Sentry Page Protection
Coccus, Cochineal
Cochinella
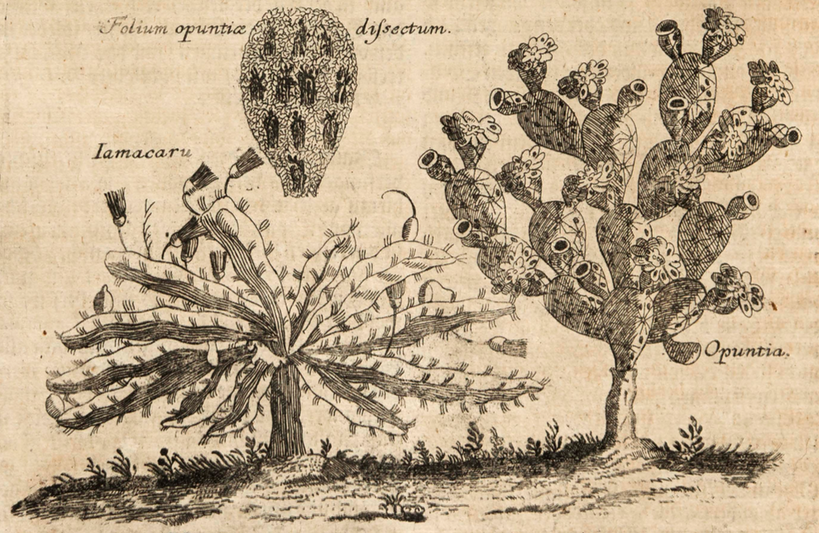
Museum Museorum, Valentini, 1704
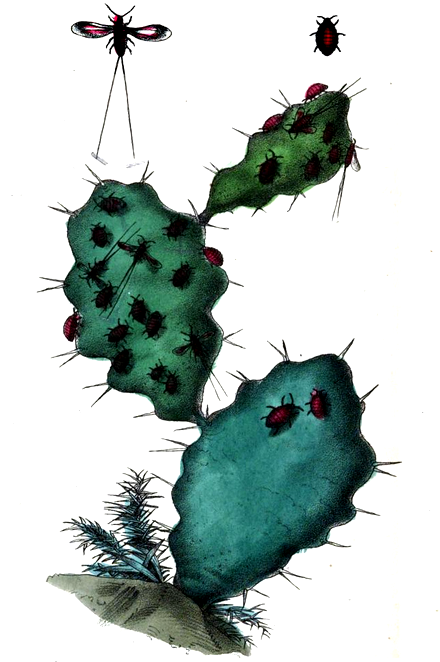
Cactus bearing Cochineal insect
Materia Medica Animalia, Peter Peyto Good, 1853
Materia Medica Animalia, Peter Peyto Good, 1853
Cochineal (Dactylopius coccus) as used in Unani Medicine.
(Adam, Kolkata Unani Medicine College, 2019)
(Adam, Kolkata Unani Medicine College, 2019)
Entomological name:
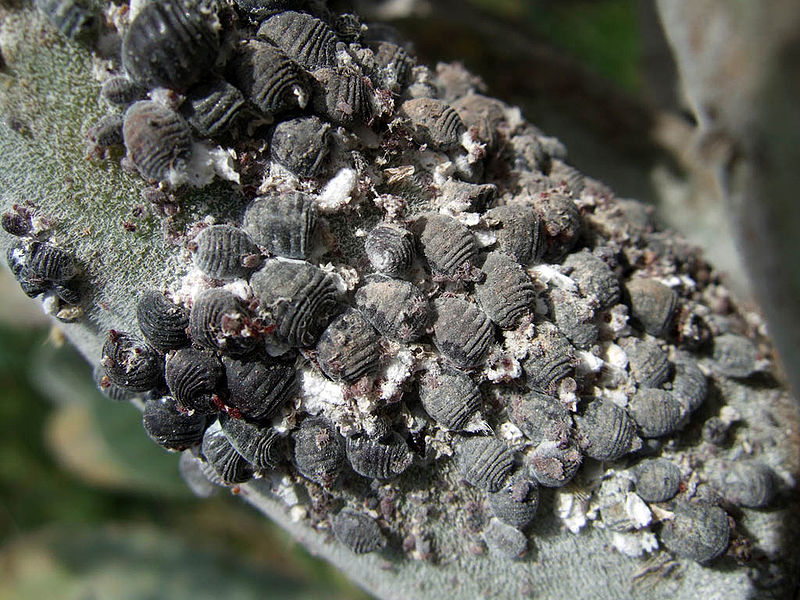
Scale insect (Dactylopius coccus [syn. Cactus cochinillifer] and others) on Catcii from the genus Opuntia (Prickly Pear), especially Opuntia ficus-indica, although there are around 200 species of Opuntia and most can be host to the Dactylopius insect.
Parts used:
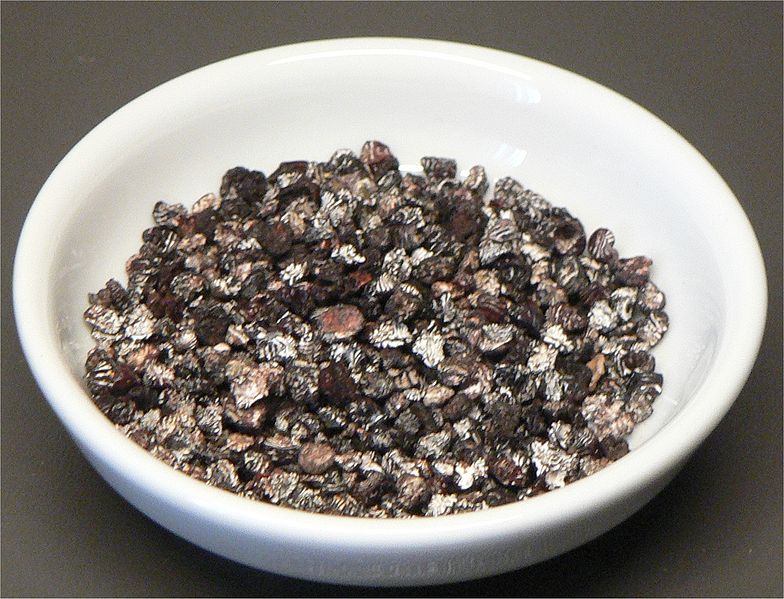
Dried female Insect; Extract (carmine)
Good quality is silver-grey externally, but deep red when crushed.
Four main varieties are differentiated:
1. Tuskalobe: blackish, dull color; the longest; wild type
2. Musteko: grey, a lesser kind; from the mountains
3. Golhace: darker grey than the preceding, and much better quality, and is also wild
4. Tlaxcala, or Rosetta: richest in color, best quality; manured and farmed
Temperature & Taste:
Cool, dry.
Scale insect (Dactylopius coccus [syn. Cactus cochinillifer] and others) on Catcii from the genus Opuntia (Prickly Pear), especially Opuntia ficus-indica, although there are around 200 species of Opuntia and most can be host to the Dactylopius insect.
Parts used:
Dried female Insect; Extract (carmine)
Good quality is silver-grey externally, but deep red when crushed.
Four main varieties are differentiated:
1. Tuskalobe: blackish, dull color; the longest; wild type
2. Musteko: grey, a lesser kind; from the mountains
3. Golhace: darker grey than the preceding, and much better quality, and is also wild
4. Tlaxcala, or Rosetta: richest in color, best quality; manured and farmed
Temperature & Taste:
Cool, dry.
Uses:
1. Clears Heat and Poison, Benefits the Heart:
-Cordial; 'Drives Infection from the Heart' (Salmon)
-Fever, Measles, Small Pox, Plague
-Cheers the Heart
2. Strengthens Qi:
-'revives Spirits ... strengthens Nature'. (Salmon)
3. Settles Wind, Stops Spasms:
-Hysteria, neuralgia, nervous diseases (King's)
-Cough, Wheezing (Unani)
-Whooping Cough, Asthma (King's)
-renal colic, urine retention
4. Coloring Agent:
-used to color tinctures and syrups a deep red, for which carmine (extracted from cochineal) may be used.
5. Externally:
-heated in oil an applied to the genitals as an aphrodisiac.
Dose:
Powder: 500mg–1200mg (8 grains–1 scruple)
Powder: 500mg–1200mg (8 grains–1 scruple)
Main Combinations:
1. To clear Heat and Poison, Infectious Diseases, and venomous Bites, with Viper powder, Cinnabar and Camphor (as in Compound Powder of Cochineal, Salmon, Seplasium, 1693)
2. Another against Infection, with Saffron and Oil of Cinnamon as a Tincture (as in Compound Tincture of Cochineal, Salmon, Seplasium, 1693)
Cautions:
None noted
1. Some people are allergic. (See here and here)
Toxicity:
Not carcinogenic (see here)
Not toxic to embryo (see here)
Main Preparations used:
Powder; Tincture; Carmine Red is extracted from Cochineal for coloring
1. Tincture of Cochineal
Take of Cochineal, in fine powder, 2.5 ounces (av.); proof-spirit, 1 pint. Macerate for 7 days in a closed vessel, with occasional agitation. Strain, press, filter, and add sufficient proof-spirit to make 1 pint (British Pharmacopoeia, 1885).
None noted
1. Some people are allergic. (See here and here)
Toxicity:
Not carcinogenic (see here)
Not toxic to embryo (see here)
Main Preparations used:
Powder; Tincture; Carmine Red is extracted from Cochineal for coloring
1. Tincture of Cochineal
Take of Cochineal, in fine powder, 2.5 ounces (av.); proof-spirit, 1 pint. Macerate for 7 days in a closed vessel, with occasional agitation. Strain, press, filter, and add sufficient proof-spirit to make 1 pint (British Pharmacopoeia, 1885).
Click the Tabs above for more information on this Medicin
Nothing at the moment
GENERAL / REVIEW:
ANTI-BACTERIAL:
ANTIOXIDANT:
PROTECTS DNA FROM DAMAGE:
–Preventive effects of anthraquinone food pigments on the DNA damage induced by carcinogens in Drosophila.
CATARACT:
–Inhibition of amyloid fibrillation of γD-crystallin model peptide by the cochineal Carmine.
ANTI-BACTERIAL:
ANTIOXIDANT:
PROTECTS DNA FROM DAMAGE:
–Preventive effects of anthraquinone food pigments on the DNA damage induced by carcinogens in Drosophila.
CATARACT:
–Inhibition of amyloid fibrillation of γD-crystallin model peptide by the cochineal Carmine.