Kurtzes Handtbuchlein, Ryff, 1599
Fuchs, L., New Kreüterbuch (1543)
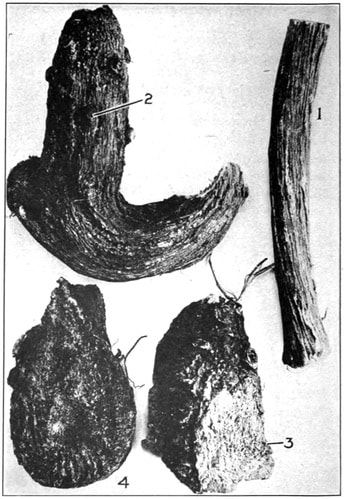
ELECAMPANE ROOT
1, Longitudinally furrowed surface. 2, Stem scar. 3, Cut
surface of the rhizome. 4. Resinous cut surface.
Squibb's Atlas of the Official Drugs, Mansfield, 1919
1, Longitudinally furrowed surface. 2, Stem scar. 3, Cut
surface of the rhizome. 4. Resinous cut surface.
Squibb's Atlas of the Official Drugs, Mansfield, 1919
Botanical name:
Inula spp.
Two main species are used:
1. I. helenium (Europe)
2. I. racemosa is used very similarly in Ayurveda and Tibetan Medicine
Parts used:
Root
Temperature & Taste:
Warm, dry. Sweet, a little Bitter and Pungent
opens, cleanses, discusses
Classifications:
2B ATTENUATERS. 2G. CLEANSING. 2H. CARMINATIVES. 2M. DRAWING. 2Q. ANODYNE. 2S. STRENGTHENING
3C. ALEXIPHARMICS. 3D. CORDIALS & CARDIACS. 3F. LITHONTRIPTIC. 3K. EXPECTORANT. 3L. ANTI-TUSSIVE. 3M. ARTHRITICS
4b. OPTHALMICS. 4c. CARDIAC. 4d. PECTORAL. 4e. STOMACHIC. 4f. SPLENETIC. 4g. HEPATIC. 4j. NERVINES. 4k. ARTHRITIC
Inula spp.
Two main species are used:
1. I. helenium (Europe)
2. I. racemosa is used very similarly in Ayurveda and Tibetan Medicine
Parts used:
Root
Temperature & Taste:
Warm, dry. Sweet, a little Bitter and Pungent
opens, cleanses, discusses
Classifications:
2B ATTENUATERS. 2G. CLEANSING. 2H. CARMINATIVES. 2M. DRAWING. 2Q. ANODYNE. 2S. STRENGTHENING
3C. ALEXIPHARMICS. 3D. CORDIALS & CARDIACS. 3F. LITHONTRIPTIC. 3K. EXPECTORANT. 3L. ANTI-TUSSIVE. 3M. ARTHRITICS
4b. OPTHALMICS. 4c. CARDIAC. 4d. PECTORAL. 4e. STOMACHIC. 4f. SPLENETIC. 4g. HEPATIC. 4j. NERVINES. 4k. ARTHRITIC
ADVERTISEMENT:
Uses:
1. Benefits the Stomach and Spleen, clears Damp, Tonifies Qi:
-strengthens Stomach and digestion; Spleen Qi deficiency (like Atractylodes Bai Zhu)
-vomiting, diarrhea (Chinese Pharmacopoeia)
-Hernia, Colic, Wind, Stitches
2. Move Qi, Eases Pain:
-'useful in all types of Cold pains'. (Avicenna)
-distention in the chest, epigastrium and hypochondria (Chinese Pharmacopoeia)
-bruise or sudden sprain of the Chest with pain during Breathing (Chinese Pharmacopoeia)
3. Clears Cold Phlegm, Stops Cough, Strengthens the Lungs:
-all diseases of the Lungs, Cough, Asthma, shortness of Breath, Whooping Cough
-Lung Ulcers, spitting of Blood
-'strengthening for the Heart'. (Avicenna)
4. Resists Poison, Promotes Sweat:
-biting of Rabid Dogs and other venomous Bites;
-infectious and epidemic diseases, both to prevent and cure
-Herpes, Eczema, putrid Sores and Leprosy
5. Benefits the Kidneys, Clears Damp, Promotes Urine:
-Edema, water retention, stoppage of Urine
-Gravel, Stones
-Sciatica, lower body joint pain
6. Moves the Blood, Promotes Menstruation:
-suppressed Menstruation, delayed or scanty Menstruation
-Pain of the Uterus
-Threatened Abortion (Chinese Pharmacopoeia)
7. Clears Wind, Stops Spasms, Benefits Sinews:
-Cramps, Convulsions, Paralysis
-useful in Sciatica and Arthralgia'. (Avicenna)
-Gout, Arthritic and Rheumatic pain, Neuralgia
8. Benefits Eyesight:
-eye weakness, poor eyesight and to strengthen the sight (Decoction in Wine, Salmon)
9. Externally:
-externally for Scabs, Itch, Herpes
-old Ulcers and Sores
-fastens the Teeth if the root is chewed.
