Triticum spleta, Spelt
Spelt Corn, Zea Dicoccos
Dinkel (German)
Dinkel (German)
Ortus Sanitatis, Meydenbach, 1491
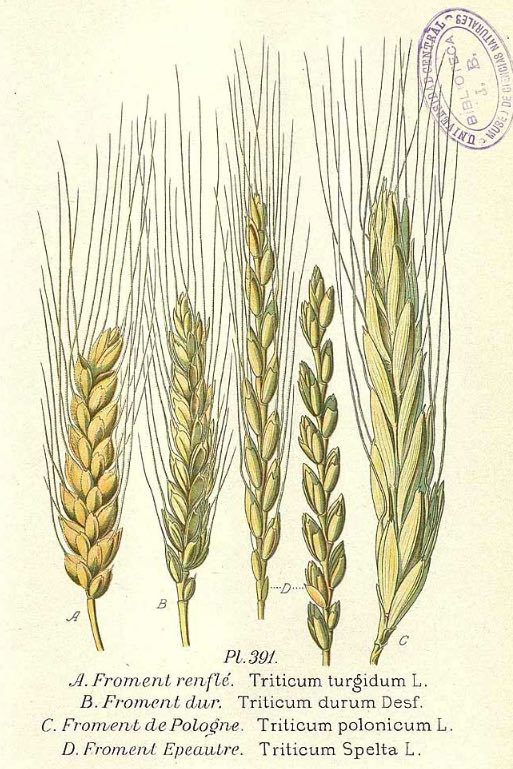
Several varieties of Triticum, that labelled 'D' being Spelt.
A. Masclef, Atlas des plantes de France, vol. 3, (1893)
A. Masclef, Atlas des plantes de France, vol. 3, (1893)
Botanical name:
Triticum spelta
Parts used:
Seed (Grain)
Temperature & Taste:
Neutral/slightly Warm. Sweet
Galen said Spelt is between Wheat and Barley in temperature.
Triticum spelta
Parts used:
Seed (Grain)
Temperature & Taste:
Neutral/slightly Warm. Sweet
Galen said Spelt is between Wheat and Barley in temperature.
Uses:
1. Benefits Spleen, Dries Damp, Increases Qi:
-weakness, poor digestion
-provides proper Blood' (Hildegard)
2. Stops Sweating:
-spontaneous sweating from Qi deficiency
-Nigh Sweats associated with Yin deficiency.
-can also be used for Urinary Incontinence in Children
3. Benefits the Heart, Calms the Spirit:
-'creates a Happy mind' (Hildegard)
-used similar to Wheat in TCM, used for Mental instability, Hysteria and excess Emotions
Dose:
Used as a food in Breads, baked goods, pasta, and can be made into porridge.
15–30 grams
Comment:
Spelt is a type of Wheat, but is less Damp than wheat, and in general is easier to digest and more wholesome. Some celiacs have found they can eat Spelt despite it still having gluten. Nevertheless, excess may still breed Phlegm and Damp.
Preparation:
It can be gently stir-fried until Golden to increase its warmth and lessen its Damp quality. This makes it lighter, easier to digest, more warming, and better to strengthen the Spleen.
Used as a food in Breads, baked goods, pasta, and can be made into porridge.
15–30 grams
Comment:
Spelt is a type of Wheat, but is less Damp than wheat, and in general is easier to digest and more wholesome. Some celiacs have found they can eat Spelt despite it still having gluten. Nevertheless, excess may still breed Phlegm and Damp.
Preparation:
It can be gently stir-fried until Golden to increase its warmth and lessen its Damp quality. This makes it lighter, easier to digest, more warming, and better to strengthen the Spleen.
Main Combinations:
1. Stomach weakness, unable to eat: cook Spelt as a porridge and add Egg Yolk. (Hildegard)
2. Spleen weakness with Damp, Spelt and Barley cooked as a porridge with Red dates (Jujubes) and fresh Ginger.
3. Cold Lumbar and Kidney Pain: A bag containing equal parts of Spelt and Millet grains is to be warmed and applied over the Kidneys, anointing the area with some warming oil after.
4. Urinary Incontinence in Children, Spelt, Barley (or Job's Tears, Yi Yi Ren, both toasted)
5. Emotionalism, Hysteria, Spelt, Licorice, Chinese Red Date. (This is a Chinese formula using Wheat, but Spelt may be used the same and is perhaps better, especially for those who are Damp)
6. Weakness, Frogs were boiled with Spelt and old Wine (Pliny)
7. Swollen legs from Cold and standing too long, make a poultice of Spelt meal, boiled in water with Red Sandalwood added, with a little oil of Roses and Lilies added. Apply hot. (Gerard)
Major Formulas:
Cautions:
Dioscorides said it is difficult to digest, although others including Hildegard said it is easy to digest.
Main Preparations used:
Dioscorides said it is difficult to digest, although others including Hildegard said it is easy to digest.
Main Preparations used: