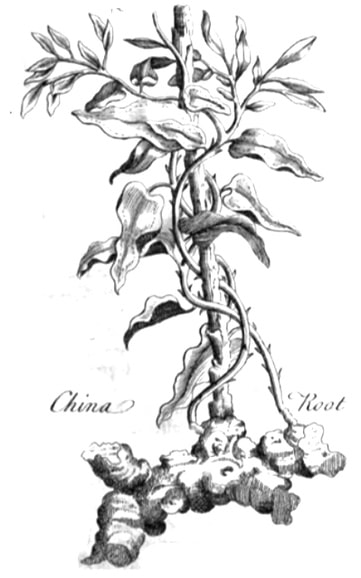
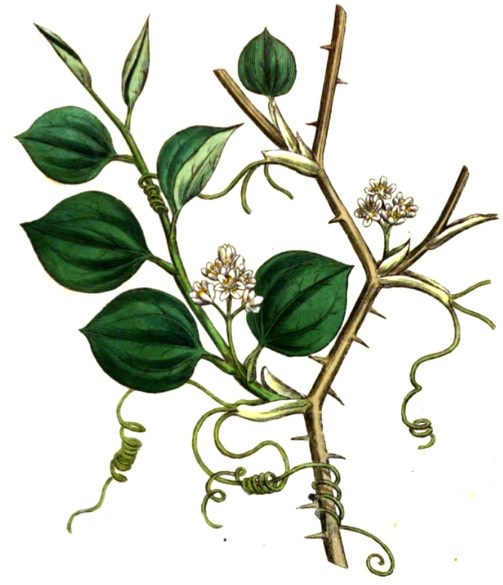
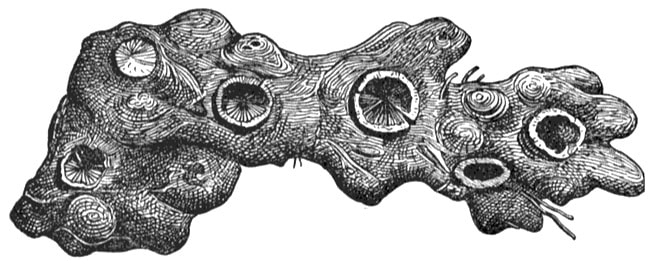
Medical Botany, Woodville, 1810
CHINA ROOT
Notes on Pharmacognosy, Otto Augustus Wall, 1902
Notes on Pharmacognosy, Otto Augustus Wall, 1902
|
Botanical name: Smilax glabra Others used include S. ovalifolia, S. zeylanica, S. macrophylla, S. lanceafolia Parts used: Root Temperature & Taste: Cool (classed as Warm in Unani), dry. Bland, Sweet Diaphoretic, Diuretic, discusses, opens Classification: B. Clear Heat and Toxin |
China root (Parkinson,
Theatrum Botanicum, 1640) |
Uses:
1. Clears Heat and Poison, Benefits the Liver:
-Good for the Liver;
-Cachexia, Edema, Arthritis, Rheumatism, Paralysis, Headache, Jaundice
-Syphilis (Specific)
-Fever, especially Intermittent Fever
-Mercury poisoning: 'Detoxifies Calomel and Vermillion'. (Li Shi Zhen)
-Scirrhus (Fibroid) and Edematous Tumors.
-effective to cleanse Melancholy and Burnt Bile
-good to clear Spleen damp (Wang Ji)
2. Benefits Qi, clears Deficient Heat:
-Strengthens and restores in Chronic weakness and Consumption
-regarded as a tonic to the Vital Organs in Unani
-regarded as promoting Longevity by ancient Daoists.
-'keeps the person to work diligently without sleep'. (Chen Cang Qi)
-as with its American relative, it has been used as an aphrodisiac (Unani)
Comment:
1. ‘It is Oriental, from the country of the Sinae called China; and Occidental, from the Spain and Peru: The Oriental is the best, which is outwardly red or blackish, inwardly white or reddish ... The Occidental is more red within’. (Schroder)
Dose:
Decoction: 6–30 grams (up to 60 or more grams). Mega doses have been advocated in Cancer treatment.
Correctives:
Sweet Pomegranate
Substitutes:
1. Sarsaparilla and various other Smilax species
2. Hemidesmus indicus
3. Phlomis tuberosa is used synonymously with China root (Smilax spp) in Tibetan Medicine of the Burat region.
1. ‘It is Oriental, from the country of the Sinae called China; and Occidental, from the Spain and Peru: The Oriental is the best, which is outwardly red or blackish, inwardly white or reddish ... The Occidental is more red within’. (Schroder)
Dose:
Decoction: 6–30 grams (up to 60 or more grams). Mega doses have been advocated in Cancer treatment.
Correctives:
Sweet Pomegranate
Substitutes:
1. Sarsaparilla and various other Smilax species
2. Hemidesmus indicus
3. Phlomis tuberosa is used synonymously with China root (Smilax spp) in Tibetan Medicine of the Burat region.
Main Combinations:
1. China root is often used with Guaiacum, Sassafras, to which Raisins or Licorice can be added. This forms a 'Diet drink' (common drink to be taken throughout the day) in various chronic and stubborn diseases such as Gout, Arthritis, chronic Skin conditions, Syphilis and other Venereal diseases, as well as Fibroids and Cancer.
2. To cleanse the Blood and Liver:
i. China root with Dandelion
ii. China root, Sarsaparilla, Gentian, Rhubarb
3. Limb spasms from Mercury poisoning, China root (Tu Fu Ling) with Coix Yi Yi Ren (Job's Tears), Saposhnikovia Fang Feng, Chinese Quince (Mu Gua) (as in Sou Feng Jie Du Tang from Ben Cao Gang Mu [Compendium of Materia Medica]).
4. Intermittent Fever:
i. China root with Ginger
ii. China root with Gentian and Cinnamon
iii. China root with Valerian and Cinnamon
iv. with Edema, China root, Calamus, Oxymel of Squill, Juniper
v. with Edema, China root, Cream of Tartar
5. Edema after Scarlet Fever, China root, Senega, Digitalis leaf, Juniper, Orange peel (Sobernheim, 1840)
6. Joint Pain from Heat and Toxin:
i. China root with Coix Yi Yi Ren (Job's Tears) or Barley
7. Jaundice from Damp-Heat:
i. China root with Dandelion (Pu Gong Ying) (TCM)
ii. China root with Barberry root-bark or Scutellaria Huang Qin
8. Skin Rashes or Lesions from Damp-Heat, China root with White Dittany root (Bai Xian Pi) (TCM)
9. Syphilis:
i. China root, Job's Tears (Yi Yi Ren), Lonicera Jin Yin Hua, Saposhnikovia Fang Feng, Chaenomelis Mu Gua, Akebia Mu Tong, Dictamnus Bai Xian Pi, Gleditsia Zao Jia, Ginseng, Dang Gui (Li Shi Zhen)
ii. China root, Sarsaparilla, Myrrh, Licorice, Cinnamon (Gazophylacium Medico-Physicum, Woyts, 1746)
10. Mercury or Calomel poisoning: China root (90 grams), Gleditsia Zao Jia, Pharbitis seed (Qian Niu Zi) (3 grams each) (Wang Ji from Ben Cao Gang Mu)
Major Formulas
Decoction of Figwort
Decoction to Sweeten
Decoction of Woods
Cautions:
According to some sources it should not be used with Tea.
Main Preparations used:
Extract with Spirit of Wine, Decoctions, usually in the form of a ‘Diet drink’, meaning that it was taken throughout the day as common drink; often with Guaiacum, Sassafras etc. for this purpose.
According to some sources it should not be used with Tea.
Main Preparations used:
Extract with Spirit of Wine, Decoctions, usually in the form of a ‘Diet drink’, meaning that it was taken throughout the day as common drink; often with Guaiacum, Sassafras etc. for this purpose.
Click the Tabs above for more information on this Medicine
Daoists texts on China root (from A Soup for the Qan, Hu Sihui et al. 2010)
The Paopuzi says:
Renjizi took China root for 18 years. The Jade Woman accompanied him. He could conceal his appearance. He did not eat grains. A glow issued from his face.
The Zhenzhong Ji of Sun the Adept says:
If one takes China root for a long time, the hundred ailments will be eliminated within a hundred days. If one takes it twice a day, at night and in the morning, for two hundred days, the ghosts and spirits will be at your command. After taking it for four years, the Jade Woman will come and wait on you.
Renjizi took China root for 18 years. The Jade Woman accompanied him. He could conceal his appearance. He did not eat grains. A glow issued from his face.
The Zhenzhong Ji of Sun the Adept says:
If one takes China root for a long time, the hundred ailments will be eliminated within a hundred days. If one takes it twice a day, at night and in the morning, for two hundred days, the ghosts and spirits will be at your command. After taking it for four years, the Jade Woman will come and wait on you.