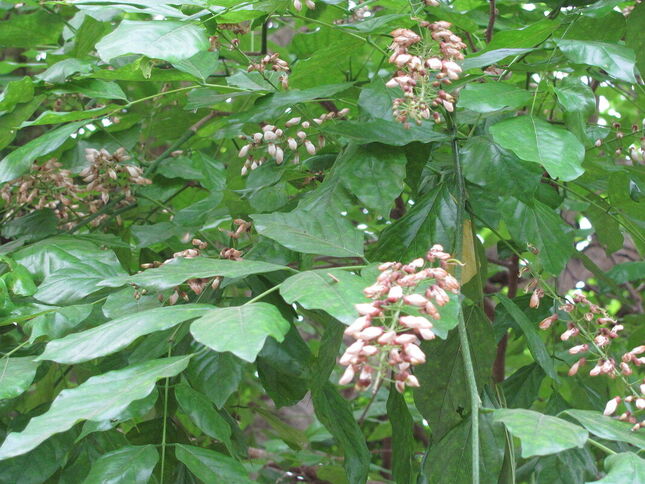
Pongamia, Indian Beech
Karakja (Ayurveda)
Karanj (Unani)
Punkum verptdai (root-bark), Punkum Viththu (Seed) (Siddha)
Jam Bras (Tibetan)
Karanj (Unani)
Punkum verptdai (root-bark), Punkum Viththu (Seed) (Siddha)
Jam Bras (Tibetan)
Pongamia pinnata
Blanco, Flora de Filipinas. (1875)
Blanco, Flora de Filipinas. (1875)
Botanical name:
Pongamia pinnata
Synonyms include P. glabra, P. mittis, Derris indica, Dalbergia arborea, Galedupa indica, Galedupa pinnata, Mellittia pinnata
Parts used:
Seed; Bark; less commonly the Leaf
Temperature & Taste:
Warm, dry. Bitter
Pongamia pinnata
Synonyms include P. glabra, P. mittis, Derris indica, Dalbergia arborea, Galedupa indica, Galedupa pinnata, Mellittia pinnata
Parts used:
Seed; Bark; less commonly the Leaf
Temperature & Taste:
Warm, dry. Bitter
Uses:
1. Clears Damp, Stops Itching, Resists Poison:
-Eczema, Scabies, Psoriasis, Leprosy, Ulcers, Tumors (leaf, seed, root; topically and internally)
-abdominal Abscesses
-Poisoning, Fevers
2. Clears Phlegm, Stops Cough:
-Irritating Cough, Bronchitis, Whooping Cough in children (seed)
3. Stops Bleeding:
-seed have been used for internal bleeding
-used after childbirth to stop bleeding and tone the uterus (Decoction of bark, Indonesia)
4. Moves Qi, Opens Obstructions:
-Spleen enlargement
-sluggish or obstructed Liver
5. Warms the Kidneys, Stops Leakage:
-Leukorrhea, dribbling Urine
-Diabetes (root, flower)
-bleeding Piles
6. Benefits Eyes:
-used for various Eye diseases (Root, fruit, Tibet)
7. Externally:
-root juice is applied to Fistulous Sores and to cleanse Foul Ulcers
-seed oil is used for skin diseases including Herpes, Scabies, Leukoderma
-oil is applied to the chest for Colds, Cough and Pneumonia
-paste of the Seeds or seed oil is applied to Arthritis, Rheumatism and Leprosy.
-oil is also applied to Rheumatism
-used in baths and washes for Rheumatism
-paste of the root is applied to Scrofulous enlargements
-seed oil is applied to baldness
Dose:
Seed in Powder 250–500mg, to 1 gram;
In Decoction: 5–10 grams;
Leaf Juice: 10–20mls
Correctives:
Black Pepper, Pepper root
Substitute:
1. Leaf can be used in place of the Seed
2. Caesalpinia sepiaria
3. Podophyllum peltatum (externally in skin diseases)
Seed in Powder 250–500mg, to 1 gram;
In Decoction: 5–10 grams;
Leaf Juice: 10–20mls
Correctives:
Black Pepper, Pepper root
Substitute:
1. Leaf can be used in place of the Seed
2. Caesalpinia sepiaria
3. Podophyllum peltatum (externally in skin diseases)
Main Combinations:
1. Worms, with Butea monosperma and Sapindus trifoliatus
Cautions:
None noted
Main Preparations used:
None noted
Main Preparations used: