Sentry Page Protection
Ephedra spp.
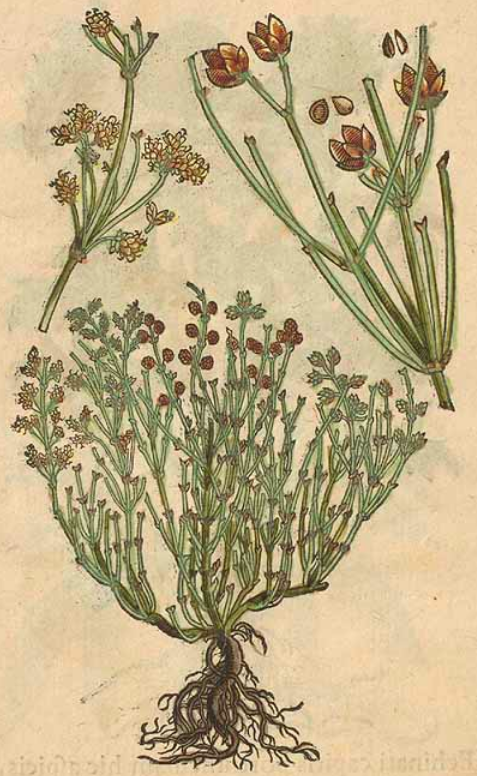
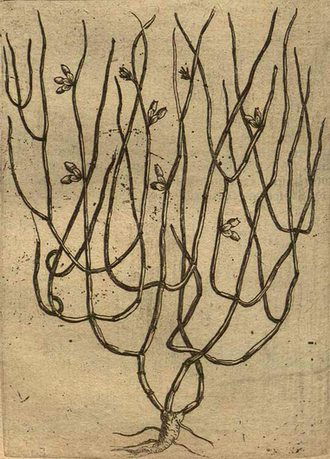
Alpini, P., De plantis exoticis libri duo, 1629
Alpini, P., De plantis exoticis libri duo, 1629
E. distachya
Camerarius, J., Hortus medicus et philosophicus, 1588
Camerarius, J., Hortus medicus et philosophicus, 1588
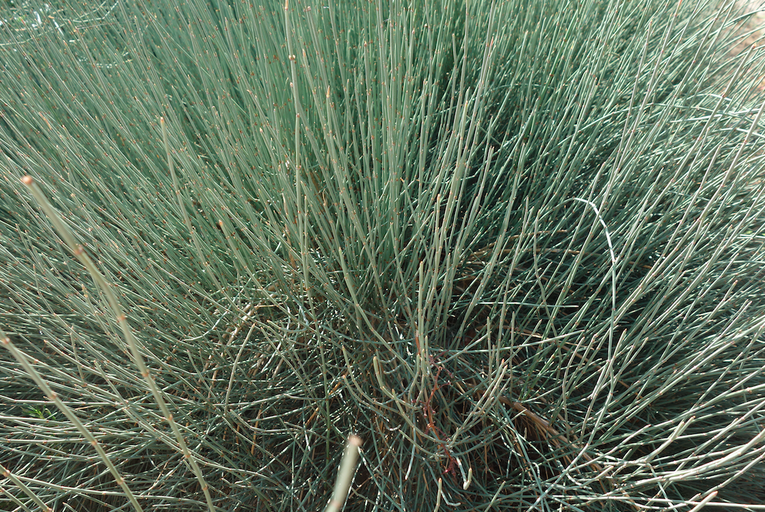
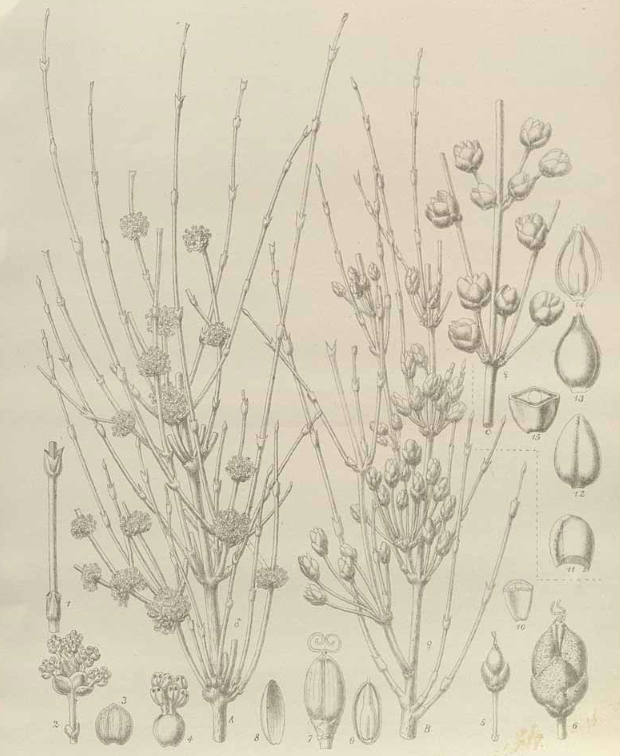
E. pachyclada
Transactions of the Linnean Society of London, 2nd series: Botany, (1887)
Transactions of the Linnean Society of London, 2nd series: Botany, (1887)
Botanical name:
Ephedra spp.
