Sentry Page Protection
Dioscorides Materia Medica, Mathias, 1563
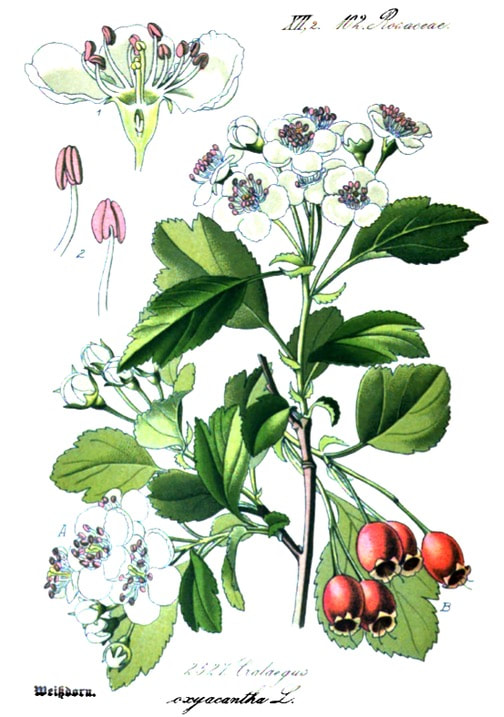
C. oxyacantha
Flora von Deutschland (25), Kohler, 1886
Flora von Deutschland (25), Kohler, 1886
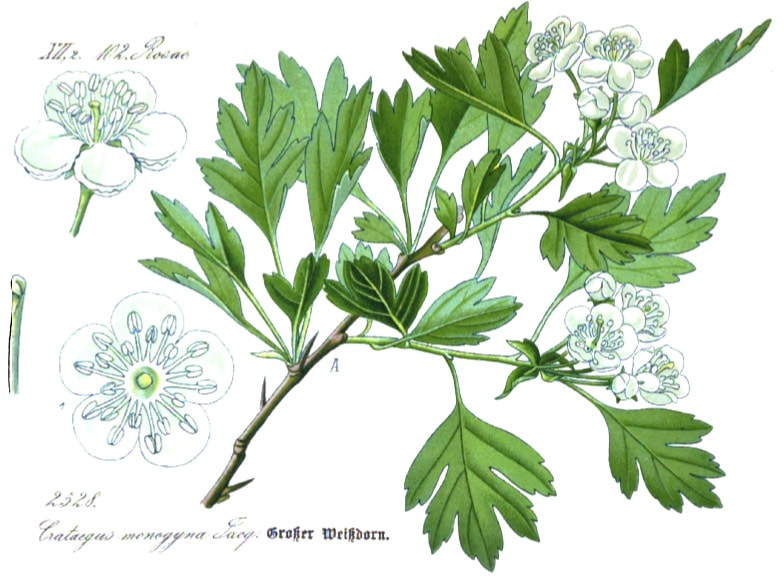
C. monogyna
Flora von Deutschland (25), Kohler, 1886
Flora von Deutschland (25), Kohler, 1886
Chinese Hawthorn fruit slices (Adam, 2017)
Botanical name:
Crataegus spp.
In Europe:
Parts used:
Fruit; also the leaf, seed and flower
Temperature & Taste:
Warm, Dry. Sour and Sweet
Classifications:
H. Nourish the Heart
O. Promote Digestion
Crataegus spp.
In Europe:
- C. laevigata (formerly C. oxyacantha); Branched Hawthorn
- C. monogyna; Single Hawthorn
- C. pentagyna; Five-headaed Hawthorn
- C. nigra; Black or Dark Hawthorn
- C. azarolus; Italian Medlar
- C. cuneata
- C. oxycantha var. pinnatifida
Parts used:
Fruit; also the leaf, seed and flower
Temperature & Taste:
Warm, Dry. Sour and Sweet
Classifications:
H. Nourish the Heart
O. Promote Digestion
Uses:
1. Moves the Blood, Clears Blood Stasis, Regulates the Circulation, Eases Pain (West, TCM):
-Heart disease, Heart pain including Angina Pectoris, Hypertension and Hypotension, Atherosclerosis, Arteriosclerosis, paroxysmal Tachycardia and various disturbances of Heart rhythm as well as disorders such as Pericarditis.
-absent or prolonged first sound or murmur, with a fast, intermittent and irregular pulse;
-Irregular Pulse with Chest Pain or Restlessness are good indications for the flower and berry.
-degenerative Heart conditions, and in the aftermath of Heart attack.
-clinically useful where there is intolerance of Digitalis.
-seeds are decocted in wine and taken for internal pain associated with blood stagnation.
-recommended it for Asthma (esp. of Cardiac origin). (Ellingwood)
2. Nourishes the Heart, Settles the Spirit (West):
-calms the mind and Spirit when the Heart is unsettled. (esp. flower)
-insomnia, palpitations with anxiety and nervousness.
-Menopausal symptoms associated with Heart disease or blood stagnation, and is good for despondency, and fear of death related to Heart deficiency.
-‘general curative effect upon the functional action of the Central Nervous System’ (Ellingwood).
-It gives a sense of Well-being to those anxious due to Heart weakness.
-It has also been used for Vertigo and Dizziness etc. (Flowers, or Flowers and Fruit are often combined)
3. Moves the Blood, Benefits the Womb (West, TCM):
-Prevents Miscarriage (low dose)
-Postpartum abdominal pain and to return the uterus to its normal position after birth. (full doses, TCM)
-Amenorrhea from blood stasis
4. Promotes Digestion, Clears Food Stagnation:
-food accumulation, particularly due to excess meat and fat consumption with abdominal pain, distention and diarrhea.
-indigestion in infants due to improper nursing.
-Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Gall Bladder deficiency (Berries are stir-fried until yellow to enhance this function) (TCM).
-‘The appetite increases, assimilation and nutrition improve’ (Ellingwood’s Therapeutist, March, 1909)
-also useful to help reduce weight and reduce Cholesterol.
5. Promotes Urine, Clears Stones:
-retained fluid, as well as edema, especially cardiac edema
-‘the seeds in the berries beaten to powder being drunk in wine are good against the Stone and Dropsy’ (Culpeper)
-traditionally also used for Gout; also occasionally used for Leukorrhea.
-inguinal Hernias, as well as swollen, painful testicles or scrotum. (TCM)
-Gall Stones. (TCM)
6. Others Uses:.
-Exopthalmic Goiter (Ellingwood)
-some older writers commended it for Epilepsy
7. Stops Leakage:
-The charred fruit is used for diarrhea, chronic dysentery and bleeding from food stagnation, or damp heat (TCM)
-in Europe the leaves were also given for various Leakages.
-Dioscorides used the Berries for diarrhea, excessive Menstruation, and other Bloody Fluxes.
-‘The distilled Water of the flowers stays the Lax’. (Culpeper)
-It has been used as an aid in Diabetes Insipidus (especially in children with poor circulation and cold extremities)
Dose:
Fruit, Flower or Leaf in Infusion: 1–2 teaspoonful (3–6 grams)
Decoction of the Fruit: 6–15 grams daily (up to 20 or 30 grams)
Decoction of the Carbonised Fruit: 5–15 or 20 grams.
Fruit in Powder: 1–4 grams
Seed in Powder: 1–3 grams
Tincture of the Fruit, Fruit and Flower, or Leaf and Flower (1:5): 2–5 mls., 2–3 times daily.
Fluid Extract of the Fruit (1:1): 10–25 drops; 30–50 drops, or up to 1 teaspoonful hourly in Angina Pectoria.
Preparation:
1. To prepare the fruit for drying, they are dipped into boiling water for 1 minute, then sliced and dried (TCM)
2. Stir-Fried Fruit is used for Food Stagnation in TCM.
3. Unripe fruit is stronger for Diarrhea.
4. Charred Fruit is hemostatic and astringent, used for Diarrhea, Dysentery and Bleeding.
Comment:
1. Hawthorn in the East and West can be considered largely synonymous. While traditional indications are different, Modern TCM uses Hawthorn for Heart and circulatory conditions based on Western usage.
2. Hawthorn Leaf (C. pinnatifida) is listed in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia. It has the effect of moving the Blood and regulating the flow of Qi. Used for Chest constriction, Palpitation, Amnesia, Vertigo and Tinnitus from Qi and Blood stagnation. Dose: 3–10 grams in Decoction.
Fruit, Flower or Leaf in Infusion: 1–2 teaspoonful (3–6 grams)
Decoction of the Fruit: 6–15 grams daily (up to 20 or 30 grams)
Decoction of the Carbonised Fruit: 5–15 or 20 grams.
Fruit in Powder: 1–4 grams
Seed in Powder: 1–3 grams
Tincture of the Fruit, Fruit and Flower, or Leaf and Flower (1:5): 2–5 mls., 2–3 times daily.
Fluid Extract of the Fruit (1:1): 10–25 drops; 30–50 drops, or up to 1 teaspoonful hourly in Angina Pectoria.
Preparation:
1. To prepare the fruit for drying, they are dipped into boiling water for 1 minute, then sliced and dried (TCM)
2. Stir-Fried Fruit is used for Food Stagnation in TCM.
3. Unripe fruit is stronger for Diarrhea.
4. Charred Fruit is hemostatic and astringent, used for Diarrhea, Dysentery and Bleeding.
Comment:
1. Hawthorn in the East and West can be considered largely synonymous. While traditional indications are different, Modern TCM uses Hawthorn for Heart and circulatory conditions based on Western usage.
2. Hawthorn Leaf (C. pinnatifida) is listed in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia. It has the effect of moving the Blood and regulating the flow of Qi. Used for Chest constriction, Palpitation, Amnesia, Vertigo and Tinnitus from Qi and Blood stagnation. Dose: 3–10 grams in Decoction.
Main Combinations:
1. Heart diseases, Hawthorn berry with Lily of the Valley
2. To strengthen Heart and Circulation:
i. Hawthorn berry with Rosemary, Rosehip, Motherwort, Calendula
ii. Hawthorn berry with Mistletoe, Dandelion, Motherwort, Fumitory, Couch grass, Balm, Rue, Yarrow, Shepherd's Purse (Treben)
3. Hypertension:
i. Hawthorn berry with Mistletoe, Balm
ii. Hawthorn berry with Linden flower
iii. Hawthorn berry with Motherwort, Rosemary, Angelica, Hyssop, Nettle
4. Hypotension, Hawthorn, Camphor
5. Angina Pectoris:
i. Hawthorn berry with Mistletoe and Valerian
ii. Hawthorn berry with Valerian and Camphor
6. High cholesterol and Hypertension, Hawthorn berry with Mistletoe and Garlic (modern combination)
7. Arteriosclerosis, Hawthorn berry with Mistletoe, Valerian, Horsetail
8. Post Stroke, Hawthorn, Notoginseng San Qi, Ligusticum Chuan Xiong, Safflower (Hong Hua)
9. Varicose veins:
i. Hawthorn berry with Yarrow and Horse Chestnut
ii. Hawthorn flowers, Yarrow, Calendula
10. Anxiety with Palpitations, Nervous exhaustion, Hawthorn flowers, Balm, St. Johns wort, Valerian
11. Restlessness and Insomnia in Children, Hawthorn berry, Camomile, Rose
12. Nervousness in Children, Hawthorn berry, Balm, Rosehip
13. Food stagnation with abdominal distention, fullness, belching, poor appetite:
i. stir-fried Hawthorn fruit (Shan Zha), Radish seed, Malted Barley (Mai Ya) (TCM)
ii. Hawthorn, Medicated Leaven (Shen Qu), Malted Barley (Mai Ya), all charred and powdered (as in Jiao San Xian, the 'Three Charred Miracles' of TCM).
14. Childhood nutritional impairment with Fever and poor appetite, Hawthorn berry (Shan Zha) with Atractylodes Bai Zhu, Picrorhiza (TCM)
15. Lower Cholesterol, reduce Weight, Hawthorn, Perilla Zi Su Ye, Calamus (Shi Chang Pu), Water Plantain (Ze Xie) (TCM)
16. Obesity, Hawthorn, Citrus Chen Pi
17. Inguinal Hernia, Hawthorn berry with Fennel seed (TCM)
18. Edema, take equal parts of powdered Hawthorn seed and Honey, mix and take in teaspoonful doses twice daily.
Major Formulas:
Da Shan Zha Wan
Bao He Wan
Eight Treasure Congee
Jiao San Xian
Cautions:
1. Use cautiously in those with marked digestive weakness (add Qi tonics).
2. Avoid in those with Gastric Ulcers.
3. Hawthorn Herb Increases the Risk of Bleeding after Cardiac Surgery: An Evidence-Based Approach.
Drug Interactions:
May potentiate Cardiac Glycosides (such as Digitalis)
Main Preparations used:
1. Use cautiously in those with marked digestive weakness (add Qi tonics).
2. Avoid in those with Gastric Ulcers.
3. Hawthorn Herb Increases the Risk of Bleeding after Cardiac Surgery: An Evidence-Based Approach.
Drug Interactions:
May potentiate Cardiac Glycosides (such as Digitalis)
Main Preparations used:
Click the Tabs above for more information on this Medicine