Sentry Page Protection
Gart der Gesundheit, Cuba, 1485
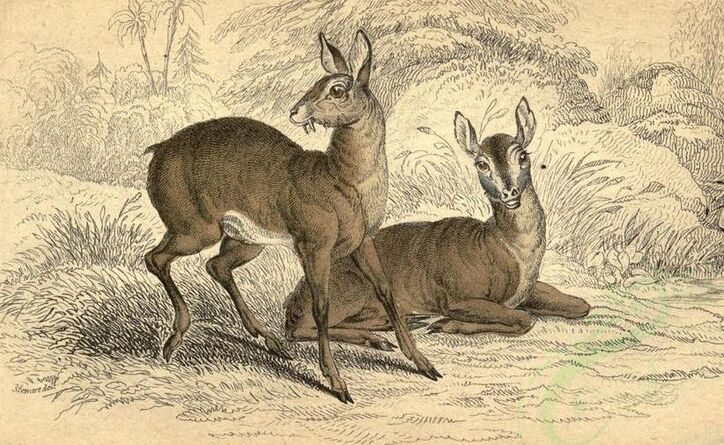
Left: Tonkin Musk; Right: Russian Musk
Handbook of Pharmaceutical Practice, Hager, 1878
Handbook of Pharmaceutical Practice, Hager, 1878
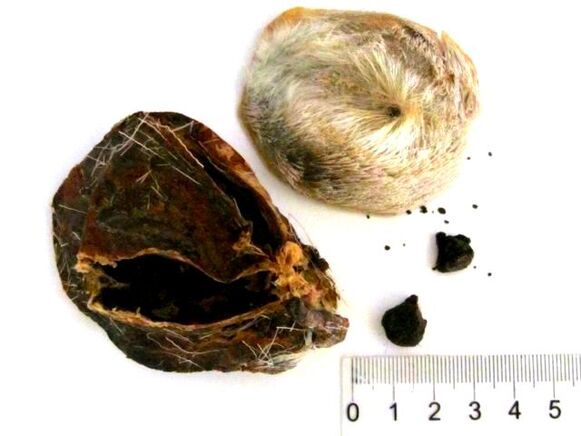
Musk Pods with grains of Musk
(Adam, 2009)
(Adam, 2009)
Zoological name:
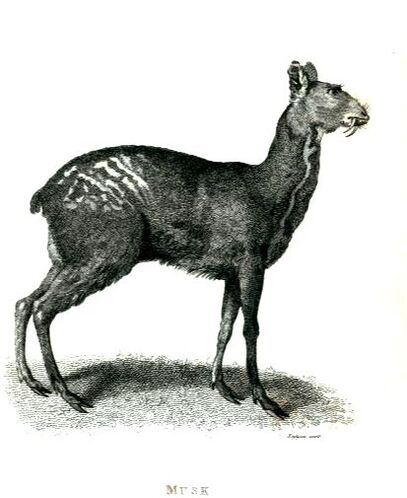
Moschus moschiferus
Parts used:
Dried secretion from the Musk Gland of the male Musk Deer
Temperature & Taste:
Warm, dry. Pungent, Aromatic
Classifications:
2B ATTENUATERS 2H. CARMINATIVES 2I. ANTISPASMODICS 2S. STRENGTHENING MEDICINES
3A. SUDORIFICS & DIAPHORETICS 3C. ALEXIPHARMICS 3D. CORDIALS & CARDIACS 3I. APHRODISIACS 3J. INCREASE SEMEN
4a. CEPHALIC 4c. CARDIAC
TCM:
J. Aromatics that Open the Orifices
Moschus moschiferus
Parts used:
Dried secretion from the Musk Gland of the male Musk Deer
Temperature & Taste:
Warm, dry. Pungent, Aromatic
Classifications:
2B ATTENUATERS 2H. CARMINATIVES 2I. ANTISPASMODICS 2S. STRENGTHENING MEDICINES
3A. SUDORIFICS & DIAPHORETICS 3C. ALEXIPHARMICS 3D. CORDIALS & CARDIACS 3I. APHRODISIACS 3J. INCREASE SEMEN
4a. CEPHALIC 4c. CARDIAC
TCM:
J. Aromatics that Open the Orifices
Uses:
1. Opens the Orifices, Clears Phlegm, Regulates the Mind, Stops Spasms: (all Traditions)
-Convulsions, Epilepsy, Nervousness, Unconsciousness, Coma and Cerebral Palsy
-it restores the lost sense of smell
-Prolonged treatment cures Nightmare
-Hysteria and sleeplessness
-used for numerous chronic or stubborn diseases related to obstruction
2. Moves the Blood, Clears Obstructions and Tumors: (all Traditions)
-severe pain in the chest or abdomen, immobile abdominal masses
-Angina Pectoris, Heart disease
-Avicenna used it for ‘Coldness of the Heart’.
-Tumors and Tuberculosis Lymphadenitis.
-clears the circulation in chronic joint diseases: Rheumatism, Arthritis, as well as chronic stiffness of the neck etc.
-‘A circulatory stimulant benefiting the muscles and bones’.
-fixed pain and bruising from Trauma
-obstinate skin diseases including Leprosy.
-"Strengthens the Heart, acts as an exhilarant and proves to be useful in Palpitation and Restlessness". (Avicenna)
3. Clears Heat and Toxin: (all Traditions)
-infectious and febrile diseases including common cold, Typhoid fever, Malaria, Meningitis and advanced stages of other febrile diseases
-toxic heat diseases such as Tonsillitis.
-‘destroy Evil things and expel Evil Parasites’ (TCM)
-bites of Snakes, Rats, and other venomous creatures; some have claimed it specific in Hydrophobia.
-topically or internally for sores, abscesses, carbuncles, and all kinds of boils with pus.
-various types of Worms and Parasites.
-"Antidote for poisons specially for Aconite" (Avicenna)
4. Warms the Kidneys:
-traditionally used as a sexual stimulant (the Oil being commonly applied externally for this purpose);
-Leukorrhea, Spermatorrhea, nephritis and general weakness.
5. Promotes Labor, Expels the Afterbirth: (all Traditions)
-induces and quickens Labor (best not used for this purpose now: read below)
-removes a dead Fetus, helps promote Expulsion of the Placenta
-Tibetan Medicine also uses it for pain during or after delivery
-abortifacient
-potent Uterine Stimulant
Dose:
In Pills or Powders: 60–100mg (up to 200mg with a maximum single dose of 1 gram)
Tincture of Musk (1 in 20): 1–5 drops
Comment:
This monograph is only given to show traditional use, and also to show how modern acceptable substitutes can replace this traditional medicine. MedicineTraditions DOES NOT CONDONE THE USE OF ENDANGERED OR UNETHICAL ANIMAL MEDICINES.
Correctives:
1. Rose water
2. Tabasheer. (Unani)
3. Sandalwood (Unani)
Substitutes:
1. Storax is considered in TCM to be a suitable plant substitute; Musk and Storax are often combined in traditional formulas. Storax is best for Phlegm and Damp obstructing the mind, nerves and senses.
2. In cases where a purely ‘opening’ effect is desired, especially in formulas intended for Heat, Fever, Delirium etc., Camphor may be used, especially if combined with Storax.
3. Ferula sumbul ('Musk root') was previously commonly used as a substitute for Musk
4. Musk Mallow seed has an aroma of Musk and has previously been sold as Grani Moschati.
5. Delphinium brunonianum is widely used in Tibetan Medicine as a Musk substituite.
6. Cinnamon tamal leaf ('India leaf') has been used in Unani.
8. In perfumery, Labdanum is an accepted vegetable substitute for Musk.
9. Castoreum and Civet may also be used similarly (if they are easier to get).
10. ‘American Musk’ derived from the Muskrat or Musquash, and called Fiber zibethius has been used in place of Musk, but is far inferior.
11. Synthetic Musk (synthetic musk ketone) has been used in place of the natural product and is commonly used in modern Traditional medicine.
