Sentry Page Protection
|
Indian Spikenard
De Materia Medica, Dioscorides, 1555 |
Indian Spikenard
Krauterbuch, Danz & Uffenbach, 1610 |
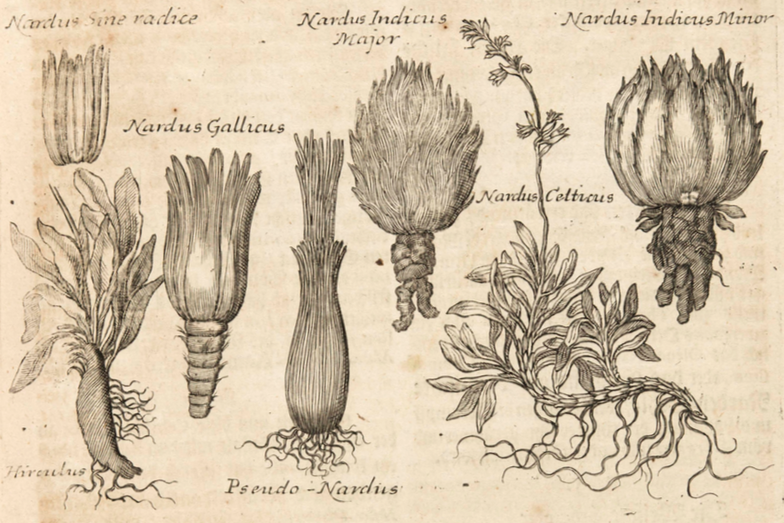
Various types of Spikenard, including Indian and Celtic Spikenard
Museum Museorum, Valentini, 1704
Museum Museorum, Valentini, 1704
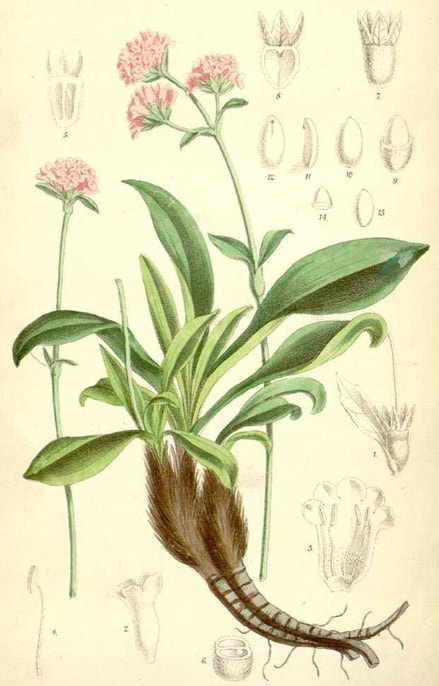
Indian Spikenard
Curtis’s Botanical Magazine, vol. 107 (1881)
Curtis’s Botanical Magazine, vol. 107 (1881)
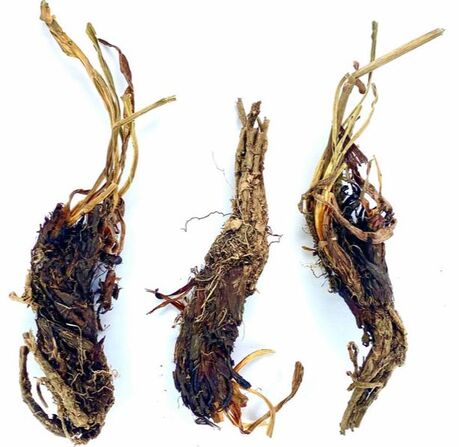
Nardostachys jatamansi (Adam, 2024)
Botanical name:
Nardostachys jatamansi (syn. N. grandiflora)
In the Chinese Pharmacopoeia, N. chinensis, as well as N. jatamansi is listed as the source of Gan Song.
