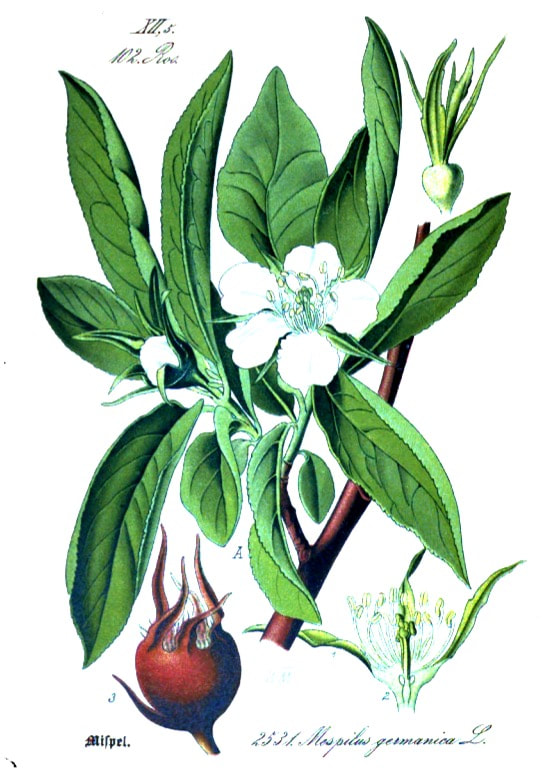
Mespilus, Medlar
Dutch Medlar
|
Ortus Sanitatis, Meydenbach, 1491
|
Krauterbuch, Lonitzer, 1578
|
Kreutterbuch, Matthiolus, 1586
Flora von Deutschland (25), Kohler, 1886
Botanical name:
Mespilus germanica (syn. M. vulgaris)
The Mediterranean Medlar is Crataegus azarolus (syn. Mespilus azarolus), called Azarole, and was used similarly.
Pliny listed three varieties:
Parts used:
Unripe Fruit; rarely the Kernel or Leaf
Temperature & Taste:
Cool, dry. Sour. Green fruit are more Sour and Dry. Ripe fruit is less dry and Sweet.
"Some experts opine it is Cold and Moist". (Avicenna)
Mespilus germanica (syn. M. vulgaris)
The Mediterranean Medlar is Crataegus azarolus (syn. Mespilus azarolus), called Azarole, and was used similarly.
Pliny listed three varieties:
- Anthedon (Crataegus azarolus)–Mespilon Eteron of Dioscorides
- Setania (Italian Medlar)
- Gallic (French Medlar)
Parts used:
Unripe Fruit; rarely the Kernel or Leaf
Temperature & Taste:
Cool, dry. Sour. Green fruit are more Sour and Dry. Ripe fruit is less dry and Sweet.
"Some experts opine it is Cold and Moist". (Avicenna)
Uses:
1. Astringes to Stop Leakage:
-chiefly for Diarrhea and Dysentery
-Leukorrhea, Spermatorrhea
-Mesue used it to astringe (firm) the Uterus and Vulva
-Dried Green fruit is strongest; Green fruit, Ripe fruit and Leaf also share this function in descending order of strength
2. Promotes Urine, Clears Stones
-Edema
-expel stones from the Kidneys
-Medlar kernels are more often used for this purpose, especially for stones
3. Externally:
-Vomiting and Fluxes (Cataplasm over the Stomach)
-Plaster applied to the lower back prevents Miscarriage
-in Gargles for pain and swelling of the mouth, tongue or throat
-in Baths for the Uterus for excess menstruation
Dose:
Powder of the Fruit: 3–6 grams
Powder of the Kernel: 1–2 grams (for Stones)
Decoction: 3–9 fruit
Syrup of the Juice: 1–2 spoonfuls
Preparations:
The fruits were commonly preserved with Honey or Sugar.
Comment:
1. As with similar fruit such as Apple and Hawthorn, they are sour when unripe, becoming sweet when ripe. The unripe fruit were preferred, being a grateful sour and beneficial to the stomach.
2. Mespilus azarolus (syn. Crataegus azarolus) was used as a type of Medlar. Avicenna said of this species: "It eliminates yellow bile and prevents excessive secretions. In this respect it is more effective than any other fruit"
Powder of the Fruit: 3–6 grams
Powder of the Kernel: 1–2 grams (for Stones)
Decoction: 3–9 fruit
Syrup of the Juice: 1–2 spoonfuls
Preparations:
The fruits were commonly preserved with Honey or Sugar.
Comment:
1. As with similar fruit such as Apple and Hawthorn, they are sour when unripe, becoming sweet when ripe. The unripe fruit were preferred, being a grateful sour and beneficial to the stomach.
2. Mespilus azarolus (syn. Crataegus azarolus) was used as a type of Medlar. Avicenna said of this species: "It eliminates yellow bile and prevents excessive secretions. In this respect it is more effective than any other fruit"
Main Combinations:
1. Vomiting or Diarrhea, with Rose, Clove, Nutmeg and Red Coral
2. Gravel, Stones:
i. Medlar kernels powdered and taken with decoction of Parsley root expels Stones.
ii. Medlar kernel with Nutmeg, Juniper berry, Bay berry (as in Powder of Maximillian for Gravel)
iii. Medlar, with Chicken Gizzard skin, Fennel seed, Aniseed
Major Formulas:
Powder of Maximillian for Gravel
Cautions:
1. The fruit hurts the Stomach, especially when green and hard. (Schroder)
Main Preparations used:
1. The fruit hurts the Stomach, especially when green and hard. (Schroder)
Main Preparations used: