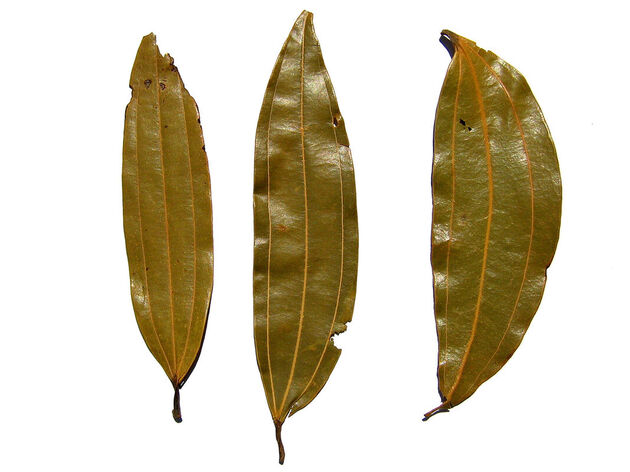
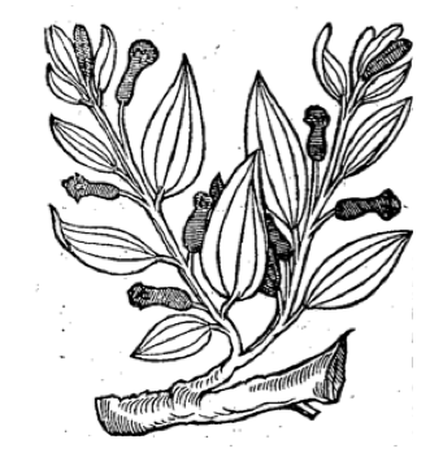
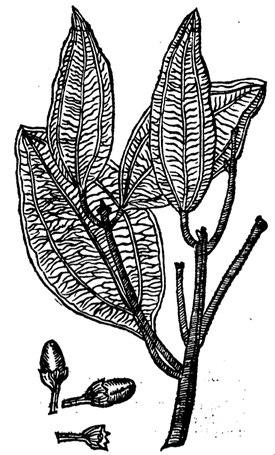
Cinnamon leaf, Indian leaf, Tejapatra
Folium Indicum, Malabathrum
Tejapatra, Tamalapatra (Ayurveda)
San Tiao Jin (TCM)
Tejapatra, Tamalapatra (Ayurveda)
San Tiao Jin (TCM)
|
Dioscorides Materia Medica, Ruellio, 1549
|
Parkinson, Theatrum Botanicum, 1640
|
Botanical name:
Cinnamomum tamala
Cinnamomum zeylanica and C. malabathrum have been listed as alternate sources.
Parts used:
Leaf
Temperature & Taste:
Warm, dry. Pungent
Classifications:
4e. STOMACHIC 4g. HEPATIC
Cinnamomum tamala
Cinnamomum zeylanica and C. malabathrum have been listed as alternate sources.
Parts used:
Leaf
Temperature & Taste:
Warm, dry. Pungent
Classifications:
4e. STOMACHIC 4g. HEPATIC
ADVERTISEMENT:
Uses:
1. Clears Wind-Cold-Damp, Clears the Channels, Eases Pain:
-Wind-Cold-Damp pain; Rheumatism, Arthritis
-Cough, Cold, Sinusitis
-also for Edema and Ascites
2. Warms the Stomach, Moves Qi;
-poor appetite, indigestion, colic
-pain in the Stomach and abdomen
3. Moves the Blood, Clears Stasis:
-Amenorrhea, Dysmenorrhea
-Bruising and Trauma
-Cold-type Chest pain, Palpitation
-also in formula for Infertility
4. Benefits the Heart, Cheers the Spirit:
-Palpitation, Heart debility, Heart pain
-Mental disorders, Insanity, Melancholy (Unani)
-regarded as Exhilarant in Unani
5. Externally:
-paste with vinegar over the lower abdomen to promote Urine and menses.
-topically to cold pain and cold swellings
-chewed for bad breath
Dose:
Powder: 500mg–2 grams
Substitute:
... available in PRO version
Correctives:
... available in PRO version
Powder: 500mg–2 grams
Substitute:
... available in PRO version
Correctives:
... available in PRO version
Main Combinations:
1. Liver obstruction, Indian leaf with ... available in PRO version
2. Liver disease, Indian leaf with ... available in PRO version
3. Swelling and Tumors, Indian leaf with ... available in PRO version
4. Anxiety, Restlessness, Palpitations, Indian leaf with ... available in PRO version
5. Epilepsy, Indian leaf with ... available in PRO version
6. Uterine pain, Dysmenorrhea, Indian leaf with ... available in PRO version
7. Infertility from Blood stagnation, Indian leaf with ... available in PRO version
8. Edema, Ascites, Indian leaf with ... available in PRO version
9. To strengthen the Head, Indian leaf with ... available in PRO version
10. Increase strength and endurance, Indian leaf with ... available in PRO version
11. Diabetes, Indian leaf with ... available in PRO version
Major Formulas:
Syrup of Agrimony Mesue
Powder to Strengthen the Head
Powder for Ascites (Isaac)
Troches of Coral (Diacorallium) (Nicholas)
Troches of Ten Things
Electuary of Peony
Electuary of Indian leaf (Zenon)
Electuary of Lacca (Andrezeos)
Electuary of Rhubarb (Zenon)
Electuary of Aloeswood (Diaxyloaloes) (Mesue)
Electuary of Frankincense (Diaolibanum) (Nicholas)
Electuary of Seseli (Nicholas)
Electuary for a Duke (Electuarium Ducis) (Nicholas)
Electuary for Crass and Viscid Humors (Azaricon)
Electuary for Sadness and Worry
Antidotum Immortale
Triphera of the Saracens (Triphera Saracenica Magna)
Hiera Logadii
Nutmeg Powder (Jatiphaladi Churna) (Ayurveda)
ADVERTISEMENT:
Cautions:
1. Hot and dry. Not for Heat or Yin deficiency.
2. Overdose is said to harm Kidneys and Lung (Unani)
Main Preparations used:
1. Hot and dry. Not for Heat or Yin deficiency.
2. Overdose is said to harm Kidneys and Lung (Unani)
Main Preparations used:
Click the Tabs above for more information on this Medicine