-wine decoction is gargled for toothache, loose teeth and to prevent putrefaction of the gums
-topically to the joints to tighten loose ligaments, strengthen the joints, and to help remove their pain.
-applied to Sciatica and Hemicrania
-Saline tincture (tincture in salt water) is used as a wash for Dandruff, Spots, Freckles, Herpes, Eczema etc.
1. Benefits the Stomach and Spleen, clears Damp, Tonifies Qi:
-strengthens Stomach and digestion; Spleen Qi deficiency (like Atractylodes Bai Zhu)
-vomiting, diarrhea (Chinese Pharmacopoeia)
-Hernia, Colic, Wind, Stitches
2. Move Qi, Eases Pain:
-'useful in all types of Cold pains'. (Avicenna)
-distention in the chest, epigastrium and hypochondria (Chinese Pharmacopoeia)
-bruise or sudden sprain of the Chest with pain during Breathing (Chinese Pharmacopoeia)
3. Clears Cold Phlegm, Stops Cough, Strengthens the Lungs:
-all diseases of the Lungs, Cough, Asthma, shortness of Breath, Whooping Cough
-Lung Ulcers, spitting of Blood
-'strengthening for the Heart'. (Avicenna)
4. Resists Poison, Promotes Sweat:
-biting of Rabid Dogs and other venomous Bites;
-infectious and epidemic diseases, both to prevent and cure
-Herpes, Eczema, putrid Sores and Leprosy
5. Benefits the Kidneys, Clears Damp, Promotes Urine:
-Edema, water retention, stoppage of Urine
-Gravel, Stones
-Sciatica, lower body joint pain
6. Moves the Blood, Promotes Menstruation:
-suppressed Menstruation, delayed or scanty Menstruation
-Pain of the Uterus
-Threatened Abortion (Chinese Pharmacopoeia)
7. Clears Wind, Stops Spasms, Benefits Sinews:
-Cramps, Convulsions, Paralysis
-useful in Sciatica and Arthralgia'. (Avicenna)
-Gout, Arthritic and Rheumatic pain, Neuralgia
8. Benefits Eyesight:
-eye weakness, poor eyesight and to strengthen the sight (Decoction in Wine, Salmon)
9. Externally:
-externally for Scabs, Itch, Herpes
-old Ulcers and Sores
-fastens the Teeth if the root is chewed.
-wine decoction is gargled for toothache, loose teeth and to prevent putrefaction of the gums
-topically to the joints to tighten loose ligaments, strengthen the joints, and to help remove their pain.
-applied to Sciatica and Hemicrania
-Saline tincture (tincture in salt water) is used as a wash for Dandruff, Spots, Freckles, Herpes, Eczema etc.
Dose:
Decoction: 3–15 grams
Powder: 1500mg–5 grams
Comment:
1. I. helenium and I. racemosa are similar in taste, appearance and effect. Inula helenium and I. racemosa are used as the source for a type of Costus (Mu Xiang) under the name Tu Mu Xiang, indicating they are used synonymously.