Parts used:
Herb
Temperature & Taste:
Warm, dry. Pungent, slightly Bitter
Classification:
A. Clear Exterior Wind-Cold
Ephedra spp.
- E. sinica (China-Official)
- E. intermedia (China-Official, central Asia)
- E. equisetina (China-Official)
- E. przewalskii (Japan)
- E. vulgaris (Central Asia to Europe)
- E. gerardiana (Central Asia to Europe)
- E. pachyclada (Central Asia to Europe)
Parts used:
Herb
Temperature & Taste:
Warm, dry. Pungent, slightly Bitter
Classification:
A. Clear Exterior Wind-Cold
Uses:
1. Clears Wind-Cold, Clears the Exterior:
-wind-cold cold and flu with chills, fever, headache, lack of sweating
-acute and chronic Fever (Tibetan Medicine)
-used in medicinal baths in Tibet
2. Opens the Lungs, Stops Cough and Wheezing:
-Cough and Wheezing from wind-cold
-can be used for Wheezing and Asthma from any cause depending on the medicines it is combined with
3. Clears Cold and Damp, Promotes Urine:
-Edema (especially of an acute nature in TCM)
4. Clears Wind-Cold-Damp, Opens Obstruction, Relieves Pain:
-painful Obstruction of the muscles and joints from Wind, Cold and Damp
-acute muscular and articular Rheumatism
-also toxic sores which don't form a head
-disperses Tumors and Swellings (Tibetan Medicine)
Dose:
1. Low-moderate doses promote sweat and diffuse the Lungs to stop Cough and Wheezing.
2. Note the froth that forms when boiling should be removed as this part can cause agitation. Some have preboiled Ephedra briefly to remove the froth. This is especially useful when larger doses are used.
3. Large doses of 10–15 grams can be used for Edema and fluid swelling, but expereince shows that large doses are best used with 3 times the amount of raw Gypsum (Shi Gao) to inhibit the diaphoretic effect and promote urine.
Decoction: 2–9 grams (up to 15 grams as a daily dose)
Powder: 500mg–1 ½ gram
Preparation:
1. Removing the Nodes:
Sometimes the nodes are removed; th nodesy are said to decrease the diaphoretic effect, so removing them enhances diaphoresis.
2. Hot-water prepared Ephedra:
Steeping in boiling water until the froth rises, then removing the herb and drying lessens agitation, but is slightly weaker to cause sweating.
3. Stir-fried Ephedra:
The herb can be stir-fried with a little water. This reduces the diaphoretic effect, and is better for the Lungs.
4. Honey-fried Ephedra:
This is a way of correcting Ephedra. It is not as dispersing, not as strong to promote sweat, and is milder in effect, but has a secondary strengthening and more prolonged effect on the Lungs.
Comment:
1. The raw herb is stronger to promote sweat and disperse the exterior, but is apt to cause agitation and is more prone to cause side effects. Preparing with hot water, stir-frying and especially Honey-frying has the effect of reducing its sweat-promoting effect but is better for the Lungs and because these preparations are milder in effect, have a wider range of use for Cough and Wheezing. The Honey-fried herb is also slightly tonifying to the Lungs, so is better for Cough and Asthma with deficiency, as long as it is combined with suitable tonic medicines.
2. In Tibetan medicine it (E. gerardiana) is used for hemorrhage, acute and chronic heat disorders, and Bile diseases.
Correctives:
1. Honey, Licorice
2. Tragacanth, Gum Arabic
3. Almonds reduce the drying effect while enhancing the tonic effect on the Lungs. This is amplified when Licorice is added.
4. Research has shown Chebula to reduce toxicity when coadministered. The pair reduced agitation of the nervous system caused by Epedhra taken alone, increased bronchodilation while showing hepatoprotective effects. In addition, new epedrine derivitives were found to be made in vivo when both herbs were taken together.
Substitutes:
1. Hyssop, Adhatoda vasica (Unani)
2. Maidenhair
3. Ficus religiosa bark has been used as a substitute for Ephedra in the Himalayas.
1. Low-moderate doses promote sweat and diffuse the Lungs to stop Cough and Wheezing.
2. Note the froth that forms when boiling should be removed as this part can cause agitation. Some have preboiled Ephedra briefly to remove the froth. This is especially useful when larger doses are used.
3. Large doses of 10–15 grams can be used for Edema and fluid swelling, but expereince shows that large doses are best used with 3 times the amount of raw Gypsum (Shi Gao) to inhibit the diaphoretic effect and promote urine.
Decoction: 2–9 grams (up to 15 grams as a daily dose)
Powder: 500mg–1 ½ gram
Preparation:
1. Removing the Nodes:
Sometimes the nodes are removed; th nodesy are said to decrease the diaphoretic effect, so removing them enhances diaphoresis.
2. Hot-water prepared Ephedra:
Steeping in boiling water until the froth rises, then removing the herb and drying lessens agitation, but is slightly weaker to cause sweating.
3. Stir-fried Ephedra:
The herb can be stir-fried with a little water. This reduces the diaphoretic effect, and is better for the Lungs.
4. Honey-fried Ephedra:
This is a way of correcting Ephedra. It is not as dispersing, not as strong to promote sweat, and is milder in effect, but has a secondary strengthening and more prolonged effect on the Lungs.
Comment:
1. The raw herb is stronger to promote sweat and disperse the exterior, but is apt to cause agitation and is more prone to cause side effects. Preparing with hot water, stir-frying and especially Honey-frying has the effect of reducing its sweat-promoting effect but is better for the Lungs and because these preparations are milder in effect, have a wider range of use for Cough and Wheezing. The Honey-fried herb is also slightly tonifying to the Lungs, so is better for Cough and Asthma with deficiency, as long as it is combined with suitable tonic medicines.
2. In Tibetan medicine it (E. gerardiana) is used for hemorrhage, acute and chronic heat disorders, and Bile diseases.
Correctives:
1. Honey, Licorice
2. Tragacanth, Gum Arabic
3. Almonds reduce the drying effect while enhancing the tonic effect on the Lungs. This is amplified when Licorice is added.
4. Research has shown Chebula to reduce toxicity when coadministered. The pair reduced agitation of the nervous system caused by Epedhra taken alone, increased bronchodilation while showing hepatoprotective effects. In addition, new epedrine derivitives were found to be made in vivo when both herbs were taken together.
Substitutes:
1. Hyssop, Adhatoda vasica (Unani)
2. Maidenhair
3. Ficus religiosa bark has been used as a substitute for Ephedra in the Himalayas.
Main Combinations:
Ephedra & Apricot/Almond kernel
1. Wind-Cold Cold and Flu:
i. Ephedra with Cinnamon twig Gui Zhi (TCM)
ii. Ephedra with Cinnamon, Ginger (Ayurveda)
2. Cough and Wheezing:
i. Ephedra with Bitter Almond / Apricot kernel Xing Ren and Licorice
ii. from Heat, Ephedra with Bitter Almond / Apricot kernel Xing Ren, Gypsum Shi Gao, Licorice (as in Ma Xing Shi Gan Tang)
iii. from Heat, Ephedra, Scutellaria Huang Qin, Anemarrhena Zhi Mu, Licorice
iv. Cough, Asthma, Bronchitis, Ephedra with Licorice, Platycodon Jie Geng, Morus Sang Bai Pi (Mulberry root-bark) (as in Zhen Ke Ning Tang Jiang of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia)
v. acute Heat-Phlegm, Ephedra with Fritillaria Chuan Bei Mu, Platycodon Jie Geng, Arisaema Tian Nan Xing, Bitter Almond (Xing Ren), Scutellaria Huang Qin, Citrus Chen Pi, Licorice (as in Bao Ke Ning Keli of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia)
vi. from Cold, Ephedra with Bitter Almond / Apricot kernel Xing Ren, Cinnamon twig Gui Zhi and Licorice (as in Ma Huang Tang)
vii. from deficiency, Ephedra with Ginseng and Licorice
viii. Lung congestion, allergic Bronchitis or Asthma, Ephedra, Adhatoda, Long Pepper (Ayurveda)
3. Pneumonia, Ephedra Ma Huang, Scutellaria Huang Qin. (This has been studied)
3. Edema, Water retention:
i. Ephedra, Gypsum (Shi Gao), Atractylodes Bai Zhu, Licorice, fresh Ginger, Jujube (Da Zao)
ii. Ephedra, Tribulus, Coriander seed
4. Obesity: Epedhra Ma Huang, Rhubarb Da Huang, Laminaria (this has been studied)
5. For Wind-Cold-Damp arthritic pain, combine Ephedra with Aconitum Fu Zi
6. Yin-type Abscess (flat, no redness, dark in color), Phlegm nodes and masses:
i. Ephedra, Rehmannia Shu Di Huang, White Mustard seed (Bai Jie Zi), Dang Gui.
