Sentry Page Protection
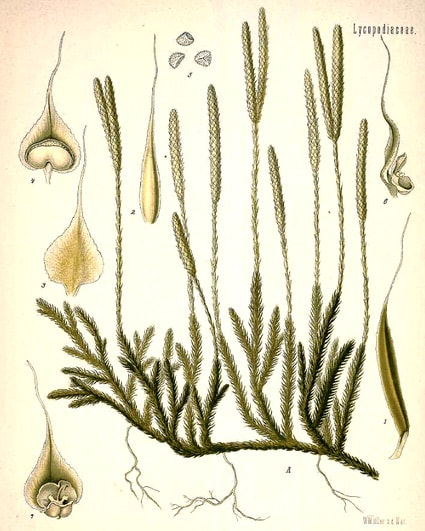
Lycopodium clavatum
Eicones plantarum seu stirpium, Jacobus Theodorus, 1590
Eicones plantarum seu stirpium, Jacobus Theodorus, 1590
Lycopodium clavatum
F.E. Koehler, Medizinal Pflanzen, vol. 1 (1887)
F.E. Koehler, Medizinal Pflanzen, vol. 1 (1887)
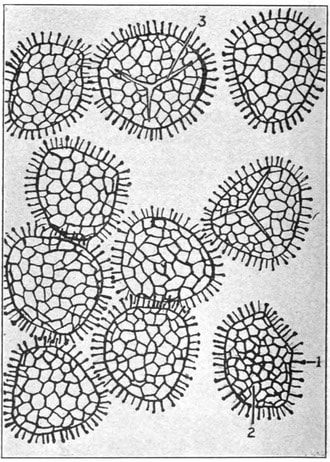
Lycodium spores under magnification
Squibb's Atlas of the Official Drugs, Mansfield, 1919
Squibb's Atlas of the Official Drugs, Mansfield, 1919
Botanical name:
Lycopodium spp.
In different countries, a range of Clubmoss species have been used similarly.
In the Western Tradition, a number of Ground Moss were used:
Parts used:
Herb; Spores
Temperature & Taste:
Warm, dry. Bitter, Pungent (TCM)
Classification:
D. Clear Wind and Damp
Lycopodium spp.
- L. clavatum (Common Clubmoss) (West, TCM)
- L. japonicum (TCM)
- L. cernnum (TCM)
In different countries, a range of Clubmoss species have been used similarly.
In the Western Tradition, a number of Ground Moss were used:
- Common Ground Moss: two varieties
- Muscus scoparius; Beeson Moss
- Club Moss: Greater and Lesser (dealt with here)
- Muscus Denticularis: Toothed Moss
- Muscus Pennatus: Winged Moss, Greater and Lesser
- Muscus Spicatus: Creeping Moss with Spiked Heads
- Muscus Erectus: Branched Moss, Greater and Lesser
- Muscus Parvus Stellaris: Heath Moss
- Muscus Stellatus; Star-like Moss
- Muscus Corniculats: Horned Moss, amongst others
Parts used:
Herb; Spores
Temperature & Taste:
Warm, dry. Bitter, Pungent (TCM)
Classification:
D. Clear Wind and Damp
Uses:
1. Warms the Kidneys, Clears Damp, Promotes Urine: (West, TCM)
-Edema (West, TCM)
-Dysuria, Retention of Urine, especially from spasm; Incontinence (West)
-nocturnal micturation in children or adults (West)
-Catarrhal Cystitis
-Kidney disease and Stones (West)
-in the west it has been used as a fold remedy for Impotence
-spores are used similarly, especially for Stones
2. Clears Wind-Damp, Relaxes Spasms: (TCM, West)
-Wind-Damp joint pain, especially with stiffness and tightness of the sinews (TCM)
-Arthritis, Rheumatism (TCM, West)
-Back Pain (West, TCM)
-Cramps, Leg Cramps (West, TCM)
-Sequelae of Polio (TCM)
-Epilepsy (West)
3. Moves the Blood, Stops Bleeding: (TCM, West)
-swelling and pain from Trauma (TCM)
-Amenorrhea, Dysmenorrhea (West, Ayurveda)
-it has been demonstrated to promote Uterine contractions
-in the west for Bleeding
4. Clears Phlegm, Stops Cough: (West)
-Cold, Sore Throat, Tonsillitis
-Cough; Decoction is used for Whooping Cough (Salmon)
5. Used as a Pill Coating:
-the spores are used in pill coating to make them tasteless and prevent them sticking together.
