Sentry Page Protection
Gentiana macrophylla, Qin Jiao 秦艽
Large Leaf Gentian
Qin Jiao (TCM)
Kyi lche (Tibetan–one type of)
Qin Jiao (TCM)
Kyi lche (Tibetan–one type of)
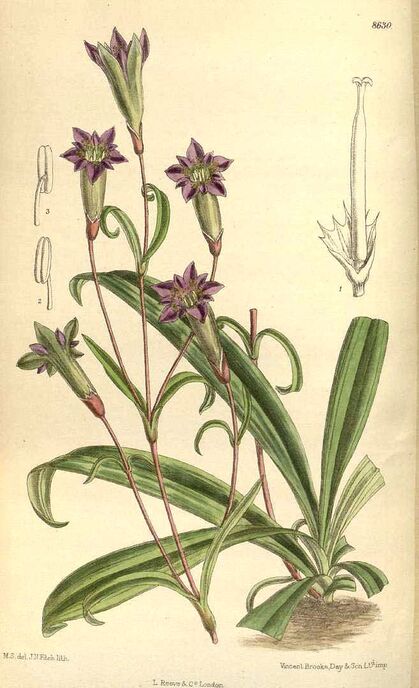
G. dahurica
Curtis’s Botanical Magazine, vol. 141 (1915)
Curtis’s Botanical Magazine, vol. 141 (1915)
Botanical name:
Gentiana spp.
A number of species are used for Qin Jiao in TCM
In Tibetan Medicine
Parts used:
Root
Temperature & Taste:
Neutral/slightly Cool, neutral in regards to dryness. Bitter, Pungent
Classification:
D. Clear Wind and Damp
Gentiana spp.
A number of species are used for Qin Jiao in TCM
- G. macrophylla
- G. straminea
- G. crassicaulis
- G. dahurica
In Tibetan Medicine
Parts used:
Root
Temperature & Taste:
Neutral/slightly Cool, neutral in regards to dryness. Bitter, Pungent
Classification:
D. Clear Wind and Damp
Uses:
1. Clears Wind-Damp, Soothes the Sinews:
-Wind-Damp joint pain, with muscular contracture and tightness of the Sinews
-Arthritis, Rheumatoid Arthritis
-Arthralgia due to Cold, Damp and Wind (Shen Nong Ben Cao)
-Hemiplegia with hypertonicity, tightness and contortion of the sinews
-Paralysis of the hands and feet. (Li Shi Zhen)
-can be used for acute or chronic, hot or cold disorders
2. Clears Deficient Heat:
-Heat from Yin deficiency
-Night Sweats, Low-Grade Fever, Afternoon Fever; 'Fever in the Bones'
-low fever in infants with malnutrition (Chinese Pharmacopoeia)
-'good for treating consumptive and infectious diseases, hectic fever due to Yin deficiency'. (Da Ming)
-deficient Heat after prolonged Febrile disease
3. Clears Damp-Heat, Opens Obstructions:
-Damp-Heat obstruction of the Liver; Jaundice
-'jaundice due to alcoholism' (Zhen Quan)
-severe Diarrhea (Ben Cao Gang Mu)
-painful or obstructed Urine (Ben Cao Gang Mu)
-'relieves contractures and spasms in any part of the body' (Ming Yi Bie Lu)
-also for acute conditions with Damp
-also for Pus in the Lungs and swelling of the Breasts (Tibetan Medicine)
4. Moves the Bowels:
-gentle laxative, useful for dryness of the Intestines
5. Externally:
-powder is applied to chronic Skin Ulcers (Ben Cao Gang Mu)
Dose:
1. Used in decoctions, pills, powders, or medicated Wines.
Decoction: 5–10 grams (up to 30 grams); best decocted for a short time.
Powder: 1–3 grams
The powder can be mixed with water, a suitable decoction, wine, or alcohol for topical application.
Comment:
Gentians are widely used in the various traditions. In general, they are viewed as Cold, and good to clear Heat and Damp from the Liver. The standard species such as the European Gentian and the Chinese Long Dan Cao are largely synonymous. The Western Gentian has been used in formulas for Arthritis and Joint disease, similar to Gentian Qin Jiao. This suggests that most or all the Gentians may be used for this function, but that Gentiana Qin Jiao is more specific for this indication.
Substitute:
Centuary is closely related therapeutically and taxonomically to the Gentians. It has been widely used for Joint disease, Arthritis and tightness of the Sinews. It can be regarded as a suitable substitute for Gentian Qin Jiao.
1. Used in decoctions, pills, powders, or medicated Wines.
Decoction: 5–10 grams (up to 30 grams); best decocted for a short time.
Powder: 1–3 grams
The powder can be mixed with water, a suitable decoction, wine, or alcohol for topical application.
Comment:
Gentians are widely used in the various traditions. In general, they are viewed as Cold, and good to clear Heat and Damp from the Liver. The standard species such as the European Gentian and the Chinese Long Dan Cao are largely synonymous. The Western Gentian has been used in formulas for Arthritis and Joint disease, similar to Gentian Qin Jiao. This suggests that most or all the Gentians may be used for this function, but that Gentiana Qin Jiao is more specific for this indication.
Substitute:
Centuary is closely related therapeutically and taxonomically to the Gentians. It has been widely used for Joint disease, Arthritis and tightness of the Sinews. It can be regarded as a suitable substitute for Gentian Qin Jiao.
Main Combinations:
1. Joint Pain, Arthritis:
i. hot joint pain, Gentiana macrophylla Qin Jiao with Anemarrhena Zhi Mu, Lonicera Caulis Ren Dong Tang
ii. Wind-Damp joint pain, Gentiana macrophylla Qin Jiao with Saposhnikovia Fang Feng, Angelica pubescens Du Huo
iii. Wind-Damp joint pain, Gentiana macrophylla Qin Jiao with Gastrodia Tian Ma, Notopterygium Qiang Huo, Dang Gui, Ligusticum Chuan Xiong (as in Qin Jiao Tian Ma Tang from Yi Xue Xin Wu [Medical Revelations])
iv. Wind-Cold-Damp Joint pain, Gentiana macrophylla Qin Jiao with Notopterygium Qiang Huo, Ligusticum Chuan Xiong, Aconitum Chuan Wu.
2. Body pain with fever and restlessness, Gentiana macrophylla Qin Jiao with Bupleurum Chai Hu and Licorice, powder and take 3 grams with hot water. (Ben Cao Gang Mu)
3. Tuberculosis, Gentiana macrophylla Qin Jiao with Bupleurum and Licorice
4. Pus in the Lungs, decoction of Gentiana macrophylla with Costus (Tibet)
5. Swelling of the Breasts, decoction of Gentiana macrophylla with Chebula (Tibet)
6. Deficient Heat, Low-grade Fever after Febrile diseases:
i. Gentiana macrophylla Qin Jiao with Soft-Shelled Turtle Shell (Bie Jia), Artemisia annua Qing Hao, Lycium Cortex Di Gu Pi (as in Large Gentian and Soft-Shelled Turtle Shell Powder [Qin Jiao Bie Jia San])
ii. Gentiana macrophylla Qin Jiao with Soft-Shelled Turtle Shell (Bie Jia), Ginseng, Bupleurum Chai Hu (as in Qin Jiao Fu Lei Tang from Yang Shi Jia Cang Fang (Yang Family Depository of Formulas).
iii. Hectic Fever in children, Gentiana macrophylla Qin Jiao with Licorice and Mint. (Li Shi Zhen)
7. Hemiplegia with tightness of the sinews, Gentiana macrophylla Qin Jiao with Dang Gui, Paeonia Bai Shao, Ligusticum Chuan Xiong, Gastrodia Tian Ma (as in Major Large Gentian Decoction [Da Qin Jiao Tang]).