2. Inula and Costus are similar and mutually benefiting, often being used together in the Eastern systems. Inula is a better Qi tonic, Costus is better to regulate Qi. In this way Inula is similar to Atractylodes Bai Zhu, another close relative with similar properties. Together, they mutually enhance. It is also noted that in some parts of China,
3. The preserved Root is a greater tonic, increases Qi and benefits Digestion. It is better for deficiency and chronic diseases of the Lungs and Kidneys; Consumption, lower body weakness, Night Sweats etc.
Preparation:
... available in PRO version
Correctives:
... available in PRO version
Substitutes:
... available in PRO version
Decoction: 3–15 grams
Powder: 1500mg–5 grams
Comment:
1. I. helenium and I. racemosa are similar in taste, appearance and effect. Inula helenium and I. racemosa are used as the source for a type of Costus (Mu Xiang) under the name Tu Mu Xiang, indicating they are used synonymously.
2. Inula and Costus are similar and mutually benefiting, often being used together in the Eastern systems. Inula is a better Qi tonic, Costus is better to regulate Qi. In this way Inula is similar to Atractylodes Bai Zhu, another close relative with similar properties. Together, they mutually enhance. It is also noted that in some parts of China,
3. The preserved Root is a greater tonic, increases Qi and benefits Digestion. It is better for deficiency and chronic diseases of the Lungs and Kidneys; Consumption, lower body weakness, Night Sweats etc.
Preparation:
... available in PRO version
Correctives:
... available in PRO version
Substitutes:
... available in PRO version
Main Combinations:
Elecampane & Licorice
1. Asthma:
i. Elecampane with ... available in PRO version
ii. Tincture Against Asthma, Elecampane with ... available in PRO version
iii. Elecampane with ... available in PRO version
iv. Elecampane with ... available in PRO version
2. Bronchitis, Elecampane with ... available in PRO version
3. Whooping Cough, combine Elecampane with Thyme
4. Lung deficiency, Cough, Asthma:
i. Elecampane with ... available in PRO version
ii. Elecampane with ... available in PRO version
5. Persistent Cough, Elecampane with ... available in PRO version
6. Pectoral Elixir, Elecampane with ... available in PRO version
7. Hernia, Elecampane with Rue (School of Salerno)
8. Spleen Yang and Qi deficiency, Elecampane with ... available in PRO version
9. Kidney Yang Deficiency, back pain, impotence, Leukorrhea etc:
i. Elecampane with ... available in PRO version
ii. Elecampane with ... available in PRO version
10. Promote Menstruation:
i. Elecampane with ... available in PRO version
ii. Elecampane with ... available in PRO version
11. Paralysis:
i. Elecampane with ... available in PRO version
12. Herpes, Elecampane as an ointment with ... available in PRO version
Major Formulas
Decoction of Elecampane and Rue
Decoction of Horehound
Decoction to Strengthen the Lungs
Syrup for Asthma (Wirtzung)
Powder of Cinnamon Compound (Mesue)
Electuary of Clove and Costus (Caryocostinum)
Electuary for Paralysis (Wirtzung)
Electuary which is Remarkably Effective
Antidote for Cold Kidneys and to Excite Libido (Nicholas)
Tincture Against Asthma
ADVERTISEMENT:
Cautions:
1. Used cautiously during Pregnancy.
Main Preparations used:
Candied and Conserved root, Distilled Water, Extract of the Root and a Wine
1. Used cautiously during Pregnancy.
Main Preparations used:
Candied and Conserved root, Distilled Water, Extract of the Root and a Wine
Click the Tabs above for more information on this Medicine
|
'The plant was known to the ancient writers on agriculture and natural history, and even the Roman poets were acquainted with it, and mention Inula as affording a root used both as a medicine and a condiment. Vegetius Renatus, about the beginning of the 5th century, calls it Inula Campana, and St. Isidore in the beginning of the 7th names it as Inula, adding—"quam Alum rustici vocant." It is frequently mentioned in the Anglo-
|
Saxon writings on medicine current in England prior to the Norman Conquest; it is also the "marchalan" of the Welsh Physicians of the 13th century and was generally well known during the middle ages. Not only was its root much employed as a medicine, but it was also candied and eaten as a sweetmeat'. (Pharmacographia, Fluckiger & Hanbury, 1879)
|