6. Externally:
-applied topically to joint stiffness and pain, and to Trauma with pain and swelling
-herb being briefly boiled is applied to inflammations and arthritis coming with Heat
-ointment is used for Shingles (TCM)
-topically for Herpes (West)
-topically for suppurating Eczema, Psoriasis, Erysipelas
-spores applied as a dusting powder to relieve itchiness
-spores can be applied as a drying, protective cover for Ulcers
Dose:
Decocted in wine to promote Urine, break Stones and for Joint pain and stiffness.
Decoction of the Herb: 6–15 grams
Spore Powder: 2–5 grams of Powder; One dram of the powder was a common dose, being taken with wine.
Tincture (1:10): 15–60 drops
Comment:
1. The appearance and constituents of the Clubmoss species used in East and West is very similar. The Chinese use focuses on Wind-Damp joint pain with stiffness, while Traditional Western use focuses on the use in urinary disorders. However, the Chinese variety has also been used for Edema. It appears they are probably synonymous.
2. The spores explode when ignited and have been used to make fireworks. This is related to their name 'Vegetable Sulphur'
3. The spores are water resistant and were used to coat tablets. This signature suggested their ability to dispel water from the body.
4. In the Western Tradition, a number of types of Moss were recognised, all having similar effects. Common Moss, Club Moss and Cup Moss were regarded as the most effective.
5. Clubmoss was also called 'Wine herb'. This is because if wine had started to turn bad, a bunch of Club Moss hung in the barrel was said to be able to 'recover' it.
Substitutes:
Various other Mosses can be used similarly, according to Western Traditional sources. 'Common Moss' and Cup Moss can be used synonymously.
Decocted in wine to promote Urine, break Stones and for Joint pain and stiffness.
Decoction of the Herb: 6–15 grams
Spore Powder: 2–5 grams of Powder; One dram of the powder was a common dose, being taken with wine.
Tincture (1:10): 15–60 drops
Comment:
1. The appearance and constituents of the Clubmoss species used in East and West is very similar. The Chinese use focuses on Wind-Damp joint pain with stiffness, while Traditional Western use focuses on the use in urinary disorders. However, the Chinese variety has also been used for Edema. It appears they are probably synonymous.
2. The spores explode when ignited and have been used to make fireworks. This is related to their name 'Vegetable Sulphur'
3. The spores are water resistant and were used to coat tablets. This signature suggested their ability to dispel water from the body.
4. In the Western Tradition, a number of types of Moss were recognised, all having similar effects. Common Moss, Club Moss and Cup Moss were regarded as the most effective.
5. Clubmoss was also called 'Wine herb'. This is because if wine had started to turn bad, a bunch of Club Moss hung in the barrel was said to be able to 'recover' it.
Substitutes:
Various other Mosses can be used similarly, according to Western Traditional sources. 'Common Moss' and Cup Moss can be used synonymously.
Main Combinations:
1. Promote Urine in Edema:
i. Lycopodium Shen Jin Cao with Betel Nut (Bing Lang) (TCM)
2. Wind-Damp Muscle and Joint pain:
i. acute joint pain, Lycopodium Shen Jin Cao with Notopterygium Qiang Huo, Saposhnikovia Fang Feng
ii. Wind-Damp pain with tightness and spasms, Lycopodium Shen Jin Cao with Polygonum cuspidatum Hu Zhang, Sargentodoxa Hong Teng
iii. Wind-Damp with swollen, painful joints, Lycopodium Shen Jin Cao with Stephania Han Fang Ji, Geranium Lao Guan Zao, Earthworm (Di Long)
3. Sequelae of Polio, Lycopodium Shen Jin Cao with Pine node (Song Jie) and Clematis Wei Ling Xian
4. Trauma with swelling and pain:
i. Lycopodium Shen Jin Cao with Ground Ivy.
ii. Lycopodium Shen Jin Cao with Notoginseng San Qi and Safflower (Hong Hua)
5. Herpetic eruptions, persistent Psoriasis, chapped nipples and sore lips, Zinc oxide, Lycopodium seed powder (1 scruple each), Ointment of Roses (½ oz.), Mix. (Sobernheim, 1840)
Major Formulas:
Cautions:
1. Not used during pregnancy or in people with Bleeding.
2. Large doses are reportedly Emetic
Main Preparations used:
1. Not used during pregnancy or in people with Bleeding.
2. Large doses are reportedly Emetic
Main Preparations used: