wirtzung)
Powder for Congealed Blood in the Chest
Powder for Edema (Wirtzung)
Powder for Trauma
Troches of Gum Lacca (Trochisci de Lacca) (Mesue)
Electuary for Internal Bruising
Pills of Madder
Pills for Retention of Urine (Wirtzung)
Amomum 11 (Ko la 11) (Tibetan)
Antelope Horn 14 (Rgya ru bcu bzhi) (Tibetan)
Antidotal 18 (Gnyen po bco brgyad)
An Chong Tang (TCM)
Betel nut 28 (Go yu nyer brgyad) (Tibetan)
Chebula 10 (A Ru 10) (Tibetan)
Chebula 18 (A Ru 18) (Tibetan)
Eliminator of All Lung Imbalances (Khrugs glo bcu gsum) (Tibetan)
Madder Pill (Tibetan)
Manjistha Kvatha (Madder Decoction) (Ayurveda)
Podophyllum 25 ('Ol se nyer lnga) (Tibetan)
Possessor of Ruby Color (Pad rag mdog ldan) (Tibetan)
Red Pony (Rta zi dmar po) (Tibetan)
Rhododendron 18 (Dwa lis bco brgyad) (Tibetan)
Sandalwood 18 (Tibetan)
Thlaspi 13 (Bre ga bcu gsum) (Tibetan)
Three Reds Decoction (Tibetan)
Cautions:
1. Use carefully in Kidney inflammation
2. Not used in Cold and weak digestion, or Qi deficiency in TCM.
3. It can aggravate Wind diseases
4. It tinges the Urine and even the Bones a red color
5. Toxic in large doses
Toxicity:
1. Around 10 grams (3 drams) of the powder was said to affect the nervous system and cause delirium.
2. Madder decoction given to mice in a dose of 150 gm/kg showed no fatalities or toxicity, however at 175 gm/kg one of five mice died.
3. Lucidine is found (in small amounts) in some species and is highly mutagenic. Hydroxyanthraquinone is a by-product of metabolism and is carcinogenic.
Main Preparations used:
1. Extract of Madder:
i. Madder (1 lb.), Water (3 lbs.). Boil, express, clarify with an egg white, then evaporate to an extract. (Farmacopea Ferrarensis, 1825)
ii. Madder (2 parts), Alcohol (3 parts), Water (9 parts). Digest in a covered vessel, express; distil off the alcohol slowly, evaporate to an extract. (Pharmacopoeia Hannoverana, 1819)
1. Use carefully in Kidney inflammation
2. Not used in Cold and weak digestion, or Qi deficiency in TCM.
3. It can aggravate Wind diseases
4. It tinges the Urine and even the Bones a red color
5. Toxic in large doses
Toxicity:
1. Around 10 grams (3 drams) of the powder was said to affect the nervous system and cause delirium.
2. Madder decoction given to mice in a dose of 150 gm/kg showed no fatalities or toxicity, however at 175 gm/kg one of five mice died.
3. Lucidine is found (in small amounts) in some species and is highly mutagenic. Hydroxyanthraquinone is a by-product of metabolism and is carcinogenic.
Main Preparations used:
1. Extract of Madder:
i. Madder (1 lb.), Water (3 lbs.). Boil, express, clarify with an egg white, then evaporate to an extract. (Farmacopea Ferrarensis, 1825)
ii. Madder (2 parts), Alcohol (3 parts), Water (9 parts). Digest in a covered vessel, express; distil off the alcohol slowly, evaporate to an extract. (Pharmacopoeia Hannoverana, 1819)
Click the Tabs above for more information on this Medicine
|
'Madder is used in Hindu medicine as a colouring agent: medicated oils are boiled with Madder to give them colour. It is also a useful external astringent, and is applied to inflamed parts, ulcers, fractures, &c. Chakradatta recommends Madder rubbed with honey as an application to the brown spots of pityriasis versicolor. The Sanskrit name for Madder is Manjishtha. Under the names of Fuvvah and Runas, Arabic and Persian writers treat of Madder, probably the produce of R. tinctorium (as the roots which come from Afghanistan appear to be identical with those of the European species). They do not, however, make any distinction between the species, but simply mention a wild and a cultivated variety. The Mahometans consider the drug to be deobstruent and prescribe it in paralytic affections, jaundice, obstructions in the urinary passages and amenorrhoea. They mention the fruit as useful in hepatic obstruction, and a paste made from the roots with honey, as a good application to freckles and other discolorations of the skin. The whole plant is reputed to be alexipharmic; it is also hung up in houses to avert the evil eye, and tied to the necks of .
|
animals with the same object. Ainslie observes that the hakims are in the habit of prescribing an infusion of Madder root as a grateful and deobstruent drink in cases of scanty lochial discharge after lying-in. (Materia Indica II., p.182.) In another notice of the article {Op. cit. I. p.202), he remarks that it would appear to be chiefly produced in Cuchar, and the root is in great demand in the adjacent countries, for dyeing their coarse cloths and stuffs red; the Nepalese are in the habit of bartering it for rock salt and borax. Kinnier and Tavernier notice the abundauce of Madder in Persia and Makran. Dr. G. Playfair, in a note appended to his translation of the Talif-i-sharifi (p. 150), states that if taken to the extent of about 3 drachms several times daily, it powerfully affects the nervous system, inducing temporary delirium, &c, with evident determination to the uterine system. The plant is common on the higher ghauts in the Bombay Presidency, but the Bombay market draws its supplies chiefly from Khelat through Sind. The imported article fetches a higher price than that grown in India. (Vegetable Materia Medica of Western India, Dymock, 1885)
|