ii. Ephedra, Rehmannia Shu Di Huang, White Mustard seed (Bai Jie Zi), Deer horn gelatin (Lu Jiao Jiao), fried Ginger (Pao Jiang), Cinnamon (Rou Gui), Licorice
7. Raynaud's disease, Phlebitis, Ephedra, Rehmannia Shu Di Huang, White Mustard seed (Bai Jie Zi), Cinnamon twig (Gui Zhi), Safflower (Hong Hua), degelatinated Deer horn (Lu Jiao Shuang)
8. Typhoid and other Fevers, Ephedra, Apricot kernel (Xing Ren), Rhubarb, decocted in Snow water and reduced to form a pill mass. (Chinese Materia Medica, Stuauoft)
9. Trauma, Bruising, Pain, Swelling, Fractures, Ephedra with Frankincense, Myrrh, prepared Nux Vomica. (as in Jiu Fen San)
10. Traumatic injury, Sprain, Strain, Bruising, stabbing pain, Dislocation, Fracture, Ephedra with Dang Gui, Ligusticum Chuan Xiong, Frankincense, Myrrh, Dragons Blood, Eupolphaga Tu Bie Chong (Wingless Cockroach) (as in Die Da Wan).
Major Formulas:
Ma Huang Tang
Ma Xing Shi Gan Tang
Ding Chuan Wan
Xiao Qing Long Tang
Fang Feng Tong Sheng San
Die Da Wan
Jiu Fen San
Feng Shi Ma Qian Pian
Safflower Supreme 7 (Gur gum mchog bdun) (Tibetan)
Cautions:
1. Avoid overdose.
2. It can drain the Lung Qi so should be used carefully in those with deficiency. Combining with Licorice and/or Ginseng can correct this.
3. Not used for sweating or night sweats from deficiency.
4. Not used in Hypertension.
Toxicity:
1. Toxic in large doses; 30 grams can be toxic to an adult.
2. The Adverse Effects of Ephedra Herb and the Safety of Ephedrine Alkaloids-free Ephedra Herb Extract (EFE).
3. Bilateral acute myopia and angle closure glaucoma induced by Ma-huang (Ephedra): A case report.
Antidotes:
1. Licorice
2. Cinnamon twig (Gui Zhi) was shown to ameliorate the chronic effects of Ephedra toxocity. (See here)
Drug Interactions:
Due to Ephedrine content, may interact with:
1. Caffeine and MAO inhibitors, increasing blood pressure
–Cardiotoxicity of Ma Huang/caffeine or ephedrine/caffeine in a rodent model system.
2. Beta-Blockers (reduces efficacy due to opposing action)
3. Ephedrine medication (such as Sudafed), causing ephedrine toxicity, arrhythmia etc.
4. Steroids (dexamethasone), enhancing clearance thereby reducing effectiveness.
Main Preparations used:
1. Avoid overdose.
2. It can drain the Lung Qi so should be used carefully in those with deficiency. Combining with Licorice and/or Ginseng can correct this.