‘there is a false Spikenard of Narbo, and a mountain Spikenard like Valerian’. (Schroder)
Parts used:
Root (Rhizome)
Temperature & Taste:
Slightly Warm (Cool according to some sources), dry. Sweet, Pungent, Aromatic
"Nard is Hot in the First and Dry in the Second degree". (Avicenna)
Cool in Tibetan Medicine
Classifications:
2A APERIENT. 2H. CARMINATIVE. 2I. ANTISPASMODIC. 2S. STRENGTHENING
3C. ALEXIPHARMIC. 3G. EMMENAGOGUE. 3J. INCREASE SEMEN
4c. CARDIAC. 4i. UTERINE. 4j. NERVINE
TCM:
J. Regulate Qi
Nardostachys jatamansi (syn. N. grandiflora)
In the Chinese Pharmacopoeia, N. chinensis, as well as N. jatamansi is listed as the source of Gan Song.
‘there is a false Spikenard of Narbo, and a mountain Spikenard like Valerian’. (Schroder)
Parts used:
Root (Rhizome)
Temperature & Taste:
Slightly Warm (Cool according to some sources), dry. Sweet, Pungent, Aromatic
"Nard is Hot in the First and Dry in the Second degree". (Avicenna)
Cool in Tibetan Medicine
Classifications:
2A APERIENT. 2H. CARMINATIVE. 2I. ANTISPASMODIC. 2S. STRENGTHENING
3C. ALEXIPHARMIC. 3G. EMMENAGOGUE. 3J. INCREASE SEMEN
4c. CARDIAC. 4i. UTERINE. 4j. NERVINE
TCM:
J. Regulate Qi
Uses:
1. Regulates Qi, Settles Wind, Clears Phlegm:
-Epilepsy, Hysteria, Convulsions, Palpitations, Hypertension.
-opens the orifices of the brain to improve consciousness and clear the senses
-disturbed Mental state and Insomnia (API)
-excessive worrying that has damaged the Spleen (Chen & Chen)
-regarded as rejuvenative for the Brain; "Strengthens the brain" (Avicenna)
-"All kinds of Nard are useful in Palpitation". (Avicenna)
2. Moves the Qi, opens Obstructions:
-Colic, Bloating, Gastrointestinal spasms and pain
-good for the Stomach, poor appetite, nausea; used for ‘corrosions’ of the Stomach
-Epigastric and abdominal distension with anorexia and vomiting (Chinese Pharmacopoeia)
-sudden onset epigastric and abdominal pain and distention (Ben Cao Gang Mu)
-promotes Urine; also for Jaundice
-Liver Qi obstruction; Jaundice
-aromatically revives the senses when blocked by Phlegm and Damp
-"Nard removes the obstructions of the Liver and Stomach and strengthens them". (Avicenna)
3. Moves Qi, Regulates Menstruation:
-painful or obstructed Menstruation
-"Stops excessive Bleeding from the Uterus". (Avicenna)
-"Useful in all kinds of Uteritis. For this purpose the patient is given a sitz bath in its decoction". (Avicenna)
4. Clears Wind-Damp, Resists Poison:
-skin diseases including Erysipelas (API)
-Toxicity associated with Heat (Tibet)
5. Externally:
-in hair oils to stop Loss of hair and for premature greying of Hair.
-Freckles, Acne, Black spots (Ben Cao Gang Mu)
-Gargle for Toothache and Caries (Ben Cao Gang Mu, Chinese Pharmacopoeia)
-Swollen legs and feet; can be used as a wash
-externally in Lixiviums for the head and baths for the Womb
-as a collyrium applied with an eye pencil it promotes growth of eyelashes (Avicenna)
-Hemorrhoids (Ben Cao Gang Mu)
Dose:
Decoction: 3–6 grams
Powder: 500mg–3 grams (up to 5 grams)
Tincture (1:4 in 50% alcohol): 1–5 mls.
Essential Oil: 1–3 drops, three times daily
Substitute:
1. Valerian and Indian Spikenard have been used as substitutes for one another.
2. Celtic Spikenard is also used similarly, but is weaker.
3. Selinum tenuifolium is used as a substitute in the Himalayas.
Correctives:
1. Tabasheer corrects the harmful effects (Unani)
2. It is enhanced with Atractylodes Cang Zhu and Aconitum Fu Zi. (Ben Cao Gang Mu)
Decoction: 3–6 grams
Powder: 500mg–3 grams (up to 5 grams)
Tincture (1:4 in 50% alcohol): 1–5 mls.
Essential Oil: 1–3 drops, three times daily
Substitute:
1. Valerian and Indian Spikenard have been used as substitutes for one another.
2. Celtic Spikenard is also used similarly, but is weaker.
3. Selinum tenuifolium is used as a substitute in the Himalayas.
Correctives:
1. Tabasheer corrects the harmful effects (Unani)
2. It is enhanced with Atractylodes Cang Zhu and Aconitum Fu Zi. (Ben Cao Gang Mu)
Main Combinations:
Wind / Nervous / Brain:
1. Nervous disorders:
i. Indian Spikenard with Centella, Convolvulus Shakhapushpi
ii. Indian Spikenard with Withania and Bacopa
2. Epilepsy, Convulsions, Indian Spikenard with Withania, Centella, Calamus, Henbane seed
3. Parkinson's Disease, Indian Spikenard with Withania, Mucuna, Henbane seed, Sida cordifolia
4. Forgetfulness, Amnesia:
i. Indian Spikenard, Calamus, Frankincense
ii. Indian Spikenard with Black Pepper, Long Pepper, Galangal, Calamus, Saffron, Asarabacca
5. Depression:
i. Indian Spikenard, Balm, Licorice
ii. Indian Spikenard, St. John's wort, Lavender
iii. Indian Spikenard (8 parts), Withania (4 parts), Henbane seed (1 part). This is an Ayurvedic compound called Mamsyadi Kwatha and has proven Antipressant effects)
6. Excessive worry causing Spleen deficiency, Indian Spikenard with Amomum Sha Ren, Atractylodes Bai Zhu
Liver, Qi Stagnation:
7. Liver Obstruction and Jaundice:
i. Indian Spikenard, Wormwood
ii. Indian Spikenard, Wormwood, Rose, Quince juice (as in Syrup of Wormwood)
iii. Indian Spikenard with Bitter Almond, Aniseed, Wormwood (as in Troches for the Liver and Jaundice)
iv. Indian Spikenard with Myrrh, Cassia Wood, Saffron, Costus, Cinnamon (as in Electuary of Saffron Lesser of Mesue)
v. Jaundice, Complex Fever, Chronic disease, Indian Spikenard with Rose, Rhubarb, Licorice, Tabasheer, Agrimony (as in Troches of Rose and Agrimony of Mesue)
vi. with Liver Heat, Indian Spikenard with Rose, Sandalwood, Wormwood, Tabasheer, Chicory
8. Hardness of the Liver and Spleen, Indian Spikenard, Saffron, Long Birthwort, Ammoniac, Costus (Syrian 'Book of Medicine', Budge, 1913)
9. Obstruction and Pain of the Liver, Spleen, Stomach, Kidneys, Jaundice, and chronic Cough, Spikenard, Costus, Cinnamon, Pepper, Rock Parsley seed, Calamus, Orris, Raisins (Syrian 'Book of Medicine', Budge, 1913)
10. To purge Bile and Liver Heat, Indian Spikenard with Rhubarb and Mastic (as in Powder of Rhubarb of Fuchs)
11. Qi Stagnation with Cold, Indian Spikenard with Cinnamon, Clove
Digestion:
12. Stomach weakness:
i. Indian Spikenard with Amomum Sha Ren, Citrus Chen Pi, Licorice
ii. Indian Spikenard with Wormwood, Rose, Wine Quince (as in Syrup of Wormwood)
13. Colic, Stomach discomfort:
i. Indian Spikenard, Fennel, Costus
ii. Indian Spikenard with Cardamon, Ginger, Licorice
14. Spleen Dampness, Indian Spikenard with Cinnamon, Rose, Sandalwood, Nutmeg, Greater Cardamon, Mastic (as in Indian Electuary Greater of Mesue)
15. Gastric Ulcer, Indian Spikenard, Licorice, Rose (see research here)
Cough / Catarrh:
16. Catarrh, Indian Spikenard with Myrrh and Storax
17. Spasmodic Cough, Indian Spikenard with Elecampane, Adhatoda
Urinary:
18. Urinary Incontinence, Indian Spikenard with Cyperus, French Lavender, Frankincense bark, Acorn cups, Cumin Powder for Incontinence)
19. Edema, Urinary obstruction:
i. Indian Spikenard with Agaric, Cardamon, Costus, Rhubarb, Cinnamon (as in Pills of Spikenard)
ii. Indian Spikenard with Cinnamon, Asarum, Mastic, Fennel, Wormwood, Rhubarb, Parsley (as in Antidote for Edema of Nicholas)
Heart:
20. Palpitations, Arrhythmias:
i. Indian Spikenard, Arjuna
ii. Indian Spikenard, Arjuna, Boerhaavia, Sida cordifolia (Ayurveda)
iii. Indian Spikenard with Mastic, Aloeswood, Cinnamon (as in Aloeswood Powder for Palpitations)
iv. Indian Spikenard with Aloeswood, Rose, Mastic, Cinnamon, Clove, Nutmeg (as in Troches of Aloeswood)
v. Indian Spikenard with Mastic, Aloeswood, Cinnamon, Clove, Nutmeg, Cardamon, Citron peel, Musk
vi. Indian Spikenard, Isatis Folium Da Qing Ye, Codonopsis Dang Shen, Ginseng, Cinnamon twig (Gui Zhi), Bitter Orange (Zhi Ke), Licorice. This was used in a clinical trial with an effectiveness of 83%. (Chen & Chen)
vii. Indian Spikenard, Codonopsis Dang Shen, Notoginseng San Qi, Polygonatum Huang Jing, Amber (this formula has been studied for effectiveness)
21. Angina Pectoris:
i. Indian Spikenard, Arjuna, Nutmeg
ii. Indian Spikenard, Olibanum, Saffron, Camphor
Gynecology / Obstetrics:
22. Dysmenorrhea, Indian Spikenard, Cyperus rotundus, Asparagus racemosus, Bishop's Weed seed
23. Dysmenorrhea, Muscle pain or Headache from Qi and Blood stagnation:
i. Indian Spikenard with Bdellium and Ginger (Ayurveda)
ii. Indian Spikenard with Cyperus rotundus
24. Infertility from Uterus obstruction:
i. Indian Spikenard with Aloe, Agaric, Myrrh, Madder, Cinnamon, Saffron
ii. Indian Spikenard with Peony root, Cinnamon, Cyperus, Mugwort, Clove, Olibanum, Mastic
25. Difficult Childbirth:
i. Indian Spikenard with Cinnamon, Saffron
ii. Indian Spikenard with Savin, Marjoram, Lavender
Other:
26. Cold-Damp Arthritis, Rheumatism, Back Pain, Indian Spikenard with Aloe, Gum Ammoniac, Myrrh, Rue, Dodder herb, Cinnamon, Saffron
27. Watering Eyes, Indian Spikenard with Cinnamon, Mastic, Agaric (as in Electuary for Watering of the Eyes of Andrezeos)
28. Toothache from Kidney deficiency, Indian Spikenard, Sulphur (equal parts). Powder and soak in hot water and rinse the mouth with it. (Jing Xiao Ji Shi Fang)
Major Formulas
Decoction for Difficult Childbirth (Barbette)
Syrup of Wormwood
Hiera Picra
Warming Pearl Powder (Diamargariton Calidum) (Mesue)
Powder to Ascertain if Pregnant (Gabelhover)
Troches of Agrimony
Troches of Aloeswood (Trochisci Aquilaria) (Mesue)
Troches of Rose Lesser (Mesue)
Troches of Rose and Agrimony (Mesue)
Troches of Nutmeg (Rhasis)
Troches of Gallia Sebellinae (Mesue)
Troches for the Liver and Jaundice (Nicholas)
Electuary of Aloeswood (Unani)
Electuary of Saffron Lesser (Diacrocon Minus) (Mesue)
Electuary of Roman Spikenard
Electuary of Indian leaf (Zenon)
Electuary for Back Pain (Galen)
Confection for Catarrh
Antidotum Immortale
Antidotum Augustini (Nicholas)
Antidotum Epilepticus (Nicholas)
Electuarium Acharistum (Nicholas)
Electuary for Sadness and Worry
Electuary Against Forgetfulness
Electuary for Watering of the Eyes of Andrezeos
Athanasia Minor Nicholas
Athanasia Greater Nicholas
Indian Electuary Greater (Mesue)
Diacameron Minus (Nicholas)
Diacameron Magna (Diathamaron) (Nicholas)
Triphera of the Saracens (Triphera Saracenica Magna)
Foetid Pills (Mesue)
Pills of Spikenard
Pills Proven for Vision (Galen)
Pills to Clarify Pilulae Lucis Majores Mesue
Chebula 7 (A ru bdun pa) (Tibetan)
Nutmeg Powder (Jatiphaladi Churna) (Ayurveda)
Sarpagandha Ghana Vati (Ayurveda)
Supreme 25 (Bla med nyer lnga) (Tibetan)
Universal Conquering Vajra (Tibetan)
Cautions:
Generally Safe.
