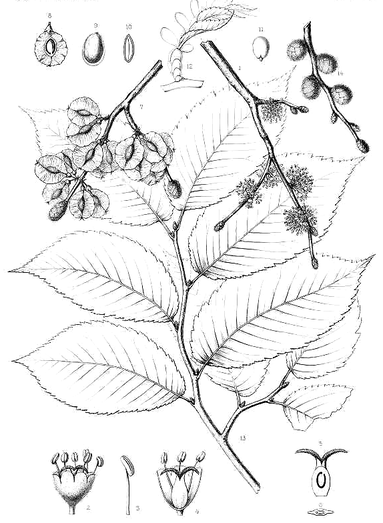
Ulmus rubra, Slippery Elm
Red Elm
C.S. Sargent, The Silva of North America, (1898)
F.A. Michaux, The North American sylva, vol. 3 (1819)
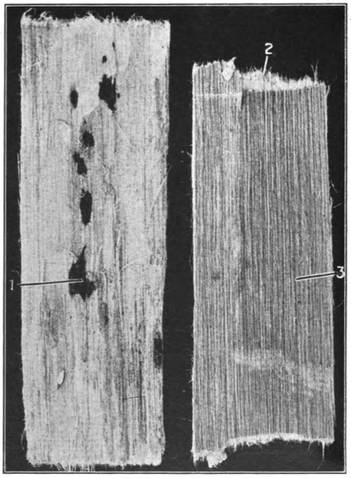
Slippery Elm bark
1, Outer surface of the peeled bark with adhering patches of cork.
2, Fibers showing at the broken ends. 3, The long, coarsely striated inner surface.
(Squibb's Atlas of the Official Drugs, Mansfield, 1919)
1, Outer surface of the peeled bark with adhering patches of cork.
2, Fibers showing at the broken ends. 3, The long, coarsely striated inner surface.
(Squibb's Atlas of the Official Drugs, Mansfield, 1919)
Botanical name:
Ulmus rubra (syn. U. fulva)
Two different varieties of Slippery Elm were known by early Physicians:
1. One with hard, tough bark
2. One with very brtille bark (best)
Parts used:
Peeled bark / Inner bark
Temperature & Taste:
Cool, moist. Sweet
Ulmus rubra (syn. U. fulva)
Two different varieties of Slippery Elm were known by early Physicians:
1. One with hard, tough bark
2. One with very brtille bark (best)
Parts used:
Peeled bark / Inner bark
Temperature & Taste:
Cool, moist. Sweet
Uses:
1. Nourishes Yin, Benefits Lungs:
-Lung deficiency; Lung dryness with dry Cough, Wheezing
-Breathlessness, Chronic Lung disease with Yin deficiency
-Hemoptysis
2. Clears Heat, Nourishes Stomach Yin:
-Stomach dryness with excess Thirst
-Heartburn, Acid reflux, Hyperacidity
-Ulcers
3. Clears Heat:
-applied to Redness and irritation of the skin, Dermatitis, Eczema
-topically for Burns, Scalds (paste externally)
-topically for Vaginitis and Vaginal infections
Dose:
Powder: 500mg–2 grams
Fluid Extract (1:1 in 60% alcohol): 3–5 mls., 2–3 times daily.
To make a mucilage, add 1 teaspoonful of the powdered bark with an equal amount of sugar, mixed well. Mix with a little cold water to a paste, then add hot water to form a jelly. Taken in teaspoonful doses for sore throat, stomach irritation etc. If more water is added it can be taken as drink.
Correctives:
1. Ginger; Cinnamon
2. Honey
Substitutes:
1. Marshmallow root
Powder: 500mg–2 grams
Fluid Extract (1:1 in 60% alcohol): 3–5 mls., 2–3 times daily.
To make a mucilage, add 1 teaspoonful of the powdered bark with an equal amount of sugar, mixed well. Mix with a little cold water to a paste, then add hot water to form a jelly. Taken in teaspoonful doses for sore throat, stomach irritation etc. If more water is added it can be taken as drink.
Correctives:
1. Ginger; Cinnamon
2. Honey
Substitutes:
1. Marshmallow root
Main Combinations:
1. Chronic Lung Yin deficiency with dry Cough, weak voice, Slippery Elm with Comfrey, Licorice
2. Heartburn:
i. Slippery Elm, Ginger, Fennel seed
ii. Slippery Elm, Red Earth, Licorice
3. Stomach Ulcers:
i. Slippery Elm, Golden Seal, Licorice
ii. Slippery Elm, Marshmallow, Yarrow, Comfrey leaf
4. Topically for Eczema, Slipper Elm, Plantain leaf, Comfrey leaf, Calendula as a wash.
5. Poultice:
i. burns, scalds, old sores, whitlow, Slippery Elm with Ginger
ii. Burns and Scalds, Slippery Elm with Raspberry leaf
Major Formulas:
Cautions:
Generally safe and well tolerated.
1. Not suitable in Cold-Phlegm conditions
Main Preparations used:
Generally safe and well tolerated.
1. Not suitable in Cold-Phlegm conditions
Main Preparations used: