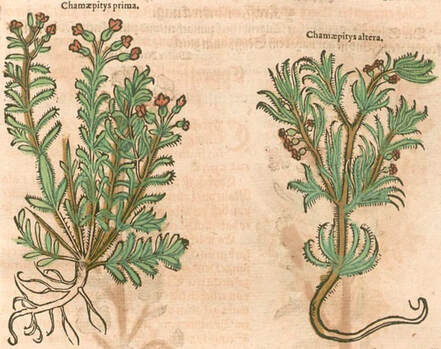
New Kreuterbuch, Matthiolus, 1563
Two types of Ground Pine traditionally used (left is the primary)
Krauterbuch, Lonitzer, 1578
Krauterbuch, Lonitzer, 1578
Two types of Ground Pine traditionally used (left is the primary)
Dioscorides Materia Medica, Mathias, 1563
Dioscorides Materia Medica, Mathias, 1563
Botanical name:
Ajuga chamaepitys (syn. Teucrium chamaepitys)
Other varieties were listed by Galen and Dioscorides including A. chia, A. iva
Parts used:
Herb
Temperature & Taste:
Warm, dry. Bitter, pungent
"hot in the Second and dry in the third degree" (Avicenna)
Classifications:
2A APERIENT. 2B ATTENUATER. 2C INCIDER. 2F. PURIFYING. 2G. CLEANSING. 2K. RESOLVENT
3E. DIURETIC. 3F. LITHONTRIPTIC. 3M. ARTHRITIC
4f. SPLENETIC
Ajuga chamaepitys (syn. Teucrium chamaepitys)
Other varieties were listed by Galen and Dioscorides including A. chia, A. iva
Parts used:
Herb
Temperature & Taste:
Warm, dry. Bitter, pungent
"hot in the Second and dry in the third degree" (Avicenna)
Classifications:
2A APERIENT. 2B ATTENUATER. 2C INCIDER. 2F. PURIFYING. 2G. CLEANSING. 2K. RESOLVENT
3E. DIURETIC. 3F. LITHONTRIPTIC. 3M. ARTHRITIC
4f. SPLENETIC
Uses:
1. Clears Wind, Strengthens the Nerves and Brain:
-Epilepsy, Cramps, Paralysis
2. Clears Wind-Damp, Promotes Urine, Eases Pain:
-important herb for Gout and Arthritic complaints; all aches and pains of the Limbs
-Sciatica, taken with Hydromel for 40 days (Dioscorides, Avicenna)
-strangury, difficult Urination
-"It cures Dysuria .. also useful in Nephralgia". (Avicenna)
3. Opens Obstructions:
-Jaundice, taken with wine (Dioscorides)
-"removes Hepatic obstructions and is useful in some Hepatic and Splenic diseases" (Avicenna)
-"Its continuous intake for seven days is also useful in Black Jaundice". (Avicenna)
4. Moves the Blood, Promotes Menstruation:
-powerfully promotes Menstruation when obstructed
-‘all diseases of the Mother [Uterus]’.
-Traditionally used to expel a Dead Fetus or the Afterbirth.
-in pessaries with honey to cleanse the Uterus (Dioscorides)
-"removes the Uterine obstructions" (Avicenna)
5. Resists Poison:
-acute Cough, Cold
-antidote to Aconite, Hemlock etc. (since Dioscorides)
-‘It is an especial remedy for the poison of the Aconites of all sorts, and other poisonful Herbs, as also against the stinging of any Venomous Creature’ (Culpeper)
6. Kills Worms
7. Externally:
-fresh herb beaten and applied dissolves hardness of the Breasts, and all hard swellings of other parts. (Dioscorides, Avicenna)
-fresh herb beaten, or the juice mixed with Honey and applied was used for all old ‘putrid, stinking, foul and malignant Ulcers and Sores of all sorts’, as well as fresh Wounds. (Culpeper, Avicenna))
-applied to Honey to Shingles (Dioscorides, Avicenna)
-"dissolves the hardness of Gout" (Avicenna)
Dose:
Usually only used in Compounds
Powder: 1–3 grams
Substitutes:
1. Germander
2. Mixture of half the weight of Asafetida, and one-quarter weight of Chinese Cassia (Rhazes)
3. "Lovage in half its quantity and Cassia bark in one-fourth its quantity act as its substitutes" (Avicenna)
Usually only used in Compounds
Powder: 1–3 grams
Substitutes:
1. Germander
2. Mixture of half the weight of Asafetida, and one-quarter weight of Chinese Cassia (Rhazes)
3. "Lovage in half its quantity and Cassia bark in one-fourth its quantity act as its substitutes" (Avicenna)
Main Combinations:
Ground Pine & Germander
1. Often combined with Germander for Arthritic and Joint disease:
i. see Germander for Combinations
2. For Arthritic conditions, Pills were prepared from Ground Pine and Colchicum, made up with Turpentine oil.
3. Pains of the Head, Ground Pine with Horehound, Wormwood, Mastic, Rhubarb, Germander, Hyssop, Agaric (as in Theriac for Pain in the Head)
Major Formulas
Powder Against Joint Pain
Powder for Gout of the Duke of Portland
The Powder of Trithemius
Antidote of Seven Things (Paulus Aegineta)
Theriac for Pain in the Head
Cautions:
1. Not used during Pregnancy.
2. Very drying, so not suitable for use in Yin deficiency.
Main Preparations used:
Distilled Water and compound Pills
1. Not used during Pregnancy.
2. Very drying, so not suitable for use in Yin deficiency.
Main Preparations used:
Distilled Water and compound Pills
Click the Tabs above for more information on this Medicine
Pliny on Ground Pine:
|
'The chamapitys, called in Latin " abiga," because it promotes abortion, and known to some as incense of the earth, has branches a cubit in length, and the odour and blossoms of the pine. Another variety of it, which is somewhat shorter, has all the appearance of being bent down wards; and there is a third, which, though it has a similar smell, and consequently the same name, is altogether smaller, with a stem the thickness of one's finger, and a diminutive, rough, pale leaf: it is found growing in rocky localities. All these varieties are in reality herbaceous productions; but in consequence of the resemblance of the name, I have thought it as well not to defer the consideration of them.
'These plants are good for stings inflicted by scorpions, and are useful as an application, mixed |
with dates or quinces, for maladies of the liver: a decoction of them with barley-meal is used for the kidneys and the bladder. A decoction of them in water is used also for jaundice and for strangury. The kind last mentioned, in combination with honey, is good for wounds inflicted by serpents, and a pessary is made of it, with honey, as a detergent for the uterus. Taken in drink it brings away coagulated blood, and rubbed upon the body it acts as a sudorific: it is particularly useful also for the kidneys. Pills of a purgative nature are made of it for dropsy, with figs. Taken in wine, in doses of one victoriatus, it dispels lumbago, and cures coughs that are not of an inveterate description. A decoction of it in vinegar, taken in drink, will instantaneously bring away the dead foetus, it is said.' (The Natural History of Pliny, trans. by Bostock and Riley, Vol. 5, 1856)
|