1. Caution in Qi deficiency (use with Qi tonics)
2. Use cautiously in Yin deficient Heat or Heat in the Blood.
Toxicity:
Oral LD50 of the isolated sesquiterpene valeranone was reported to be greater than 3160 mg/kg in rats and mice
Main Preparations used:
Oil of Spike (made by boiling in water, wine and oil), and a Compound Oil
Generally Safe.
1. Caution in Qi deficiency (use with Qi tonics)
2. Use cautiously in Yin deficient Heat or Heat in the Blood.
Toxicity:
Oral LD50 of the isolated sesquiterpene valeranone was reported to be greater than 3160 mg/kg in rats and mice
Main Preparations used:
Oil of Spike (made by boiling in water, wine and oil), and a Compound Oil
Click the Tabs above for more information on this Medicin
|
'This plant, in Sanskrit Jatamansi, has from a very remote period been in use among the Hindus as a perfume and medicine. It is mentioned by Susruta, and is prescribed by Hindu physicians as a nervine tonic and aromatic adjunct in the preparation of medicinal oils and ghritas (butters). In the Pharmacopoeia of India it is stated that Jatamansi enters into the composition of a nostrum, highly recommended in the treatment of epilepsy by Susruta. Dutt, in his Hindu Materia Medica (p. 180), says:— "I do not find in Susruta's work any prescription for epilepsy, containing Jatamansi, except the following, in which, however, it can hardly be said to be an active ingredient. Take of the pulse of Phaseolus Roxburghii, barley, jujube fruit, seeds of Crotalaria juncea, bdellium, jatamansi root, the ten drugs collectively called dasamula, and chebulic myrobalans equal parts, and prepare a decoction in the usual manner. This decoction is recommended to be administered with the addition of clarified butter and goat's urine. Arabic and Persian writers describe Jatamansi under the name of Sumbul aud Sumbul-i-Hindi, the latter term being used to distinguish it from Valerian, which is sometimes called Sumbul. The author of the Makhzan-el-Adwiya says that it is the Nardin of the Greeks (Dioscorides, I.6), and compares the root to the tail of a sable. He considers it to be deobstruent and stimulant, diuretic and
|
emmenagogue, and recommends it in various disorders of the digestive and respiratory organs, and as a nervine tonic in hysteria, He also notices the popular opinion that it promotes the growth and blackness of the hair. Jatamansi in doses of 45 grains is often employed as an expectorant in coughs and colds.
Ainslie notices that the Vytians in Lower India prepare a fragrant and cooling liniment for the head from this drug, and also prescribe it internally as a purifier of the blood. Sir W. Jones thought that the Spikenard ointment of the ancients might have been made from N. Jatamansi. (Asiat. Res. II. p. 405, and IV., p. 109.) However this may be, there can be no doubt that Jatamansi has been used in India for a similar purpose from a very early date, and that. the principal use of the drug at the present time, is for making hair washes and ointments. Sir W. O'Shaughnessy states, as the result of his experience with Jatamansi, that it is a prefect representative for Valerian. (Bengal Disp., p. 404.) It is very desirable that further trials should be instituted with this promising drug, which can be procured, at a small cost, in almost all the bazars throughout India. Care should be taken to select good specimens for trial, as the central portion of the root is often destroyed by insects. (Vegetable Materia Medica of Western India, Dymock, 1885 |