3. Not used for sweating or night sweats from deficiency.
4. Not used in Hypertension.
Toxicity:
1. Toxic in large doses; 30 grams can be toxic to an adult.
2. The Adverse Effects of Ephedra Herb and the Safety of Ephedrine Alkaloids-free Ephedra Herb Extract (EFE).
3. Bilateral acute myopia and angle closure glaucoma induced by Ma-huang (Ephedra): A case report.
Antidotes:
1. Licorice
2. Cinnamon twig (Gui Zhi) was shown to ameliorate the chronic effects of Ephedra toxocity. (See here)
Drug Interactions:
Due to Ephedrine content, may interact with:
1. Caffeine and MAO inhibitors, increasing blood pressure
–Cardiotoxicity of Ma Huang/caffeine or ephedrine/caffeine in a rodent model system.
2. Beta-Blockers (reduces efficacy due to opposing action)
3. Ephedrine medication (such as Sudafed), causing ephedrine toxicity, arrhythmia etc.
4. Steroids (dexamethasone), enhancing clearance thereby reducing effectiveness.
Main Preparations used:
Click the Tabs above for more information on this Medicine
Nothing at the moment
GENERAL / REVIEW:
–Ephedrae herba: A comprehensive review of its traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacology, and toxicology.
–[Mahuang (herbaceous stem of Ephedra spp.): chemistry, pharmacodynamics, and pharmacokinetics].
–Non-ephedrine constituents from the herbaceous stems of Ephedra sinica.
–Ethnobotanical Uses and Pharmacological Activities of Moroccan Ephedra Species.
COMBINATIONS:
Almond /. Apricot kernel:
–Interactions Between Ephedra sinica and Prunus armeniaca: From Stereoselectivity to Deamination as a Metabolic Detoxification Mechanism of Amygdalin.
–Herb pair of Ephedrae Herba-Armeniacae Semen Amarum alleviates airway injury in asthmatic rats.
–The important herbal pair for the treatment of COVID-19 and its possible mechanisms.
Cinnamon twig (Gui Zhi):
–Antipyretic Effect of Herba Ephedrae-Ramulus Cinnamomi Herb Pair on Yeast-Induced Pyrexia Rats: A Metabolomics Study.
Chebula:
–Combination of Ephedra sinica stems and Terminalia chebula fruits produces new ephedrine derivatives in vivo that diminish the permeability to BBB while retaining airway dilation and hepatoprotective effects.
Schisandra:
–A comprehensive study of Ephedra sinica Stapf-Schisandra chinensis (Turcz.) Baill herb pair on airway protection in asthma.
Gypsum:
–Ephedra sinica Stapf and Gypsum Attenuates Heat-Induced Hypothalamic Inflammation in Mice.
ANTIBACTERIAL:
–In-Vitro, Anti-Bacterial Activities of Aqueous Extracts of Acacia catechu (L.F.)Willd, Castanea sativa, Ephedra sinica stapf and shilajita mumiyo Against Gram Positive and Gram Negative Bacteria.
–A-type proanthocyanidins from the stems of Ephedra sinica (Ephedraceae) and their antimicrobial activities.
ANTI-PYRETIC:
–Antipyretic Effect of Herba Ephedrae-Ramulus Cinnamomi Herb Pair on Yeast-Induced Pyrexia Rats: A Metabolomics Study.
INFLUENZA:
–Effects of maoto (ma-huang-tang) on host lipid mediator and transcriptome signature in influenza virus infection.
COVID:
–In vitro anti-severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 effect of Ephedra przewalskii Stapf extract.
–Herbal medicines exhibit a high affinity for ACE2 in treating COVID-19.
–Active components in Ephedra sinica stapf disrupt the interaction between ACE2 and SARS-CoV-2 RBD: Potent COVID-19 therapeutic agents.
–Pseudoephedrine and its derivatives antagonize wild and mutated severe acute respiratory syndrome-CoV-2 viruses through blocking virus invasion and antiinflammatory effect.
–The important herbal pair for the treatment of COVID-19 and its possible mechanisms.
PNEUMONIA:
–Evidence of TCM Theory in Treating the Same Disease with Different Methods: Treatment of Pneumonia with Ephedra sinica and Scutellariae Radix as an Example.
–Inhibitory Effect of the Traditional Chinese Medicine Ephedra sinica granules on Streptococcus pneumoniae Pneumolysin.
ALLERGIC RHINITIS:
–ESP-B4 promotes nasal epithelial cell-derived extracellular vesicles containing miR-146a-5p to modulate Smad3/GATA-3 thus relieving allergic rhinitis: ESP-B4/miR-146a-5p in AR.
