Sentry Page Protection
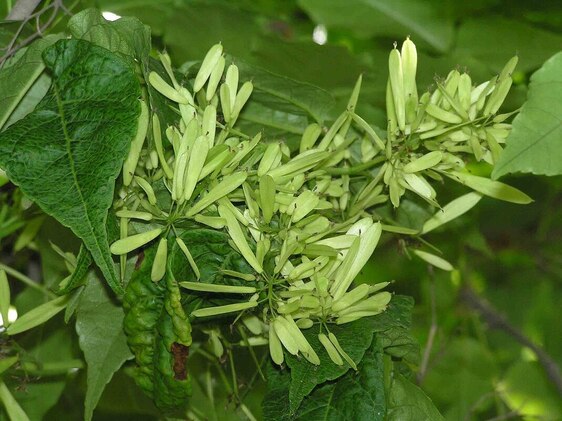
Fraxinus rhynchophylla, Qin Pi 秦皮
Korean or Chinese Ash tree
Qin Pi (TCM)
Stab seng སྟབ་སེང༌ (Tibet)
Qin Pi (TCM)
Stab seng སྟབ་སེང༌ (Tibet)
F. chinensis
Nakai, T., Trees and shrubs indigenous in Japan proper [Dai Nihon jumokushi] (1935-1951)
Nakai, T., Trees and shrubs indigenous in Japan proper [Dai Nihon jumokushi] (1935-1951)
Botanical name:
Fraxinus rhynchophylla (syn. F. chinensis)
Other sources reportedly used in TCM include: F. bungeana, F. szaboana (syn. F. chinensis var acuminata), F. stylosa, F. mandshurica, F. axiana
In Tibet: F. suaveolens, F. axiana var. sikkimensis
See also the Western Ash tree.
Parts used:
Bark
Temperature & Taste:
Cool, dry. Astringent
Fraxinus rhynchophylla (syn. F. chinensis)
Other sources reportedly used in TCM include: F. bungeana, F. szaboana (syn. F. chinensis var acuminata), F. stylosa, F. mandshurica, F. axiana
In Tibet: F. suaveolens, F. axiana var. sikkimensis
See also the Western Ash tree.
Parts used:
Bark
Temperature & Taste:
Cool, dry. Astringent
Uses:
1. Clears Heat and Damp, Resists Toxin: (TCM, Tibet)
-Diarrhea, Dysentery (TCM)
-abdominal pain from Heat and Damp obstruction (Tibet)
-Leukorrhea with foul-smelling yellow discharge, or with Blood (TCM)
2. Clears Liver Heat, Benefits the Eyes: (TCM)
-red, swollen, sore eyes from Liver heat
-superficial visual obstruction
-Childhood Convulsions from Liver heat
-Mental illness (old use)
-"It brightens the eye and eliminates red and swollen eyes with pain" (Zhen Quan)
-also used as a wash topically for red, sore, swollen eyes.
3. Benefits Kidneys, Heals Bones: (Tibet, TCM)
-Essence deficiency causing Lumbago, Impotence, Spermatorrhea (TCM)
-Fractures (Tibet)
-older texts said it is beneficial for lack of Sperm in men
-Wind-Damp painful obstruction (TCM)
-'Bone Fever' (Tibet)
-"good for treating arthralgia due to an attack of pathogenic Wind, Cold and Humidity" (Shen Nong Ben Cao Jing)
4. Clears Heat, Stops Cough: (TCM)
-Lung Heat Cough and Wheezing
-chronic Bronchitis
5. Externally:
-as a wash for sore, red eyes
-decoction as a wash for red and itchy skin, Eczema, Psoriasis
-as a wash for vaginal itchiness
-grind to a powder and apply to Snake Bite
-"It can be stewed in water to make a decoction to wash the eye and keep it in good condition. Long-term use makes one’s skin lustrous and moist". (Ming Yi Bie Lu)
Dose:
Decoction: 6–12 grams
Powder: 2–5 grams
Comment:
This is an interesting medicine as its use in TCM and Tibetan Medicine is quite different. In TCM it is primarily used as an astringent that clears Heat, for Diarrhea, Dysentery and Leukorrhea. It benefits the Eyes, and clears Liver Heat.
In Tibetan Medicine, it is primarily indicated for Fractures, hence the recommendation of Eucommia Du Zhong as a suitable substitute. However, older TCM texts list it as having an Essence-tonifying action, suggesting a strengthening effect on the Kidneys. Its Essence-building quality was noted as being due to both its astringency (which stops loss of Essence), along with a tonifying action of its own. Thus, it also strengthens the Kidneys, Bones and Lower Back which is also related to its TCM indication of being useful for Wind-Damp pain (arthritis and rheumatic pain).
It's also worth noting that Ash tree 'keys' (seed pods) were highly regarded as an aphrodisiac Kidney tonic in the Western Tradition, indicating a Kidney tonic action of the tree.
Substitute:
1. Eucommia Du Zhong has been used as a substitute by Tibetan sources (in Russia). This is an effective substitute for one of the primary indications in Tibetan Medicine, to heal fractures, and for weak and aching lower back. It is not a suitable substitute to clear Heat and Damp in Diarrhea and Dysentery, however.
2. For Damp-Heat Diarrhea and Dysentery, and for the Eyes, Walnut tree bark has been used similarly.
Preparation:
Charred Fraxinus Qin Pi:
The bark is dry-fried until well scorched. This enhances its astringent effect and lessens its coldness. It makes it more effective to stop Bleeding and restrain Diarrhea and Dysentery, so is useful for Diarrhea with blood, pus or mucus in the stool. (TCM)
Decoction: 6–12 grams
Powder: 2–5 grams
Comment:
This is an interesting medicine as its use in TCM and Tibetan Medicine is quite different. In TCM it is primarily used as an astringent that clears Heat, for Diarrhea, Dysentery and Leukorrhea. It benefits the Eyes, and clears Liver Heat.
In Tibetan Medicine, it is primarily indicated for Fractures, hence the recommendation of Eucommia Du Zhong as a suitable substitute. However, older TCM texts list it as having an Essence-tonifying action, suggesting a strengthening effect on the Kidneys. Its Essence-building quality was noted as being due to both its astringency (which stops loss of Essence), along with a tonifying action of its own. Thus, it also strengthens the Kidneys, Bones and Lower Back which is also related to its TCM indication of being useful for Wind-Damp pain (arthritis and rheumatic pain).
It's also worth noting that Ash tree 'keys' (seed pods) were highly regarded as an aphrodisiac Kidney tonic in the Western Tradition, indicating a Kidney tonic action of the tree.
Substitute:
1. Eucommia Du Zhong has been used as a substitute by Tibetan sources (in Russia). This is an effective substitute for one of the primary indications in Tibetan Medicine, to heal fractures, and for weak and aching lower back. It is not a suitable substitute to clear Heat and Damp in Diarrhea and Dysentery, however.
2. For Damp-Heat Diarrhea and Dysentery, and for the Eyes, Walnut tree bark has been used similarly.
Preparation:
Charred Fraxinus Qin Pi:
The bark is dry-fried until well scorched. This enhances its astringent effect and lessens its coldness. It makes it more effective to stop Bleeding and restrain Diarrhea and Dysentery, so is useful for Diarrhea with blood, pus or mucus in the stool. (TCM)
Main Combinations:
1. Diarrhea or Dysentery from Damp-Heat:
i. Fraxinus Qin Pi (9 grams), decoct, sweeten with brown sugar and drink
ii. Fraxinus Qin Pi with Costus (Mu Xiang), Coptis Huang Lian
iii. Fraxinus Qin Pi with Phellodendron Huang Bai, Pulsatilla Bai Tou Weng (as in Bai Tou Weng Tang)
iv. Chronic bacillary Dysentery, Fraxinus Qin Pi with Burnet (Di Yu), Ailanthus Chun Pi
2. Sore, red, swollen Eyes from Liver heat:
i. Fraxinus Qin Pi with Chrysanthemum Ju Hua
ii. Fraxinus Qin Pi with Coptis Huang Lian
iii. Fraxinus Qin Pi with Cassia tora Jue Ming Zi, Horsetail (Mu Zei), Chrysanthemum Ju Hua
iv. Fraxinus Qin Pi with Prunella Xia Ku Cao, Chrysanthemum Ju Hua, Lycium Gou Qi Zi
3. Stye, Fraxinus Qin Pi (9 grams), Rhubarb (Da Huang) (6 grams)
4. Leukorrhea, with foul-smelling yellow discharge from Damp-Heat, Fraxinus Qin Pi with Paeonia Mu Dan Pi
5. Leukorrhea with Blood, or continuous bleeding, Fraxinus Qin Pi (3 parts), Dang Gui (2 parts), Dang Gui (1 part. Sprinkle with wine, stir-fry to dryness, and form pills with honey.
6. Childhood convulsions, Fraxinus Qin Pi, Poria Fu Ling, Licorice
Major Formulas:
Bai Tou Weng Tang
Cautions:
Caution in Cold and Weakness of the Stomach
Main Preparations used:
Caution in Cold and Weakness of the Stomach
Main Preparations used: