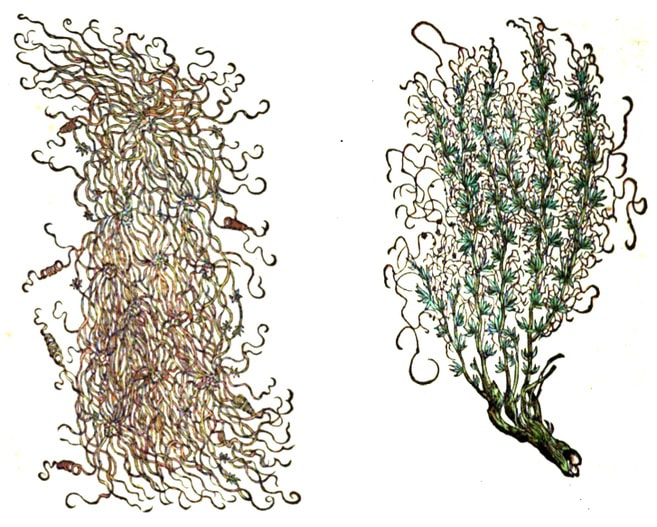
Left: Dodder, Cuscuta ; Right: Dodder of Thyme, Epithymum
Kreutterbuch, Matthiolus, 1586
Kreutterbuch, Matthiolus, 1586
|
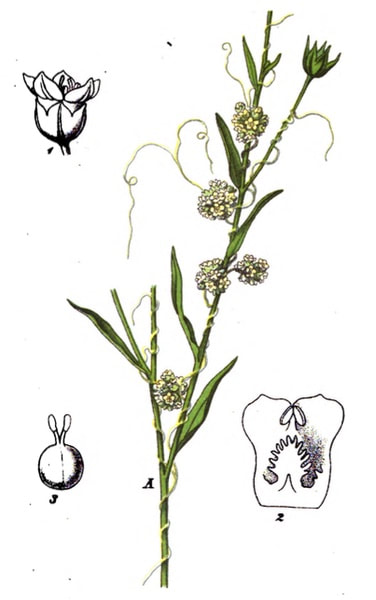
C. europea
British Phaenogamous Botany, Baxter, 1834 |
C. vulgaris (syn. C. epilinum)
Flora von Deutschland (16), Kohler, 1884 |
Botanical name:
Cuscuta spp.
European is supplied by C. europea, C. epithymum (syn. C. minor), C. vulgaris
The Chinese Dodder is C. chinensis (and others)
Parts used:
Seed
Temperature & Taste:
Neutral, Pungent and Sweet
Classification:
N. Tonify Yang
Cuscuta spp.
European is supplied by C. europea, C. epithymum (syn. C. minor), C. vulgaris
The Chinese Dodder is C. chinensis (and others)
Parts used:
Seed
Temperature & Taste:
Neutral, Pungent and Sweet
Classification:
N. Tonify Yang
ADVERTISEMENT:
Uses:
1. Tonifies Yin and Yang, Secures the Essence: (TCM, Tibet)
-Impotence, Nocturnal Emission, Premature Ejaculation (TCM)
-Urinary frequency, Vaginal Discharge (TCM, Tibet)
-'reinforces the Jing (Essence]' (Ben Cao Gang Mu)
2. Tonifies Liver and Kidneys, Settles Wind: (TCM, Tibet)
-Dizziness, Tinnitus (TCM, Tibet)
-Poor Vision, Spots in front of the Eyes
3. Strengthens the Spleen, Benefits Qi:
-Chronic Diarrhea or Loose stool from deficiency (Spleen, or Spleen and Kidney)
-'makes the patient feel happy and energetic and enjoy a long life'. (Ming Yi Bie Lu)
-also used for Melancholy as for the herb.
4. Calms the Fetus, Prevents Miscarriage:
-Threatened or Habitual Miscarriage
-Gynecological diseases (Tibet)
Dose:
Decoction: 6–15 grams
Powder: 2–5 grams
Correctives:
... available in PRO version
Substitutes:
... available in PRO version
Preparations:
... available in PRO version
Decoction: 6–15 grams
Powder: 2–5 grams
Correctives:
... available in PRO version
Substitutes:
... available in PRO version
Preparations:
... available in PRO version
Main Combinations:
1. Spermatorrhea, Premature Ejaculation, Lower Back Pain, Cuscuta Tu Si Zi with ... available in PRO version
2. Diarrhea or Loose Stool with Poor Appetite, combine Cuscuta Tu Si Zi with ... available in PRO version
3. Poor or Blurry Vision, Cuscuta Tu Si Zi with ... available in PRO version
4. Menstrual irregularity, breast distention, premenstrual depression, depression from Qi stagnation and Kidney deficiency, Cuscuta Tu Si Zi with ... available in PRO version
5. Threatened Miscarriage:
i. from Kidney deficiency Cuscuta Tu Si Zi with ... available in PRO version
ii. from Qi and Blood deficiency, Cuscuta Tu Si Zi with ... available in PRO version
iii. from Kidney deficiency, Cuscuta Tu Si Zi with ... available in PRO version
6. Impotence, Cuscuta seed with ... available in PRO version
7. Sciatica, Dodder seed ... available in PRO version
Major Formulas:
Troches for Daily Fever (Galen)
You Gui Wan
An Tai Yin
Bao Chan Wu You Fang
Bu Shen Gu Chong Wan
Ding Jing Tang
ADVERTISEMENT:
Cautions:
Not used in Deficient Heat; full doses may cause Nausea.
Main Preparations used:
Distilled Water of the whole Plant
Not used in Deficient Heat; full doses may cause Nausea.
Main Preparations used:
Distilled Water of the whole Plant
Click the Tabs above for more information on this Medicine
|
'Kushooth is the Arabic name for the Dodders, and from it have been derived tho Greek [?] and Latin Cuscuta of mediaeval writers.
An Arabian poet says:— " He is like the Kashooth; for he has neither
root, leaves, fragrance, shade or fruit." In the Indian bazars the name is applied to the fruit of a species of Cuscuta, imported from Persia, and also called Tukm-i-kasus; it is mixed with the small oblong leaves and spines of the plant upon which it has grown, and the flowers and portions of the stem may often be found. The seeds are four in number, light brown, convex on one side, concave on the other, and
|
enclosed in a nearly globular capsule about the size of a radish seed. The taste is bitter. Mir Muhammad Husain identifies this drug with the Amal-bel, Akus-bel, or Amarlata of India, and describes it as yellow, growing on thorns and other shrubs, and as having a very small, whitish flower, and seeds rather smaller than radish seeds, nearly round, and of a reddish yellow colour. Its proper ties are described as much the same as those of Aftimun. The plant may be either C. hyalina, Roth., C. chinensis, Lam., or C. planijlora, Tenore; possibly several species are collected. In India C. reflexa, Roxb., is sometimes used; it is a larger plant, and has larger fruit than the imported article." (Pharmacographia Indica, Dymock, 1891)
|