12. An Artificial Musk was prepared from Amber oil: Oil of Amber (2 parts), Nitric acid (6 parts). Digest 24 hours, then wash with cold water. (Dispensarium Lippiacum, 1792)
A Note on Synthetic Musks:
Due to the importance of Musk in both Traditional Medicine and Perfumery, synthetic Musk appears to be a very attractive substitute. The most common botanically sourced Musk is from ambrette seed (Hibiscus abelmoschus) but it costs around $20,000 per kilo. Synthetic Musks are sold for a fraction of this cost. However, there are serious health concerns with several of the synthetic Musks.
There are several varieties of synthetic Musk:
Racemic Muscone appears to be the most commonly used synthetic Musk in Traditional Medicine, having being first synthesized in 1906 and is accepted as a food additive (in low dilutions).
In Pills or Powders: 60–100mg (up to 200mg with a maximum single dose of 1 gram)
Tincture of Musk (1 in 20): 1–5 drops
Comment:
This monograph is only given to show traditional use, and also to show how modern acceptable substitutes can replace this traditional medicine. MedicineTraditions DOES NOT CONDONE THE USE OF ENDANGERED OR UNETHICAL ANIMAL MEDICINES.
Correctives:
1. Rose water
2. Tabasheer. (Unani)
3. Sandalwood (Unani)
Substitutes:
1. Storax is considered in TCM to be a suitable plant substitute; Musk and Storax are often combined in traditional formulas. Storax is best for Phlegm and Damp obstructing the mind, nerves and senses.
2. In cases where a purely ‘opening’ effect is desired, especially in formulas intended for Heat, Fever, Delirium etc., Camphor may be used, especially if combined with Storax.
3. Ferula sumbul ('Musk root') was previously commonly used as a substitute for Musk
4. Musk Mallow seed has an aroma of Musk and has previously been sold as Grani Moschati.
5. Delphinium brunonianum is widely used in Tibetan Medicine as a Musk substituite.
6. Cinnamon tamal leaf ('India leaf') has been used in Unani.
8. In perfumery, Labdanum is an accepted vegetable substitute for Musk.
9. Castoreum and Civet may also be used similarly (if they are easier to get).
10. ‘American Musk’ derived from the Muskrat or Musquash, and called Fiber zibethius has been used in place of Musk, but is far inferior.
11. Synthetic Musk (synthetic musk ketone) has been used in place of the natural product and is commonly used in modern Traditional medicine.
12. An Artificial Musk was prepared from Amber oil: Oil of Amber (2 parts), Nitric acid (6 parts). Digest 24 hours, then wash with cold water. (Dispensarium Lippiacum, 1792)
A Note on Synthetic Musks:
Due to the importance of Musk in both Traditional Medicine and Perfumery, synthetic Musk appears to be a very attractive substitute. The most common botanically sourced Musk is from ambrette seed (Hibiscus abelmoschus) but it costs around $20,000 per kilo. Synthetic Musks are sold for a fraction of this cost. However, there are serious health concerns with several of the synthetic Musks.
There are several varieties of synthetic Musk:
- Nitromusks: Moskene, musk xylene, musk ambrette, musk ketone,
- Polycystic musks: Galxaolide (HHCB), Tonalide, Cashmeran
- Macrocylic musks: muscone, ambrettolide
- Aclicylic musks: Helvetolide, Romandolide
Racemic Muscone appears to be the most commonly used synthetic Musk in Traditional Medicine, having being first synthesized in 1906 and is accepted as a food additive (in low dilutions).
Musk and Bezoar are similar in use, both powerfully opening the orifices. However Bezoar is cold and better to clear Heat and Toxin and stop Spasms and Convulsions. Musk is better to move the Blood and open obstructions. They are often combined in formulas.
Mind, Brain, Nerves
1. Musk with Aloeswood and Ambergris to strengthen the Heart and Brain, promote circulation and open Obstructions. (Gallia Moschata)
2. Headache from Cold, Musk, Saffron, Camphor
3. Vertigo, Falling Sickness, Convulsions, Palsy, Sadness, Melancholy, Fainting and Swooning from Wind and Cold, Musk with Saffron, Galangal, Aloeswood, Pearl, Amber, Red Coral, Basil seed, Nutmeg, Cinnamon (as in Sweet Powder of Musk)
4. Spasms and Convulsions:
i. Musk with Valerian
ii. Tremors and Convulsions, Musk, Antelope horn (Ling Yang Jiao), Cinnabar (Zhu Sha) (TCM)
iii. Musk (16 grains), Valerian (1 scruple), Camphor (6 grains). (Pharmacia rationalis, 1806)
5. Nervous rashes and itching, Musk with Valerian
6. Depression, Musk with Camphor
7. To enhance Memory, Musk with Calamus, Nutmeg, Frankincense
8. Hysteria, and to promote Menstruation, Musk with Asafetida
Move the Blood
9. Amenorrhea:
i. Musk, Paeonia rubra Chi Shao Yao, Dang Gui, Safflower (Hong Hua) (TCM)
ii. from Cold and Blood Stasis, Musk with Cinnamon and Saffron
10. Chest Pain from Blood Stasis, Angina Pectoris, Myocardial Infarction:
i. Musk with Aloeswood, Saffron
ii. Musk with Storax, Aloeswood, Camphor
iii. Musk, Costus (Mu Xiang), Peach kernel (Tao Ren) (TCM)
iv. Musk, Ginseng, Bezoar, Cinnamon, Styrax, Toad Venom, Borneol Camphor (as in She Xiang Bao Xin Wan)
11. Trauma with Pain and Bruising:
i. Musk with Frankincense, Myrrh, Notoginseng San Qi and Borneo Camphor
ii. Musk with Dragon's Blood, Frankincense, Myrrh, Safflower, Catechu, Borneol Camphor (as in Qi Li San)
Toxin
12. Acute Sore Throat:
i. Musk, Bezoar
ii. Musk, Coptis Huang Lian, Rhubarb (Da Huang), Licorice
13. Rabies, Musk (16 grains), Cinnabar (12 grains). Supposedly a Chinese recipe. (Pharmacopoeia Wirtembergica, 1798)
14. Toxic Swellings, Musk with Bezoar, Frankincense, Myrrh (as in Xi Huang Wan of TCM)
Other
15. Asthma, Musk with Storax, Benzoin, Aloeswood, Tragacanth, form Troches (used internally and as a fumigation of Asthma)
16. Spasmodic Asthma, Angina Pectoris, Musk, with Ammonium carbonate, Asafetida, Guiaiacum resin, Valerian, Cinnamon (Sobernheim, 1840)
17. Aphrodisiac:
i. Musk with Confectio Alkermes
ii. Cinnamon (half oz.), Ginger, Nutmeg, Long Pepper (1 dram each), Musk (1 scruple), White Sugar (4 oz.). Mix. (Memorial Pharmaceutique, 1824)
18. Lung Cancer, Musk, Frankincense, Myrrh, Bezoar (Xi Huang Wan) has been widely used in China for Lung cancer with positive results.
Major Formulas:
Powder of Musk Sweet (Diamoschu Dulce) (Mesue)
Powder of Musk Bitter (Diamoschu Amarum) (Mesue)
Aloeswood Powder for Palpitations
Species Nere
Warming Powder of Gems (Mesue)
Aromatic Musk Compound Aromaticum Moschatum (Mesue)
Troches of Musk (Gallia Muscata) (Mesue)
Troches of Musk (Gallia Muscata) (Nicholas)
Troches of Musk (Trochisci Moschata) (Rhasis)
Surgeon’s Musked Troches (Alipta Muscata) (Nicholas)
Cooling Electuary of Musk (Rhazes)
Antidote Proven for Diverse Diseases (Nicholas)
Royal Confection of Kermes (Mesue)
Chinese Medicine:
Liu Shen Wan
Zhi Bao Dan
An Gong Niu Huang Wan
Hui Chun Dan
Qi Li San
Su He Xiang Wan
Tong Qiao Huo Xue Tang
Zi Xue Dan
Xi Huang Wan
Zhen Xiang Jiao Nag (Precious Aromatic Capsules) (TCM)
Tibetan Mediicne:
Aloeswood 35 (Agar 35)
Antidotal 18 (Gnyen po bco brgyad)
Barberry 8 (Skyer shun 8)
Betel Nut 13 (Go yu 13)
Calcite 35 (Cong Zhi 35)
Cantharide 37 (Tibetan Meidicine)
Cardamon 10 (Sug Mel 10)
Chebula 18 (A Ru 18)
Chebula 23 (A Ru 23)
Chebula 35 (A Ru 35)
Cliff Garuda Pill (Brag Khung Ril Bu)
Coptis 5 Pill (Tibetan Medicine)
Costus Garuda (Ru khyung)
Eliminator of Undying Microrganisms (Chi med srin sel)
Eliminator of Inflamed Lungs (Glo tshad kun sel)
Embelia 7 (Byi Thang 7)
Garuda 5 (Khyung lnga)
Garuda 8 (Khyung lnga mchu sder can)
Garuda of Camphor
Mercury 18 (Dngul chu 18)
Mind Increasing Jewel (Sam phel nor bu)
Possessing all benefits (Phan pa kun idan)
Safflower 13 (Gur gum 13)
Sandalwood 9 (Tsan dan 9)
Shilajit 9 (Brag Zhun 9)
Universal Conquering Vajra (Tibetan Mediicne)
Cautions:
1. Not used during Pregnancy
2. Caution in very deficienct people and Yin deficiency.
It has been used to promote Labor in the past and has a proven potent uterine stimulant effect, especially on the pregnant uterus. However, without being in a hospital setting it is best not used for this purpose in case its use is associated with complications during childbirth. Also, its use is potentially toxic to the fetus (Chen & Chen, 2001)
Main Preparations used:
Troches of Musk, Sweet Powder of Musk, Gallia Moschata
1. Tincture of Musk:
i. Musk in powder (2 drams), Rectified Spirit (1 pint). Digest 7 days, filter. It is advisable to repeat the extraction with fresh alcohol to exhaust the Musk; the liquors can be added and carefully evaporated to one pint.
1. Not used during Pregnancy
2. Caution in very deficienct people and Yin deficiency.
It has been used to promote Labor in the past and has a proven potent uterine stimulant effect, especially on the pregnant uterus. However, without being in a hospital setting it is best not used for this purpose in case its use is associated with complications during childbirth. Also, its use is potentially toxic to the fetus (Chen & Chen, 2001)
Main Preparations used:
Troches of Musk, Sweet Powder of Musk, Gallia Moschata
1. Tincture of Musk:
i. Musk in powder (2 drams), Rectified Spirit (1 pint). Digest 7 days, filter. It is advisable to repeat the extraction with fresh alcohol to exhaust the Musk; the liquors can be added and carefully evaporated to one pint.
Click the Tabs above for more information on this Medicine
1. Zoology, chemical composition, pharmacology, quality control and future perspective of Musk (Moschus): a review
2. Native musk and synthetic musk ketone strongly induced the growth repression and the apoptosis of cancer cells
3. Musk ketone induces apoptosis of gastric cancer cells via downregulation of sorbin and SH3 domain containing 2
4. Inhibitory mechanism of muscone in liver cancer involves the induction of apoptosis and autophagy
5. A Network Pharmacology Approach to Investigate the Active Compounds and Mechanisms of Musk for Ischemic Stroke
2. Native musk and synthetic musk ketone strongly induced the growth repression and the apoptosis of cancer cells
3. Musk ketone induces apoptosis of gastric cancer cells via downregulation of sorbin and SH3 domain containing 2
4. Inhibitory mechanism of muscone in liver cancer involves the induction of apoptosis and autophagy
5. A Network Pharmacology Approach to Investigate the Active Compounds and Mechanisms of Musk for Ischemic Stroke