8. Childhood Malnutrition:
i. Gentiana macrophylla Qin Jiao with Peppermint (Bo He) and Honey-fried Licorice (as in Qin Jiao San from Xiao Er Yao Zheng Zhi Jue [Key to the Therapeutics of Children’s Diseases]).
ii. with Wind-Damp arthralgia, Gentiana macrophylla Qin Jiao with Lycium Cortex Di Gu Pi, Picrorrhiza Hu Huang Lian, Stellaria Yin Chai Hu.
9. Jaundice,:
i. Gentiana macrophylla Qin Jiao with Scutellaria Huang Qin, Citrus Qing Pi
ii. Gentiana macrophylla Qin Jiao with Artemisia Yin Chen Hao, Gardenia Zhi Zi, Rhubarb (Da Huang) (as in Shan Yin Chen Wan from Sheng Ji Zong Lu [Complete Record of Holy Benevolence]).
10. Constipation from dryness, Gentiana macrophylla Qin Jiao with Cannabis seed (Huo Ma Ren)
11. Severe Diarrhea, Gentiana macrophylla Qin Jiao with prepared Licorice (Zhi Gan Cao) (Ben Cao Gang Mu)
12. Threatened Miscarriage, Gentiana macrophylla Qin Jiao with prepared Licorice Zhi Gan Cao, fried Deer Horn Gelatin (Lu Jiao Jiao), Chinese Mugwort (Ai Ye) and Sticky Rice. (Ben Cao Gang Mu)
Major Formulas:
Da Qin Jiao Tang
Juan Bi Tang
Qin Jiao Tian Ma Tang
Qin Jiao San
Qin Jiao Bie Jia San
Shen Tong Zhu Yu Tang
Cautions:
Not used in Spleen and Stomach deficiency with loose bowels.
Main Preparations used:
Not used in Spleen and Stomach deficiency with loose bowels.
Main Preparations used:
Click the Tabs above for more information on this Medicin
Nothing at the moment
GENERAL / REVIEW:
–A comprehensive review of phytochemistry, pharmacology and clinical application of Gentianae Macrophyllae Radix.
–Botany, traditional use, phytochemistry, pharmacology, quality control, and authentication of Radix Gentianae Macrophyllae-A traditional medicine: A review.
–Chemical and Genetic Comparative Analysis of Gentiana crassicaulis and Gentiana macrophylla.
–Chemical constituents of Gentiana macrophylla Pall.
COMPARISON WITH GENTIANA LONG DAN CAO:
–Comparative study on "long-dan", "qin-jiao" and their adulterants by HPLC analysis.
PROCESSING:
–Effect of postharvest processing on quality traits of Radix Gentianae Macrophyllae: A integrative analysis of metabolomics and proteomics.
–Study on effects of sweating treatment and different drying methods on the quality of Gentianae macrophyllae Radix.
ANTI-BACTERIAL:
–Phytochemical analysis and antibacterial activity of Gentiana macrophylla extract against bacteria isolated from burn wound infections.
ANTI-FUNGAL:
–Identification of Antifungal Bisphosphocholines from Medicinal Gentiana Species.
–Acyl secoiridoids and antifungal constituents from Gentiana macrophylla.
ANTI-INFLAMMATORY:
–Metabolic reprogramming of proinflammatory macrophages by target delivered roburic acid effectively ameliorates rheumatoid arthritis symptoms.
–Comparison of the anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of Gentiana macrophylla Pall. and Gentiana straminea Maxim., and identification of their active constituents.
–Anti-inflammatory effects of Radix Gentianae Macrophyllae (Qinjiao), Rhizoma Coptidis (Huanglian) and Citri Unshiu Pericarpium (Wenzhou migan) in animal models. '
ANALGESIC:
–Comparison of the anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of Gentiana macrophylla Pall. and Gentiana straminea Maxim., and identification of their active constituents.
PULMONARY INFLAMMATION:
–Terpenoid Glucosides from Gentiana macrophylla That Attenuate TNF-α Induced Pulmonary Inflammation in A549 Cells.
GASTROPROTECTIVE:
–Protective effect of gentiopicroside from Gentiana macrophylla Pall. in ethanol-induced gastric mucosal injury in mice.
GASTRITIS:
–Gentiopicroside ameliorates ethanol-induced gastritis via regulating MMP-10 and pERK1/2 signaling.
GASTRIC STIMULANT:
–Iridoids and Flavonoids of Four Siberian Gentians: Chemical Profile and Gastric Stimulatory Effect.
–Attenuation of stress-induced gastrointestinal motility disorder by gentiopicroside, from Gentiana macrophylla Pall.
HEPATOPROTECTIVE:
–Lignan glucosides from Gentiana macrophylla with potential anti-arthritis and hepatoprotective activities.
–1H-NMR Based Serum Metabolomics Study to Investigate Hepatoprotective Effect of Qin-Jiao on Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Acute Hepatotoxicity in Rats.
–The Root Extract of Gentiana macrophylla Pall. Alleviates B19-NS1-Exacerbated Liver Injuries in NZB/W F1 Mice.
–Target profiling analyses of bile acids in the evaluation of hepatoprotective effect of gentiopicroside on ANIT-induced cholestatic liver injury in mice.
–Suppression of chemically and immunologically induced hepatic injuries by gentiopicroside in mice.
LIVER DISEASE:
–Anti-alcohol liver disease effect of Gentianae macrophyllae extract through MAPK/JNK/p38 pathway.
NEUROPROTECTIVE:
–Gentiopicroside protects neurons from astrocyte-mediated inflammatory injuries by inhibition of nuclear factor-κB and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways.
ARTHRITIS:
–Lignan glucosides from Gentiana macrophylla with potential anti-arthritis and hepatoprotective activities.
–Gentiopicroside attenuates collagen-induced arthritis in mice via modulating the CD147/p38/NF-κB pathway.
–Iridoid glycosides from the flowers of Gentiana macrophylla Pall. ameliorate collagen-induced arthritis in rats.
–Gentiopicroside prevents interleukin-1 beta induced inflammation response in rat articular chondrocyte.
RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS:
–Metabolic reprogramming of proinflammatory macrophages by target delivered roburic acid effectively ameliorates rheumatoid arthritis symptoms.
–Anti-Rheumatic Properties of Gentiopicroside Are Associated With Suppression of ROS-NF-κB-NLRP3 Axis in Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes and NF-κB Pathway in Adjuvant-Induced Arthritis.
–Inhibitory effects of the Gentiana macrophylla (Gentianaceae) extract on rheumatoid arthritis of rats.
STROKE:
–Neuroprotective Effect of Swertiamain on Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Inducing the Nrf2 Protective Pathway.
CANCER:
LIVER:
–Luteoloside suppresses proliferation and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome.
LUNG:
–Gentiana macrophylla flavonoids from Tibetan medicine decreases circ_0059665 to alleviate the progression of non‐small cell lung cancer under hypoxia
–Luteoloside induces G0/G1 arrest and pro-death autophagy through the ROS-mediated AKT/mTOR/p70S6K signalling pathway in human non-small cell lung cancer cell lines.
–A comprehensive review of phytochemistry, pharmacology and clinical application of Gentianae Macrophyllae Radix.
–Botany, traditional use, phytochemistry, pharmacology, quality control, and authentication of Radix Gentianae Macrophyllae-A traditional medicine: A review.
–Chemical and Genetic Comparative Analysis of Gentiana crassicaulis and Gentiana macrophylla.
–Chemical constituents of Gentiana macrophylla Pall.
COMPARISON WITH GENTIANA LONG DAN CAO:
–Comparative study on "long-dan", "qin-jiao" and their adulterants by HPLC analysis.
PROCESSING:
–Effect of postharvest processing on quality traits of Radix Gentianae Macrophyllae: A integrative analysis of metabolomics and proteomics.
–Study on effects of sweating treatment and different drying methods on the quality of Gentianae macrophyllae Radix.
ANTI-BACTERIAL:
–Phytochemical analysis and antibacterial activity of Gentiana macrophylla extract against bacteria isolated from burn wound infections.
ANTI-FUNGAL:
–Identification of Antifungal Bisphosphocholines from Medicinal Gentiana Species.
–Acyl secoiridoids and antifungal constituents from Gentiana macrophylla.
ANTI-INFLAMMATORY:
–Metabolic reprogramming of proinflammatory macrophages by target delivered roburic acid effectively ameliorates rheumatoid arthritis symptoms.
–Comparison of the anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of Gentiana macrophylla Pall. and Gentiana straminea Maxim., and identification of their active constituents.
–Anti-inflammatory effects of Radix Gentianae Macrophyllae (Qinjiao), Rhizoma Coptidis (Huanglian) and Citri Unshiu Pericarpium (Wenzhou migan) in animal models. '
ANALGESIC:
–Comparison of the anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of Gentiana macrophylla Pall. and Gentiana straminea Maxim., and identification of their active constituents.
PULMONARY INFLAMMATION:
–Terpenoid Glucosides from Gentiana macrophylla That Attenuate TNF-α Induced Pulmonary Inflammation in A549 Cells.
GASTROPROTECTIVE:
–Protective effect of gentiopicroside from Gentiana macrophylla Pall. in ethanol-induced gastric mucosal injury in mice.
GASTRITIS:
–Gentiopicroside ameliorates ethanol-induced gastritis via regulating MMP-10 and pERK1/2 signaling.
GASTRIC STIMULANT:
–Iridoids and Flavonoids of Four Siberian Gentians: Chemical Profile and Gastric Stimulatory Effect.
–Attenuation of stress-induced gastrointestinal motility disorder by gentiopicroside, from Gentiana macrophylla Pall.
HEPATOPROTECTIVE:
–Lignan glucosides from Gentiana macrophylla with potential anti-arthritis and hepatoprotective activities.
–1H-NMR Based Serum Metabolomics Study to Investigate Hepatoprotective Effect of Qin-Jiao on Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Acute Hepatotoxicity in Rats.
–The Root Extract of Gentiana macrophylla Pall. Alleviates B19-NS1-Exacerbated Liver Injuries in NZB/W F1 Mice.
–Target profiling analyses of bile acids in the evaluation of hepatoprotective effect of gentiopicroside on ANIT-induced cholestatic liver injury in mice.
–Suppression of chemically and immunologically induced hepatic injuries by gentiopicroside in mice.
LIVER DISEASE:
–Anti-alcohol liver disease effect of Gentianae macrophyllae extract through MAPK/JNK/p38 pathway.
NEUROPROTECTIVE:
–Gentiopicroside protects neurons from astrocyte-mediated inflammatory injuries by inhibition of nuclear factor-κB and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways.
ARTHRITIS:
–Lignan glucosides from Gentiana macrophylla with potential anti-arthritis and hepatoprotective activities.
–Gentiopicroside attenuates collagen-induced arthritis in mice via modulating the CD147/p38/NF-κB pathway.
–Iridoid glycosides from the flowers of Gentiana macrophylla Pall. ameliorate collagen-induced arthritis in rats.
–Gentiopicroside prevents interleukin-1 beta induced inflammation response in rat articular chondrocyte.
RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS:
–Metabolic reprogramming of proinflammatory macrophages by target delivered roburic acid effectively ameliorates rheumatoid arthritis symptoms.
–Anti-Rheumatic Properties of Gentiopicroside Are Associated With Suppression of ROS-NF-κB-NLRP3 Axis in Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes and NF-κB Pathway in Adjuvant-Induced Arthritis.
–Inhibitory effects of the Gentiana macrophylla (Gentianaceae) extract on rheumatoid arthritis of rats.
STROKE:
–Neuroprotective Effect of Swertiamain on Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Inducing the Nrf2 Protective Pathway.
CANCER:
LIVER:
–Luteoloside suppresses proliferation and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome.
LUNG:
–Gentiana macrophylla flavonoids from Tibetan medicine decreases circ_0059665 to alleviate the progression of non‐small cell lung cancer under hypoxia
–Luteoloside induces G0/G1 arrest and pro-death autophagy through the ROS-mediated AKT/mTOR/p70S6K signalling pathway in human non-small cell lung cancer cell lines.