ASTHMA:
–Ephedra sinica polysaccharide alleviates airway inflammations of mouse asthma-like induced by PM2.5 and ovalbumin via the regulation of gut microbiota and short chain fatty acid.
–An Amide Alkaloid Isolated from Ephedra sinica Ameliorates OVA-Induced Allergic Asthma by Inhibiting Mast Cell Activation and Dendritic Cell Maturation.
–A comprehensive study of Ephedra sinica Stapf-Schisandra chinensis (Turcz.) Baill herb pair on airway protection in asthma.
–Correlation study between the pharmacokinetics of seven main active ingredients of Mahuang decoction and its pharmacodynamics in asthmatic rats.
OBESITY:
–Modern and Non-Invasive Methods of Fat Removal.
–Role of herbal medicine and gut microbiota in the prevention and treatment of obesity.
–Impact of the herbal medicine, Ephedra sinica stapf, on gut microbiota and body weight in a diet-induced obesity model.
–Dietary supplements for obesity.
–The herbal composition GGEx18 from Laminaria japonica, Rheum palmatum, and Ephedra sinica inhibits visceral obesity and insulin resistance by upregulating visceral adipose genes involved in fatty acid oxidation.
–Effectiveness of herbal medicines for weight loss: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.
–Effect of Ephedrae Herba methanol extract on high-fat diet-induced hyperlipidaemic mice.
–The polyherbal composition Gyeongshingangjeehwan 18 attenuates glucose intolerance and pancreatic steatosis in C57BL/6J mice on a high-fat diet.
–The anti-obesity effect of Ephedra sinica through modulation of gut microbiota in obese Korean women.
–Beneficial effect of dietary Ephedra sinica on obesity and glucose intolerance in high-fat diet-fed mice.
ULCERATIVE COLITIS:
–Rapid Screening of Proanthocyanidins from the Roots of Ephedra sinica Stapf and its Preventative Effects on Dextran-Sulfate-Sodium-Induced Ulcerative Colitis.
PSORIASIS:
–Network Pharmacology-Based Analysis on the Mechanism of Action of Ephedrae Herba-Cinnamomi Ramulus Couplet Medicines in the Treatment for Psoriasis.
CANCER:
–Cell Death Induced by the Combination of Ephedra sinica Extract and Radiation in HNSCC is Positively Related to BAX and p-MLKL Expression.
–Assessment of the anti-cancer potential of Ephedra foeminea leaf extract on MDA-MB-231, MCF-7, 4 T1, and MCF-10 breast cancer cell lines: Cytotoxic, apoptotic and oxidative assays.
–Ephedrae herba: A comprehensive review of its traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacology, and toxicology.
–[Mahuang (herbaceous stem of Ephedra spp.): chemistry, pharmacodynamics, and pharmacokinetics].
–Non-ephedrine constituents from the herbaceous stems of Ephedra sinica.
–Ethnobotanical Uses and Pharmacological Activities of Moroccan Ephedra Species.
COMBINATIONS:
Almond /. Apricot kernel:
–Interactions Between Ephedra sinica and Prunus armeniaca: From Stereoselectivity to Deamination as a Metabolic Detoxification Mechanism of Amygdalin.
–Herb pair of Ephedrae Herba-Armeniacae Semen Amarum alleviates airway injury in asthmatic rats.
–The important herbal pair for the treatment of COVID-19 and its possible mechanisms.
Cinnamon twig (Gui Zhi):
–Antipyretic Effect of Herba Ephedrae-Ramulus Cinnamomi Herb Pair on Yeast-Induced Pyrexia Rats: A Metabolomics Study.
Chebula:
–Combination of Ephedra sinica stems and Terminalia chebula fruits produces new ephedrine derivatives in vivo that diminish the permeability to BBB while retaining airway dilation and hepatoprotective effects.
Schisandra:
–A comprehensive study of Ephedra sinica Stapf-Schisandra chinensis (Turcz.) Baill herb pair on airway protection in asthma.
Gypsum:
–Ephedra sinica Stapf and Gypsum Attenuates Heat-Induced Hypothalamic Inflammation in Mice.
ANTIBACTERIAL:
–In-Vitro, Anti-Bacterial Activities of Aqueous Extracts of Acacia catechu (L.F.)Willd, Castanea sativa, Ephedra sinica stapf and shilajita mumiyo Against Gram Positive and Gram Negative Bacteria.
–A-type proanthocyanidins from the stems of Ephedra sinica (Ephedraceae) and their antimicrobial activities.
ANTI-PYRETIC:
–Antipyretic Effect of Herba Ephedrae-Ramulus Cinnamomi Herb Pair on Yeast-Induced Pyrexia Rats: A Metabolomics Study.
INFLUENZA:
–Effects of maoto (ma-huang-tang) on host lipid mediator and transcriptome signature in influenza virus infection.
COVID:
–In vitro anti-severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 effect of Ephedra przewalskii Stapf extract.
–Herbal medicines exhibit a high affinity for ACE2 in treating COVID-19.
–Active components in Ephedra sinica stapf disrupt the interaction between ACE2 and SARS-CoV-2 RBD: Potent COVID-19 therapeutic agents.
–Pseudoephedrine and its derivatives antagonize wild and mutated severe acute respiratory syndrome-CoV-2 viruses through blocking virus invasion and antiinflammatory effect.
–The important herbal pair for the treatment of COVID-19 and its possible mechanisms.
PNEUMONIA:
–Evidence of TCM Theory in Treating the Same Disease with Different Methods: Treatment of Pneumonia with Ephedra sinica and Scutellariae Radix as an Example.
–Inhibitory Effect of the Traditional Chinese Medicine Ephedra sinica granules on Streptococcus pneumoniae Pneumolysin.
ALLERGIC RHINITIS:
–ESP-B4 promotes nasal epithelial cell-derived extracellular vesicles containing miR-146a-5p to modulate Smad3/GATA-3 thus relieving allergic rhinitis: ESP-B4/miR-146a-5p in AR.
ASTHMA:
–Ephedra sinica polysaccharide alleviates airway inflammations of mouse asthma-like induced by PM2.5 and ovalbumin via the regulation of gut microbiota and short chain fatty acid.
–An Amide Alkaloid Isolated from Ephedra sinica Ameliorates OVA-Induced Allergic Asthma by Inhibiting Mast Cell Activation and Dendritic Cell Maturation.
–A comprehensive study of Ephedra sinica Stapf-Schisandra chinensis (Turcz.) Baill herb pair on airway protection in asthma.
–Correlation study between the pharmacokinetics of seven main active ingredients of Mahuang decoction and its pharmacodynamics in asthmatic rats.
OBESITY:
–Modern and Non-Invasive Methods of Fat Removal.
–Role of herbal medicine and gut microbiota in the prevention and treatment of obesity.
–Impact of the herbal medicine, Ephedra sinica stapf, on gut microbiota and body weight in a diet-induced obesity model.
–Dietary supplements for obesity.
–The herbal composition GGEx18 from Laminaria japonica, Rheum palmatum, and Ephedra sinica inhibits visceral obesity and insulin resistance by upregulating visceral adipose genes involved in fatty acid oxidation.
–Effectiveness of herbal medicines for weight loss: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.
–Effect of Ephedrae Herba methanol extract on high-fat diet-induced hyperlipidaemic mice.
–The polyherbal composition Gyeongshingangjeehwan 18 attenuates glucose intolerance and pancreatic steatosis in C57BL/6J mice on a high-fat diet.
–The anti-obesity effect of Ephedra sinica through modulation of gut microbiota in obese Korean women.
–Beneficial effect of dietary Ephedra sinica on obesity and glucose intolerance in high-fat diet-fed mice.
ULCERATIVE COLITIS:
–Rapid Screening of Proanthocyanidins from the Roots of Ephedra sinica Stapf and its Preventative Effects on Dextran-Sulfate-Sodium-Induced Ulcerative Colitis.
PSORIASIS:
–Network Pharmacology-Based Analysis on the Mechanism of Action of Ephedrae Herba-Cinnamomi Ramulus Couplet Medicines in the Treatment for Psoriasis.
CANCER:
–Cell Death Induced by the Combination of Ephedra sinica Extract and Radiation in HNSCC is Positively Related to BAX and p-MLKL Expression.
–Assessment of the anti-cancer potential of Ephedra foeminea leaf extract on MDA-MB-231, MCF-7, 4 T1, and MCF-10 breast cancer cell lines: Cytotoxic, apoptotic and oxidative assays.